Global Warship and Naval Vessels Market: By Type (Submarines, Aircraft Carriers, Cruisers, Destroyers, Frigates, Corvettes, Amphibious Assault Ships, Others Warship); Application (Rescue, Defense, Others); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 17-Oct-2024 | | Report ID: AA1024947
Market Scenario
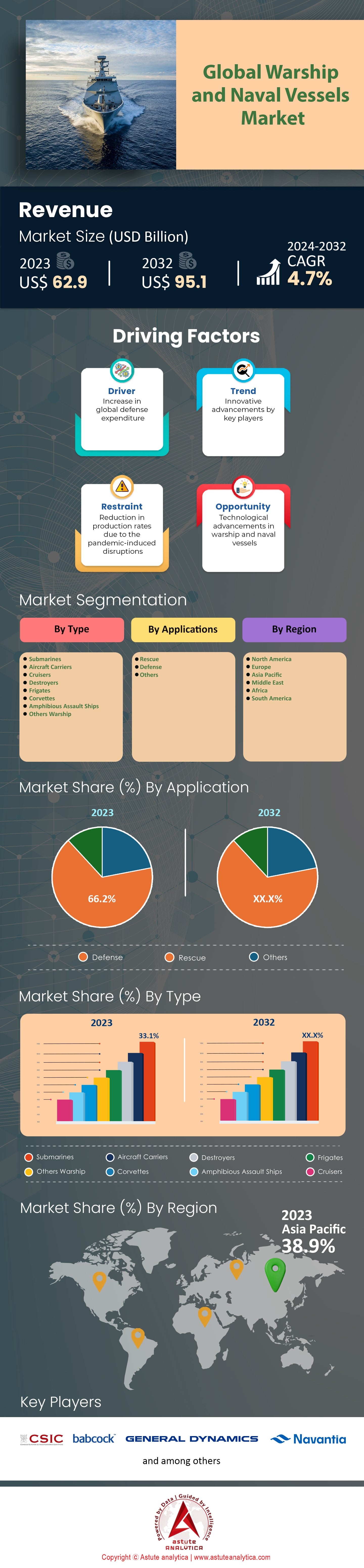
Global Warship and naval vessels market was valued at US$ 62.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 95.1 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
The global maritime defense landscape has been undergoing rapid transformation in 2023, driven by both technological advancements and geopolitical tensions. This year, major players in naval power, such as the United States, China, Russia, and India, have been at the forefront, reflecting a strategic shift towards enhancing naval capabilities. The United States maintains its position as the leader in the global warship and naval vessels market with over 290 deployable battle force ships, including 11 nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, underscoring its emphasis on power projection. China, however, has expanded its People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) to approximately 355 ships, surpassing the U.S. in sheer numbers, with three aircraft carriers and more under construction. Russia and India also continue to bolster their naval forces, with Russia focusing on its 62 submarines and India advancing indigenous shipbuilding with around 150 ships, including the INS Vikramaditya.
Investments in naval modernization have seen a significant uptick in the warship and naval vessels market, driven by the need for fleet renewal and the integration of cutting-edge technologies. The United States Department of Defense allocated $34 billion in 2023 towards shipbuilding and maritime systems, emphasizing next-generation submarines and destroyers. Meanwhile, China has increased its defense budget by 7.1%, focusing on naval expansion to support its Belt and Road Initiative. India has committed $11 billion to its naval budget, concentrating on projects like the INS Vikrant, its first domestically built aircraft carrier. The United Kingdom is also investing heavily, with a £24 billion program over the next decade targeting the development of Dreadnought-class submarines and Type 26 frigates. These investments reflect a global trend towards enhancing maritime security and maintaining strategic dominance.
Technological Landscape and Future Outlook
Technological advancements across the global warship and naval vessels market are playing a pivotal role in reshaping naval capabilities, with a strong focus on unmanned systems, hypersonic missiles, cyber warfare, and artificial intelligence. The market for unmanned naval vessels is projected to reach $4.6 billion by 2025, propelled by investments from the U.S. and China in drone technologies. Hypersonic missile development is led by Russia and China, aiming to counterbalance U.S. naval supremacy. Cyber warfare capabilities are increasingly integral to naval strategies, with NATO and the U.S. prioritizing cyber resilience. Additionally, artificial intelligence is being incorporated into naval operations to enhance decision-making processes and the deployment of autonomous systems. These technological innovations are critical in maintaining naval superiority and addressing emerging maritime threats.
