Japan Data Center Market: By Component (Hardware (Servers (Blade servers, Rack servers, Tower servers, Micro servers), Storage Systems (Storage Area Network (SAN), Network-Attached Storage (NAS), Direct-Attached Storage (DAS), Cloud storage), Power and Cooling Systems (Power Supply (Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems, Generators, Power distribution units (PDUs)), Cooling Solutions (Air conditioning units, Liquid Cooling Systems, Advanced Cooling Technologies), Racks and Enclosures (Open frame racks, Enclosed Racks, Customized Enclosures), Software (Data Centre Management Software, Virtualization Software, Security Software), Services (Professional & Managed and Training & Support)); Data Center Type (Colocation, Hyperscale, Edge, Cloud- Based, Enterprise, Managed); Tier Standard (Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3, Tier 4); Enterprise Size (Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) and Large Enterprises); Industry (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI), IT and Telecom, Government and Defense, Healthcare, Energy, Manufacturing, Retail, Media and Entertainment, Others (education, transportation, etc.))—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2035
- Last Updated: Nov-2024 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA1124983 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA1124983 | Delivery: Immediate Access
Market Scenario
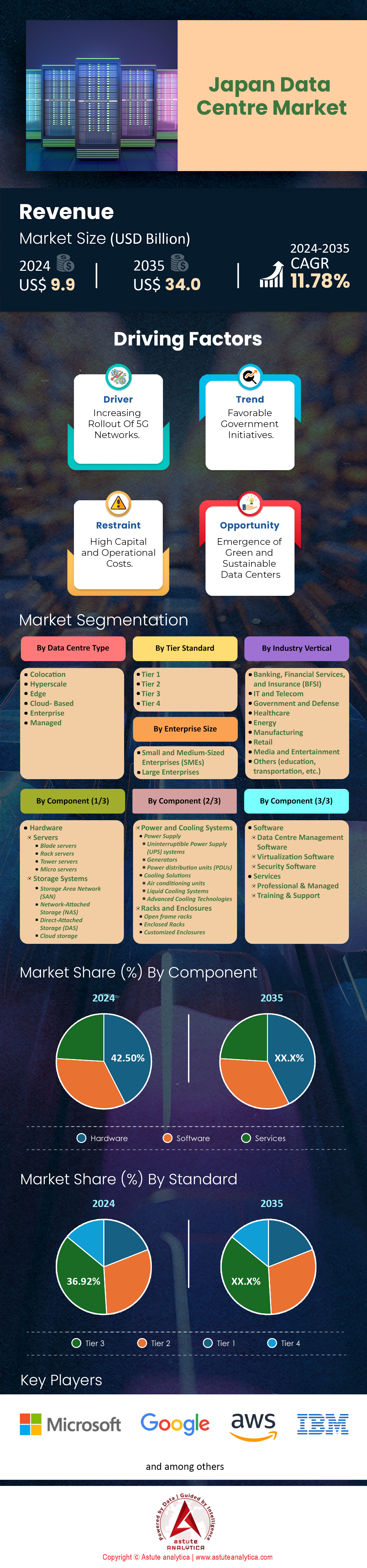
Japan data center market was valued at US$ 9.9 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 34.0 billion by 2035 at a CAGR of 11.78% during the forecast period 2024–2035.
The demand for data center market in Japan is witnessing a significant surge due to the country's rapid digital transformation and technological advancements. Japan, being the world's third-largest economy with a GDP of approximately US$4.21 trillion in 2023, is heavily investing in digital infrastructure. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has reached over 1 billion connected devices nationwide, necessitating robust data storage and processing facilities. Additionally, the rollout of 5G networks across all major cities in Japan has accelerated data generation, with average mobile data usage per user surpassing 10 GB per month.
Japan's current data center market capacity stands at around 1.4 GW in terms of total IT load, spread across more than 200 facilities nationwide. Major tech giants like Google, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft have expanded their footprint in Japan, with investments exceeding $10 billion collectively in data center infrastructure by 2023. Factors driving this demand include the government's "Society 5.0" initiative aiming for a super-smart society, and the surge in e-commerce transactions hitting an annual value of over $200 billion. Furthermore, Japan's stringent data privacy laws have prompted local companies to store data domestically, increasing reliance on regional data centers.
Digital content consumption in Japan has reached new heights, with streaming services witnessing subscribers exceeding 50 million users. The gaming industry, valued at over $20 billion, continues to grow, contributing to higher data loads. By 2035, it's projected that Japan's data center market will exceed $34 billion in value, with an additional 1 GW of capacity expected to be added by 2028. The future outlook is promising, with anticipated growth fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence and an estimated 50% increase in cloud service adoption by businesses across the country.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rapid Digital Transformation Across Industries in Japan
The rapid digital transformation across various industries in Japan is a primary driver for the increasing demand for data centers. Manufacturing firms are integrating IoT and automation, with over 70,000 industrial robots operational in factories as of 2023. The financial sector is embracing fintech solutions, leading to a digital transaction volume crossing $1 trillion annually. Healthcare providers are adopting telemedicine, with over 5 million virtual consultations conducted in 2023 alone. These advancements require robust data infrastructure, prompting businesses to invest heavily in data center services.
