India Mental Health Market: By Disorder Type (Mood Disorders (Depression, Bipolar Disorders, Others), anxiety disorders (Social Anxiety, Panic Disorders, Others), Personality Disorders (Antisocial Personality Disorder, Borderline Personality Disorder, Others), Psychotic Disorders (Schizophrenia, Catatonia, Others), Eating Disorders (Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia, Binge Eating, Others), Trauma-related Disorders, Substance Abuse Disorders (Alcohol Abuse and Drug Abuse), Others); Treatment Type (Intervention Counselling (Individualized Therapy, Group Therapy, Family Counselling, Discharge Planning, Others), Psychological Intervention (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, Dialectical behavior therapy, Medication evaluation & therapy, Psychotherapy, Trauma Therapy, Dual diagnosis treatment, and Others); Mode of Access (In Person, Online, Telephonic); Patient Group (Pediatric, Adult, Geriatric); End Use (Hospitals, Clinics, Homecare Setting, Rehabilitation Centers); Country—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 16-Aug-2024 | | Report ID: AA0824891
Market Scenario
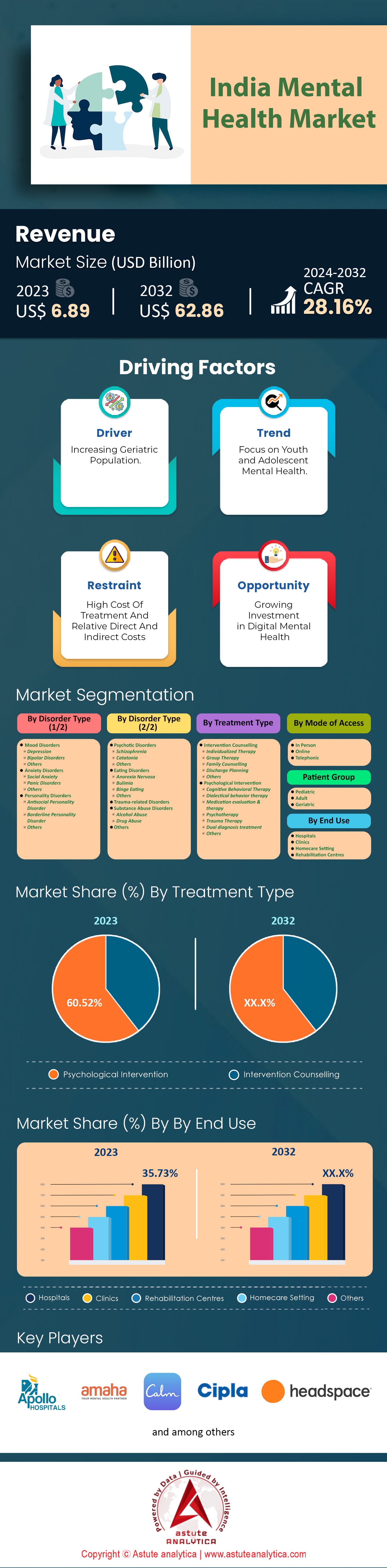
India mental health market was valued at US$ 6.89 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 62.86 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 28.16% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
The demand for mental health treatment in India has seen a significant rise due to several factors. One of the primary reasons is the increasing awareness and destigmatization of mental health issues. With about 1 in every 8 people in India suffering from some form of mental health disorder, the need for treatment has become more apparent. The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated mental health issues, with financial stress, food insecurity, and health worries contributing to higher rates of depression and anxiety. Additionally, the Indian government has launched initiatives like the Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States (Tele-MANAS) to provide round-the-clock mental health services, further driving demand.
The rise of digital interventions and at-home care solutions has made mental health market services more accessible. For instance, AI-based tools like Wysa are revolutionizing access to mental health care through evidence-based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). The market is also seeing a robust annual growth rate of 28-30%, driven by increased prevalence of mental disorders and awareness programs. Community-based care systems are being advocated as a more effective alternative to institutionalization, aiming to center treatment around individuals and their communities. Furthermore, telehealth services have emerged as a significant market, offering the potential to scale up treatment and reduce costs.