Looking ahead, the future outlook for warship and naval vessels market remains robust, with continued growth and modernization efforts anticipated. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to experience the highest growth in naval investments, with countries such as Japan and South Korea enhancing their maritime capabilities. Europe is focusing on collaborative projects like the Future Combat Air System and joint naval exercises to strengthen collective security. In the Middle East, countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are expanding their naval forces to secure maritime trade routes and counter regional threats. These developments underscore the strategic importance of naval power in maintaining geopolitical stability and safeguarding national interests.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Increasing Global Defense Budgets to Counter Emerging Geopolitical Threats
The surge in global defense budgets is driven by heightened geopolitical tensions and the pressing need for naval modernization. In 2023, the United States allocated $842 billion to its defense budget, the largest in the world, with a significant portion directed towards naval capabilities, driving growth of the warship and naval vessels market. China followed with a defense budget of $224 billion, reflecting its focus on expanding its maritime reach. India, aiming to bolster its naval fleet, earmarked $72.6 billion for defense expenses. The UK announced a $58 billion defense budget, prioritizing modern warship acquisition. Additionally, Japan's defense spending hit $51 billion, reflecting its strategic shift towards strengthening maritime security. Russia, despite economic constraints, maintained a $48 billion defense allocation, emphasizing the importance of naval forces in its military strategy. France committed $45 billion to defense, highlighting its focus on naval innovation. Germany, investing heavily in naval upgrades, allocated $43 billion. Australia's defense budget reached $42 billion, driven by regional security concerns.
Nations across the global warship and naval vessels market are responding to these challenges by prioritizing naval vessel acquisition and modernization. South Korea, for instance, allocated $46 billion to its defense budget, focusing on advanced shipbuilding. Brazil, recognizing the importance of naval presence, dedicated $30 billion to its defense sector. Turkey, aiming to enhance its maritime capabilities, announced a $27 billion defense allocation. Italy, with a $26 billion defense budget, emphasized naval expansion. Canada, focusing on Arctic sovereignty, allocated $25 billion for defense initiatives. Saudi Arabia's defense budget reached $24 billion, aimed at securing maritime trade routes. The Netherlands, investing in next-generation naval technology, allocated $14 billion. Spain, meanwhile, dedicated $13 billion, reflecting its strategic maritime interests. Norway, with a $10 billion defense budget, prioritized naval readiness. Finally, Israel announced an $8 billion defense allocation, underscoring the importance of its naval forces in regional security strategies.
Trend: Shift Towards Unmanned Naval Vessels for Enhanced Surveillance and Combat Operations
The move towards unmanned naval vessels in the warship and naval vessels market has gained momentum, driven by the need for enhanced surveillance and combat efficiency. In 2023, the U.S. Navy operated over 100 unmanned surface and underwater vehicles, significantly boosting its maritime intelligence capabilities. The United Kingdom launched its autonomous mine-hunting ship, advancing its naval technology initiatives. China deployed 50 unmanned vessels in the South China Sea, enhancing its maritime domain awareness. France developed a fleet of 30 autonomous naval drones to support its expanding maritime operations. Australia invested in over 20 unmanned vessels, focusing on coastal surveillance. The Russian Navy integrated 15 unmanned submarines for strategic deterrence missions. India introduced 10 autonomous ships to bolster its maritime reconnaissance capabilities. Israel's navy utilized 8 unmanned vessels for coastal defense operations. Japan deployed 6 autonomous ships to enhance its maritime security in contested waters. South Korea added 5 unmanned surface vehicles to its naval arsenal for enhanced patrols.
These developments reflect a broader trend towards leveraging unmanned technology to address emerging security challenges. The Netherlands invested in 4 autonomous naval platforms for environmental monitoring and defense purposes. Italy, another major player in the warship and naval vessels market, initiated the development of 3 unmanned vessels to support humanitarian and combat missions. Germany announced plans to integrate 2 unmanned ships into its naval fleet to enhance maritime surveillance. Spain focused on deploying 2 autonomous surface vehicles for coastal monitoring. Canada, with its vast maritime territories, initiated the acquisition of 2 unmanned vessels for Arctic patrols. Brazil explored the use of 2 autonomous ships for Amazon river monitoring. Turkey developed 1 unmanned vessel for strategic naval operations. Norway invested in 1 autonomous ship for maritime research and defense applications. Saudi Arabia announced plans to deploy 1 unmanned vessel to secure critical shipping lanes. Finally, Singapore tested 1 autonomous surface vehicle to enhance its maritime security infrastructure.
Challenge: Complexity in Supply Chain Management Affecting Timely Production and Delivery
The complexity of supply chain management poses significant challenges for timely production and delivery of naval vessels in the warship and naval vessels market. In 2023, the global shipbuilding industry faced disruptions due to a shortage of critical components, affecting over 200 shipyards worldwide. The U.S. Navy reported delays in the delivery of 15 new warships due to supply chain bottlenecks. The United Kingdom faced production setbacks for 10 naval vessels, highlighting vulnerabilities in its supply chain networks. China's shipbuilding industry experienced delays in 8 projects, impacting its naval expansion plans. France reported supply chain issues affecting the construction of 7 new frigates. Germany encountered challenges in sourcing materials for 5 naval vessels, delaying their completion. South Korea faced delays in the production of 4 advanced submarines due to supply chain disruptions. Italy reported setbacks in the construction of 3 naval vessels, emphasizing the need for improved logistics.