Moreover, the education sector in the data center market of Japan has seen the deployment of e-learning platforms to over 10,000 schools, catering to more than 8 million students nationwide. The entertainment industry, particularly online gaming, has over 65 million active gamers contributing to high data traffic. This surge in digital activities has led to internet bandwidth consumption peaking at 20 Tbps nationally. Consequently, data centers are expanding to accommodate the processing and storage needs of these digital transformations. Companies are also prioritizing digital resilience and cybersecurity, with the cybersecurity market in Japan valued at over $10 billion in 2023. With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, data centers are expected to offer advanced security features, further driving demand. The collective push towards a digital economy underscores the necessity for enhanced data center capabilities to support Japan’s ambitious technological growth.
Trend: Shift Towards Renewable Energy-Powered Data Centers
A significant trend shaping Japan's data center market is the shift towards renewable energy-powered facilities. With Japan committing to carbon neutrality by 2050, data centers are adopting green energy solutions. In 2023, over 100 MW of data center capacity is powered by renewable sources such as solar and wind energy. Operators are investing in on-site renewable energy generation, with solar panel installations covering more than 500,000 square meters of data center rooftops. The use of advanced cooling technologies, like liquid immersion cooling, has been implemented in facilities accounting for 150 MW of capacity, reducing energy consumption significantly in the data center market. Furthermore, waste heat recovery systems are in place in 20% of new data centers, contributing to energy efficiency. The reduction in carbon footprint aligns with corporate sustainability goals, making renewable energy-powered data centers more attractive to businesses conscious of environmental impact.
Government incentives play a role as well, with subsidies totaling over $1 billion granted to companies investing in green data center technologies. Collaborations between energy providers and data center operators have led to power purchase agreements for renewable energy supply amounting to 500 GWh annually. This trend not only supports environmental objectives but also positions Japan as a leader in sustainable data center operations.
Challenge: Limited Availability of Suitable Land for Development
Japan's geographic landscape, with over 70% mountainous terrain, restricts large-scale construction projects in the data center market. Urban areas where demand is highest, such as Tokyo and Osaka, face space constraints, with land prices exceeding $10,000 per square meter in prime locations. In 2023, data center developers reported that securing land accounted for up to 30% of total project costs.
Additionally, strict zoning laws and building regulations complicate development. Earthquake-resistant construction is mandatory, increasing structural costs by an estimated $500 per square meter. Environmental assessments required for new developments can extend project timelines by up to 12 months. To mitigate these challenges, companies in the Japan data center market are exploring vertical data center designs and retrofitting existing structures, with over 50 facilities adapted from former office buildings in 2023. Moreover, some operators are considering offshore and underground data centers as innovative solutions. Pilot projects include an underwater data center with a capacity of 1 MW deployed off the coast of Honshu Island. Despite these efforts, land scarcity remains a significant hurdle that could impact the pace at which new data centers are established, potentially limiting the market's growth unless alternative solutions become widely feasible.
Segmental Analysis
By Component
The hardware segment in Japan's data center market commands over 42.50% revenue share due to the country's focus on advanced technology infrastructure. High-performance servers are among the most prominent hardware used, with enterprises deploying servers equipped with processors like the Intel Xeon Scalable series, capable of delivering up to 28 cores per CPU. Storage systems are equally critical; data centers increasingly utilize NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) storage solutions, which offer read/write speeds exceeding 3,000 MB/s, significantly enhancing data access times. Networking equipment supporting 100 Gbps Ethernet is standard, facilitating the high-speed data transfer required for modern applications.
The actual cost of building a data center varies in Japan data center market, but hardware expenses can run into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, equipping a large-scale data center with cutting-edge servers can cost over $200 million. Factors adding to hardware costs include the integration of artificial intelligence accelerators like NVIDIA's A100 GPUs, each priced around $10,000, to handle machine learning workloads. Additionally, advanced cooling systems are essential; some data centers implement immersion cooling technology, which can reduce cooling energy consumption by up to 95%. Power distribution units (PDUs) with real-time monitoring add to the expense, ensuring efficient power management.
Energy efficiency is a significant factor driving hardware costs in data center market. Japan's data centers aim for a Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) ratio close to 1.1, necessitating investment in energy-efficient hardware. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems with lithium-ion batteries are adopted for their longevity and efficiency, despite being more expensive than traditional systems. Security hardware also contributes to costs; biometric authentication systems and next-generation firewalls are essential for protecting sensitive data. The adoption of edge computing requires additional hardware investment, with micro data centers costing approximately $100,000 each, deployed to reduce latency and improve service delivery.
By Type
Colocation data centers lead in Japan data center market, holding over 32.78% market share, driven by businesses' need for scalable and cost-effective infrastructure solutions. These facilities allow companies to rent space for servers and equipment, benefiting from shared resources and expertise. Tokyo has one of the highest concentrations of colocation data centers globally, with over 200 facilities in the metropolitan area alone. This concentration supports low-latency connectivity, essential for financial services firms requiring transaction speeds measured in microseconds.