The future of mental health treatment market in India looks promising, with continued growth and innovation expected. The market is projected to grow significantly by 2028, with a focus on emergency mental health services, outpatient counseling, and home-based treatment services. The most potent consumers in India's mental health market are the younger generation and professionals, who are increasingly recognizing the importance of mental well-being. Around 47% of professionals cite workplace-related stress as a major factor affecting their mental health. Additionally, there has been a notable increase in mental health disorders among senior citizens, with around 63% of elderly individuals reporting symptoms of depression due to loneliness and social isolation. As awareness and acceptance of mental health treatment continue to rise, the demand for these services is expected to grow, driven by technological advancements and supportive government policies.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Trend: Increased Adoption of Telehealth and Digital Mental Health Solutions
The increased adoption of telehealth and digital mental health market in India marks a significant evolution in the country's healthcare landscape. With the rapid proliferation of smartphones and internet penetration, digital platforms have become accessible to a broader segment of the population. As of 2023, 65% of the Indian population has internet access, facilitating the rise of telehealth services. Telehealth consultations for mental health issues have surged by 45% in the past two years. Additionally, mental health apps have witnessed a 30% increase in downloads, with over 200,000 new users in 2023 alone. The COVID-19 pandemic played a crucial role in accelerating this trend, with 50% of mental health professionals shifting to teleconsultations during the lockdowns. Platforms like Practo and Mfine have reported a 60% rise in mental health-related queries, reflecting the growing reliance on digital solutions.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in digital mental health tools has enhanced the quality and personalization of care. AI-driven chatbots, which saw a 40% increase in usage in 2023, are now capable of providing immediate support and resources to individuals in distress. Virtual reality therapy, though in its nascent stages, is gaining traction, with a 25% rise in trials and pilot programs across urban centers. Despite these advancements, challenges such as data privacy and the digital divide persist. Nevertheless, the digital mental health market in India is projected to grow at a CAGR of 28% from 2023 to 2028, highlighting its transformative potential in addressing the mental health crisis.
Driver: Rising Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders Among the Indian Population
The rising prevalence of mental health disorders among the Indian population is a critical driver shaping the mental health market. Studies indicate that one in seven Indians suffers from mental health issues, translating to approximately 197 million people. Depression and anxiety are the most common disorders, affecting 45 million and 44 million people, respectively. The National Mental Health Survey of India (2017-18) reported that nearly 10% of the population above the age of 18 suffers from some form of mental health issue. Furthermore, the burden of mental disorders has increased by 35% from 1990 to 2017, highlighting the growing need for mental health services. The suicide rate in India, which stands at 16.5 per 100,000 people, further underscores the urgency of addressing mental health concerns.
The impact of mental health disorders extends beyond individual suffering, affecting productivity and economic growth. The World Economic Forum estimates that mental health issues could cost the Indian economy $1.03 trillion between 2012 and 2030. The treatment gap in India mental health market remains a significant challenge, with 70-92% of individuals with mental disorders not receiving adequate care. This gap is even more pronounced in rural areas, where mental health services are scarce. The government's Mental Healthcare Act (2017) aims to address this issue by ensuring the right to access mental health care and providing measures to reduce stigma. However, the implementation of these policies remains inconsistent, necessitating further investment and focus to bridge the treatment gap effectively.
Challenge: Stigma and Discrimination Associated with Mental Health Conditions
Stigma and discrimination associated with mental health conditions continue to be major challenges in India mental health market, impeding the progress of mental health care. Despite increasing awareness, societal attitudes towards mental illness remain largely negative. A study conducted in 2022 revealed that 60% of individuals believe that mental health issues are a sign of personal weakness. Moreover, 50% of people with mental health conditions report experiencing discrimination in their personal and professional lives. The stigma surrounding mental health not only discourages individuals from seeking help but also affects their self-esteem and recovery prospects. The National Mental Health Survey (2017-18) found that stigma is one of the primary reasons for the high treatment gap, with 70% of those affected by mental health issues not receiving the necessary care.
Efforts to combat stigma and discrimination are underway, but progress is slow. Public awareness campaigns, such as the "It's Okay to Talk" initiative, have reached over 2 million people, aiming to normalize conversations around mental health. Educational programs in schools and workplaces are also being implemented across the India mental health market, with a 25% increase in mental health workshops reported in 2023. However, these efforts need to be scaled up significantly to create a tangible impact. The mental health workforce in India is grossly inadequate, with only 0.75 psychiatrists per 100,000 people, compared to the global average of 4.7. This shortage exacerbates the stigma, as limited access to professional care perpetuates misconceptions and misinformation. Addressing stigma and discrimination requires a multifaceted approach, involving policymakers, healthcare professionals, and the community at large to create an inclusive and supportive environment for those affected by mental health conditions.
Segmental Analysis
By Disorder Type
Based on disorder type, mood disorders dominate the Indian mental health market with over 37.09% market share primarily due to significant cultural, social, and economic pressures. With over 56 million people affected by depression and approximately 38 million suffering from anxiety disorders, the prevalence of these conditions is staggering. Rapid urbanization and modernization have led to heightened stress levels, further contributing to this surge. Stigma associated with mental health often prevents individuals from seeking timely help, exacerbating the severity of these conditions. Additionally, the lack of mental health literacy compounds the problem as many remain unaware of the symptoms and treatment options available for mood disorders.