Efforts are being made to address these supply chain challenges in the warship and naval vessels market through strategic partnerships and innovations. Japan introduced measures to enhance its supply chain resilience for 2 naval projects. Australia focused on diversifying its supplier base to mitigate risks for 2 ongoing shipbuilding projects. India implemented strategies to localize production for 2 naval vessels, reducing dependency on foreign suppliers. Canada explored collaborative ventures to strengthen its supply chain for 1 major naval project. The Netherlands emphasized digital transformation to streamline its supply chain operations for 1 naval initiative. Spain invested in advanced technologies to optimize its supply chain for 1 shipbuilding project. Norway leveraged artificial intelligence to enhance supply chain efficiency for 1 naval program. Brazil initiated public-private partnerships to address supply chain challenges in 1 defense project. Turkey prioritized logistics innovation to improve supply chain management for 1 naval construction. Finally, Israel explored blockchain technology to enhance transparency and efficiency in its naval supply chain.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Submarines represent a pivotal aspect of naval power due to their stealth, versatility, and strategic capabilities in the warship and naval vessels market with market share of over 33.1%. As of 2023, the global submarine fleet is robust with approximately 500 active submarines worldwide. The United States, Russia, and China lead the pack with substantial arsenals; the U.S. Navy operates about 68 submarines, while Russia maintains a fleet of around 60, and China boasts over 70. These nations invest heavily in both conventional and nuclear-powered submarines to secure maritime dominance and strategic deterrence.
Financial investments in submarines are significant. The global submarine market is valued at over $22 billion annually, with individual nuclear submarines costing upwards of $3 billion to build. Recently, Australia entered a landmark deal to acquire nuclear-powered submarines from the U.S. and the UK, marking an investment exceeding $100 billion over multiple decades. Meanwhile, India has commissioned six Scorpène-class submarines from France, with an investment of around $3.75 billion. In 2023, South Korea ordered its first indigenous ballistic missile submarine, the KSS-III, further indicating the strategic importance of submarines in modern naval warfare.
The dominance of submarines in the warship and naval vessels market stems from their unmatched strategic value. Capable of launching ballistic missiles, performing reconnaissance, and executing covert operations undetected, submarines are essential for maintaining a country's strategic deterrence and intelligence capabilities. As underwater threats grow more diverse, the demand for advanced submarines increases. The U.S. plans to build 12 Columbia-class ballistic missile submarines to replace its aging Ohio-class, while Russia continues to expand its Borei-class fleet. Additionally, advancements like the Virginia-class submarines' Virginia Payload Module, which enhances missile strike capabilities, highlight the ongoing evolution and dominance of submarines in global naval strategy. These vessels remain unmatched in their ability to provide a strategic edge in the complex theater of maritime security.
By Application
Warships and naval vessels are increasingly utilized for defense applications in the warship and naval vessels market due to the evolving nature of global threats and the strategic importance of maritime dominance. In line with this, the defense segment captured over 66.2% market share. The modern geopolitical landscape is characterized by tensions in key maritime regions such as the South China Sea, the Persian Gulf, and the Red Sea. These areas are critical for global trade and energy supply, making them focal points for potential conflicts. For instance, the U.S. Navy has been actively engaged in the Red Sea, countering threats from Houthi forces in Yemen, which have launched numerous drone and missile attacks on maritime shipping. As of 2023, the U.S. Navy operates 11 aircraft carriers, significantly more than any other nation, highlighting its commitment to maintaining naval superiority. Globally, there are approximately 4,060 active warships in service, reflecting the extensive naval capabilities maintained by countries worldwide.
The primary threats in the warship and naval vessels market being tackled by modern naval forces include piracy, terrorism, and state-sponsored aggression. In 2023, there were 116 reported piracy incidents worldwide, a significant security concern for maritime trade. Nations such as China, Iran, and North Korea have been noted for employing irregular flotillas and coastal defense systems, including cruise and ballistic missiles, to assert their influence and challenge adversaries. China's naval fleet has grown to 355 ships, making it the largest navy in the world by number of vessels. The U.S., China, and Russia are among the countries most actively engaged in enhancing their naval capabilities. The U.S. Navy has deployed over 100 destroyers and cruisers to protect maritime shipping routes from hostile actions. Additionally, the development and deployment of advanced anti-ship missiles, such as the Houthi's C-802 missiles, necessitate a robust naval presence to neutralize these threats.