The demand for colocation services in the Japan data center market is fueled by the rise of cloud computing. Major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have established partnerships with colocation centers in Japan to expand their services. Investments in this type include the construction of new facilities with capacities exceeding 50 MW of power to accommodate growing client needs. The introduction of 5G technology drives demand further, with data centers upgrading networking hardware to support speeds of up to 10 Gbps for seamless connectivity.
Key factors driving this demand in the data center market include stringent data sovereignty laws in Japan, necessitating local data storage, and the high cost of land and construction in urban areas, making colocation a more viable option for many businesses. Environmental sustainability goals also play a role; colocation providers are investing in renewable energy sources, with some facilities powered by 100% green energy, reducing carbon emissions by thousands of tons annually. Enhanced security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and 24/7 surveillance, meet compliance requirements and protect against increasing cyber threats.
By Industry
The IT & Telecom industry stands as the largest consumer of data centers in Japan due to its substantial demand for data processing and storage capabilities. With over 100 million mobile subscribers, the telecom sector requires extensive data center infrastructure to manage the vast amounts of data generated by users Moreover, Japan is home to major technology companies like NTT Group and SoftBank, which rely heavily on data centers to support their services and innovations. The proliferation of smartphones and high-speed internet services has led to increased data traffic, necessitating robust data center facilities to ensure seamless connectivity and service delivery across the nation.
This industry's capture of over 23.38% revenue share in the data center market is attributed to several factors. The deployment of 5G networks has significantly increased data processing requirements, as 5G technology can handle data speeds up to 20 gigabits per second, facilitating advanced services like real-time streaming and augmented reality Additionally, Japan's IT sector is a global leader in technology innovation, driving the need for data centers to support cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The integration of edge computing in telecom services further amplifies the reliance on data centers for low-latency data processing, essential for applications requiring immediate data analysis and response.
Key factors behind this dominance include governmental support for digital infrastructure development and a high number of internet users, exceeding 118 million individuals The industry's focus on innovation leads to continuous investment in data center expansion and modernization. For instance, major telecom operators in the Japan data center market are investing in submarine cable systems to enhance international connectivity, with projects like the Japan-Guam-Australia North Cable System spanning over 9,500 kilometers The emphasis on cybersecurity also plays a pivotal role, as secure data centers are essential for protecting sensitive information in an increasingly digital economy. Furthermore, the sector's commitment to sustainability drives the adoption of green data centers utilizing renewable energy sources, aligning with Japan's goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
By Tier Standard
Tier 3 data centers control over 36.92% of Japan's data center market due to their balance of reliability and cost-effectiveness. These facilities guarantee 99.982% uptime annually, equating to less than 1.6 hours of downtime per year, which is crucial for businesses that require near-continuous availability. The infrastructure includes redundant capacity components and multiple independent distribution paths, ensuring maintenance can occur without service interruption. Japan's focus on quality and reliability makes Tier 3 the preferred standard for many enterprises.
The demand for Tier 3 data centers is driven by industries like finance and e-commerce, where even minimal downtime can result in significant revenue loss. For example, in the financial sector, downtime costs can exceed $9,000 per minute. Macro-economic factors such as Japan's push towards digital transformation and smart city initiatives increase the need for reliable data infrastructure. Micro-economic factors include the adoption of big data analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, with an estimated 1.8 billion IoT connections in Japan by 2025, all requiring robust data center support.
Investment in Tier 3 facilities across Japan data center market includes advanced power management systems utilizing dual power sources and generators capable of supplying over 10 MW of power to ensure continuous operation. Cooling systems using advanced chillers can handle thermal loads exceeding 100 kW per rack, accommodating high-density computing requirements. Compliance with international standards like ISO 27001 for information security management adds to operational costs but ensures data protection and trustworthiness. These factors collectively contribute to the dominance and strong adoption of Tier 3 data centers in Japan.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Players in Japan Data Center Market
- Amazon Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Dell Technologies
- Google LLC
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- N+ONE Data Centers
- NTT DATA, Inc.
- Oracle Corporation
- SAP SE
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Component
- Hardware
- Servers
- Blade servers
- Rack servers
- Tower servers
- Micro servers
- Storage Systems
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
- Direct-Attached Storage (DAS)
- Cloud storage
- Power and Cooling Systems
- Power Supply
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems
- Generators
- Power distribution units (PDUs)
- Cooling Solutions
- Air conditioning units
- Liquid Cooling Systems
- Advanced Cooling Technologies
- Power Supply
- Racks and Enclosures
- Open frame racks
- Enclosed Racks
- Customized Enclosures
- Servers
- Software
- Data Centre Management Software
- Virtualization Software
- Security Software
- Services
- Professional & Managed
- Training & Support
By Data Centre Type
- Colocation
- Hyperscale
- Edge
- Cloud- Based
- Enterprise
- Managed
By Tier Standard
- Tier 1
- Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
By Enterprise Size
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Enterprises
By Industry Vertical
- Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI)
- IT and Telecom
- Government and Defense
- Healthcare
- Energy
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Media and Entertainment
- Others (education, transportation, etc.)
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA1124983 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA1124983 | Delivery: Immediate Access 
.svg)