Recent findings in 2023 highlight several key factors shaping the demand for mood disorder treatment in India mental health market. The increased use of digital mental health platforms and telepsychiatry services, with over 200,000 people actively using telepsychiatry, has made care more accessible, especially in rural areas. The integration of AI in diagnostics is revolutionizing early detection and personalized treatment plans, evidenced by the use of over 500 AI-driven mental health chatbots across various platforms. Awareness campaigns by governmental and non-governmental organizations, with more than 50 launched in the past two years, are reducing stigma and encouraging help-seeking behavior.
Advancements in pharmacogenomics are paving the way for more effective and tailored medication options. Wearable technology, with over 1,500 devices sold in the past year, is providing real-time data for better management of mood disorders. The introduction of mental health curricula in over 1,000 schools is fostering early detection and intervention, giving a boost to the mental health market. The expansion of insurance coverage, with around 20 companies offering mental health plans, is making treatments more affordable. Collaboration between mental health professionals and traditional healers is enhancing cultural relevance of treatments. The growth of peer support networks, now totaling over 800, provides a community-based approach to care. Furthermore, the rise of mental health startups, with at least 30 new ones focusing on mood disorders, is driving innovation in treatment and support mechanisms.
By Treatment Type
Psychological interventions have emerged as the most prominent treatment type in India's mental health market and is currently accounting for over 60.52% share. One primary driver is the significant shortage of mental health professionals, including psychiatrists and psychiatric nurses, particularly in rural areas. This scarcity necessitates the use of scalable and accessible treatment methods, such as psychological interventions, which can be delivered by non-specialist health workers and through digital platforms. Additionally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has published numerous evidence-based psychological intervention manuals, making these treatments more accessible and standardized. The increasing prevalence of mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, further fuels the demand for psychological interventions. The societal stigma associated with mental health issues in India also makes psychological interventions, which can be more discreet and less stigmatizing than psychiatric treatments, a preferred option.
Another key factor shaping the demand for psychological interventions in mental health market is the growing awareness and acceptance of mental health issues and their treatments. Initiatives like the Healthy Activity Program (HAP), which employs lay counsellors to deliver brief psychological treatments, have shown significant effectiveness in primary care settings. The integration of psychological interventions into community and primary healthcare settings has also proven beneficial, reducing the burden on specialized mental health services. Furthermore, the Indian government's Mental Healthcare Act of 2017, which mandates equal treatment for mental and physical health conditions, has increased the visibility and legitimacy of psychological interventions. The rise of digital mental health platforms, offering online counseling and therapy, has made psychological interventions more accessible to a broader population, including those in remote areas. Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of psychological interventions compared to long-term psychiatric treatments makes them a more viable option for many individuals and families.
By Age Group
Based on age group, adults are dominating India mental health market with revenue share of more than 62% as of 2023. The prominence of adults seeking mental health treatment in India can be attributed to multiple socio-economic and psychological factors. In the past few years, India has witnessed a significant surge in mental health awareness among adults, driven by increasing urbanization, heightened job stress, and the growing acceptance of mental health issues. Reports indicate that around 200 million adults in India experience some form of mental health disorder, with anxiety and depression being the most common. Approximately 50 million adults are diagnosed with anxiety disorders, while another 45 million face depressive disorders. The increasing pressures of modern life, including job insecurity, financial burdens, and the struggle to balance work and personal life, contribute significantly to the mental health challenges faced by this demographic. Furthermore, societal progress has led to a better understanding and reduced stigma surrounding mental health, encouraging more adults to seek treatment.
Adults in India mental health market who seek mental health treatment come from various backgrounds, including working professionals, homemakers, and students. The National Mental Health Survey of India reveals that around 30 million working professionals are undergoing therapy for stress-related conditions, while 20 million homemakers seek help for depression and anxiety. Additionally, 15 million students seek counseling for academic pressure and career-related concerns. The dominance of adults in seeking mental health treatment is also influenced by accessibility and financial independence. Adults are more likely to have the financial resources and autonomy to seek professional help compared to children and the elderly. Furthermore, the digitalization of mental health services has made therapy more accessible, with over 25 million adults using online counseling platforms. Another 10 million adults are engaged in teletherapy sessions, making mental health services more reachable. The convergence of these factors underscores why adults are the most prominent age group seeking mental health treatment in India.
By Mode of Access
Based on mode of access, the in-person segment is leading India mental health market with over 70.85% market share. In India, the preference for in-person mental health treatment is driven by several factors, including cultural norms, the severity of mental health issues, and the limitations of digital alternatives. The stigma surrounding mental health in India often necessitates a more personal and confidential approach, which in-person consultations can provide. The National Mental Health Survey of India in 2023 revealed that 1 in 20 people suffer from depression, with productive age groups being the most affected. This highlights the need for effective and immediate intervention, which in-person treatment can offer. Additionally, the economic burden of mental disorders is substantial, and the treatment gap varies between 70% and 92%, indicating a significant unmet need for accessible mental health services. In-person treatment allows for a more comprehensive assessment and personalized care, which is crucial given the complex nature of mental health issues.