Several key factors are driving the growth in naval capabilities and the increased use of warships for defense in the warship and naval vessels market. Technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated and versatile naval vessels, capable of performing a wide range of missions from anti-submarine warfare to missile defense. In 2023, the global defense budget increased by $80 billion, reflecting heightened investments in military capabilities, including naval forces. The strategic importance of maintaining control over sea lines of communication has also been a significant driver, as nations seek to protect their economic interests and ensure the free flow of trade. For example, over 90,000 vessels transit through the South China Sea annually, underscoring its importance for global commerce. Furthermore, the rise of regional powers and the shifting balance of power in the Indo-Pacific region have prompted countries to bolster their naval forces. Japan, for instance, commissioned two new Aegis destroyers in 2023, enhancing its maritime defense capabilities. These developments underscore the ongoing commitment of nations to enhance their maritime defense capabilities.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
The Asia Pacific region has emerged as the frontrunner in the global warship and naval vessels market, driven by escalating maritime disputes, regional security challenges, and a push for modernization. In 2023, the region accounted for 38.9% market share. China's ambitious naval expansion is at the forefront, with the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) now boasting over 355 ships and submarines as of 2023, making it the world's largest navy by number of vessels. China is aggressively investing in advanced capabilities, including the recent launch of its third aircraft carrier, the Fujian, which features electromagnetic catapult systems. India is also a significant contributor, with the Indian Navy operating over 150 ships and submarines. India has commissioned its first indigenous aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant, in 2022 and plans to increase its fleet to 200 vessels by 2027.
Japan's Maritime Self-Defense Force maintains a fleet of approximately 154 ships in the Asia Pacific warship and naval vessels market and is upgrading its Izumo-class helicopter carriers to support F-35B fighter operations. South Korea, with an active fleet of over 160 vessels, is investing in next-generation destroyers and submarines, including the KSS-III submarine program capable of deploying ballistic missiles. Additionally, Australia has committed to acquiring nuclear-powered submarines through the AUKUS agreement, enhancing its long-range capabilities. Collectively, these nations are driving the regional naval market with significant order books, expanding shipyards, and a focus on indigenous production to bolster their maritime dominance.
North America remains the second-largest warship and naval vessels market, predominantly led by the United States. The U.S. Navy operates a formidable fleet of around 297 deployable battle force ships as of 2023, including 11 nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, over 70 submarines, and a mix of destroyers, cruisers, and literal combat ships. The U.S. is investing heavily in modernization programs, with plans to increase its fleet size to over 355 ships in the coming decades to counter global threats. Notable programs include the Columbia-class ballistic missile submarines, with 12 vessels planned to replace the aging Ohio-class, and the ongoing procurement of Arleigh Burke-class (Flight III) destroyers equipped with advanced radar and missile systems. The U.S. Navy is also developing the Constellation-class frigates, with contracts awarded for the construction of 20 new ships to enhance multi-mission capabilities. Canada's Royal Canadian Navy is contributing to the regional market with its National Shipbuilding Strategy, which includes the construction of 15 new Canadian Surface Combatants to replace its existing fleet of frigates and destroyers, signaling a substantial investment in naval modernization.
Europe accounts for the third-largest warship and naval vessels market, with key players like the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain making significant contributions. The United Kingdom's Royal Navy operates a fleet of 72 commissioned ships, including two new Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers—HMS Queen Elizabeth and HMS Prince of Wales—each displacing around 65,000 tonnes and capable of carrying F-35B stealth fighters. France's Marine Nationale maintains a fleet of over 180 vessels, highlighted by the nuclear-powered aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, and is investing €7 billion in the Barracuda-class nuclear attack submarines program, with six submarines planned.
Germany is enhancing its naval capabilities in the warship and naval vessels market with the procurement of at least four new F126-class frigates, each over 10,000 tonnes in displacement, emphasizing multi-role functionality. Italy's navy is modernizing with the inclusion of PPA-class offshore patrol vessels, intending to commission seven units equipped with advanced combat systems. Spain is also investing in new F-110-class frigates, with five ships under construction featuring cutting-edge stealth and sensor technologies. Collectively, European nations are focusing on advanced technology integration, multinational collaboration, and fleet modernization to maintain strategic maritime security and meet NATO commitments.
Top Players in Global Warship and naval Vessels Market
- Babcock International Group
- General Dynamics
- Kawasaki Heavy Industrie
- Lockheed Martin
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- CSIC
- Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME)
- Fincantieri S.p.a.
- Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers
- Hyundai Heavy Industries
- Navantia
- Samsung Heavy Industries
- BAE Systems Maritime
- Reliance Naval and Engineering Limited
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Type
- Submarines
- Aircraft Carriers
- Cruisers
- Destroyers
- Frigates
- Corvettes
- Amphibious Assault Ships
- Others Warship
By Applications
- Rescue
- Defense
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)