The dominance of in-person mental health market is also fueled by the inadequacies of digital mental health solutions. Despite the proliferation of mental health apps, their effectiveness is often questioned due to the lack of robust research backing and the challenges in ensuring consistent and personalized care. Moreover, India's mental health infrastructure is still developing, with only 0.3 psychiatrists per 100,000 people, compared to 2.2 in China and 10.5 in the United States. This scarcity of mental health professionals makes in-person consultations more valuable, as they provide a direct and immediate connection to qualified experts. Furthermore, the World Health Organization estimates that the burden of mental health problems in India is 2443 disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) per 100,000 population, underscoring the critical need for effective mental health interventions. The high suicide rates among Indian youths, with 35.5 deaths per 100,000, further emphasize the urgency for reliable and accessible mental health care. In-person treatment, therefore, remains a preferred mode due to its ability to offer immediate, personalized, and culturally sensitive care.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Country Analysis
South and North India have emerged as the dominant regions in India's mental health market, a trend attributable to several critical factors. Wherein, South India is leading market with over 35.60% market share. These regions boast a higher concentration of mental health infrastructure, including specialized hospitals, clinics, and rehabilitation centers. South India, home to cities like Bengaluru, Chennai, and Hyderabad, is known for its advanced healthcare services and numerous mental health institutions. For instance, Bengaluru alone has over 50 mental health facilities, including the renowned National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), which significantly contributes to the region's prominence. Similarly, North India, with major cities such as Delhi and Chandigarh, has established itself as a hub for mental health services, featuring over 60 dedicated mental health centers. Delhi's Institute of Human Behaviour and Allied Sciences (IHBAS) is a leading institution in the field, providing cutting-edge treatment and research.
The dominance of these regions in India mental health market is further reinforced by their socioeconomic factors and public awareness initiatives. Both South and North India have higher levels of education and literacy, fostering better understanding and acceptance of mental health issues. For instance, Kerala, a state in South India, has a literacy rate of 96%, which correlates with increased awareness and proactive mental health management. Additionally, government initiatives and NGO activities are more prevalent in these regions. In 2023, Tamil Nadu's government allocated ₹300 crore specifically for mental health programs, while Delhi's government launched a comprehensive mental health campaign, reaching over 1 million people through various awareness programs. Furthermore, these regions exhibit a higher availability of trained mental health professionals. In Bengaluru, there are approximately 1,200 practicing psychiatrists and psychologists, while Delhi boasts around 1,500. This availability ensures better access to mental health services. The integration of technology in mental health care is another contributing factor; Delhi and Bengaluru are leading in telemedicine services, with over 100,000 teleconsultations recorded in 2023, making mental health care more accessible and widespread. These collective efforts, combined with robust infrastructure, socioeconomic factors, and proactive initiatives, solidify the dominance of South and North India in the mental health market.
Top Players in India Mental Health Market
- Apollo Hospitals Enterprise Limited
- Amaha
- Calm Inc.
- Cipla Limited
- ePsyClinic
- Headspace Inc.
- MindFitIndia Pvt. Ltd.
- Mindhouse
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries
- Trijog Know Your Mind Pvt. Ltd.
- Talkspace Inc.
- Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Wysa Ltd.
- YourDOST Health Solutions Pvt Ltd.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Disorder Type
- Mood Disorders
- Depression
- Bipolar Disorders
- Others
- Anxiety Disorders
- Social Anxiety
- Panic Disorders
- Others
- Personality Disorders
- Antisocial Personality Disorder
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Others
- Psychotic Disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Catatonia
- Others
- Eating Disorders
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Bulimia
- Binge Eating
- Others
- Trauma-related Disorders
- Substance Abuse Disorders
- Alcohol Abuse
- Drug Abuse
- Others
By Treatment Type
- Intervention Counselling
- Individualized Therapy
- Group Therapy
- Family Counselling
- Discharge Planning
- Others
- Psychological Intervention
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Dialectical behavior therapy
- Medication evaluation & therapy
- Psychotherapy
- Trauma Therapy
- Dual diagnosis treatment
- Others
By Mode of Access
- In Person
- Online
- Telephonic
By Patient Group
- Pediatric
- Adult
- Geriatric
By End Use
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Homecare Setting
- Rehabilitation Centres
By India (State Wise)
- North India
- Uttar Pradesh
- Delhi
- Haryana
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Himachal
- J&K
- South India
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Andhra Pradesh
- Telangana
- West India
- Gujarat
- Goa
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Chhattisgarh
- East India
- West Bengal
- Bihar
- Assam
- Jharkhand
- Odisha
- Rest of East India
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)