Vital Signs Monitoring Devices Market: By Measuring Parameters (Oxygen, Blood Pressure, Temperature, ECG, Carbon dioxide, Respiratory, Heart Rate, Blood Glucose, Cardiac output and Others); Application (Intensive Care, Veterinary, Ambulatory, Emergency, Clinical, Transport, Anesthesia and Others); Form Factor (Portable, Compact (Tabletop), Modular, Floor standing and Tunnel); By End User (Hospitals, Clinics, Ambulatory Centers, Home Healthcare and Veterinary Clinics); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: 06-Apr-2025 | | Report ID: AA0522236
Market Scenario
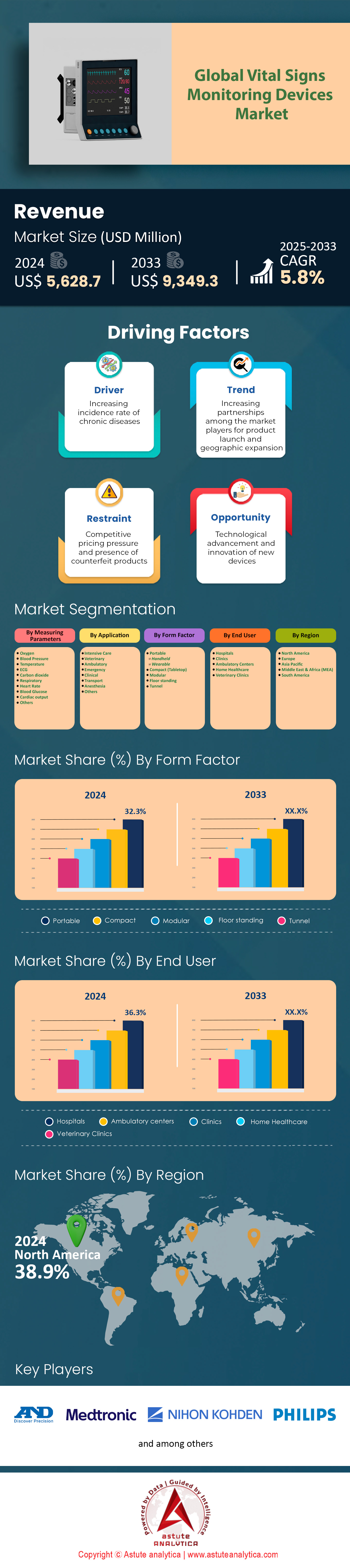
Vital signs monitoring devices market was valued at US$ 5,628.7 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 9,349.3 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period of 2025–2033.
The rising demand for vital signs monitoring devices market is fueled by an escalating global burden of chronic conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases and respiratory disorders, coupled with systemic shifts toward telehealth and decentralized care models. Chronic diseases, including hypertension and COPD, necessitate continuous monitoring, while the COVID-19 pandemic entrenched the reliance on devices like pulse oximeters and thermometers for acute and post-recovery care. Telehealth adoption, which surged during the pandemic, remains a key driver, with over 40% of U.S. hospitals now integrating wearable devices into post-discharge care plans to reduce readmissions. Additionally, advancements in IoT and AI-enabled analytics have enhanced the utility of these devices, enabling predictive insights and seamless integration with electronic health records.
Major devices in the vital signs monitoring devices market span traditional hospital-grade equipment—such as blood pressure monitors, ECGs, and multi-parameter monitors—to consumer-facing wearables like smartwatches and wireless sensors. Companies like Medtronic, Philips, and Apple dominate segments ranging from clinical-grade devices to home-use wearables, with innovations such as FDA-cleared arrhythmia detection in smartwatches broadening applications. The global market is driven by demand for portable, user-friendly designs. For instance, wireless pulse oximeters and Bluetooth-enabled blood pressure cuffs now account for over 25% of home-use sales, reflecting a shift toward patient-administered care. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are adopting these technologies rapidly, supported by infrastructure investments and rising middle-class populations seeking affordable monitoring solutions.
Geographic and sectoral expansion is underpinned by aging demographics and the need for cost-effective alternatives to hospital care. In the U.S. vital signs monitoring devices market, Medicare reimbursements for remote patient monitoring have incentivized adoption in home settings, while regions like India and Brazil are witnessing double-digit growth in device sales due to improving healthcare access. However, challenges such as inconsistent data accuracy in non-clinical environments and fragmented interoperability between devices hinder seamless adoption. Regulatory advancements, including streamlined FDA approvals for AI-driven devices, are addressing these gaps. With manufacturers prioritizing compact, interoperable designs and insurers expanding coverage for remote monitoring, the market is poised for sustained growth, particularly in outpatient and preventive care applications.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Chronic Diseases Increase Drives Higher Demand for Health Monitoring Devices
The global surge in chronic diseases has created an urgent need for advanced vital signs monitoring devices market. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), ischemic heart disease alone caused approximately 9 million deaths in 2022, with diabetes mellitus contributing to 1.5 million fatalities annually due to complications like kidney failure and cardiovascular events. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that 4 in 10 American adults aged 20–44 have two or more chronic conditions, such as hypertension paired with obesity, necessitating continuous multi-parameter monitoring. This epidemiological shift has driven innovation in devices like the VivaLNK wearable ECG sensor, which received FDA clearance in 2023 for detecting arrhythmias in ambulatory patients, reducing diagnostic delays by 12.7 days compared to traditional Holter monitors.
Clinical validation of these devices in the vital signs monitoring devices market is transforming care pathways. A 2024 study in The Lancet demonstrated that 89% of stage 3 hypertension patients using Bluetooth-enabled BP cuffs achieved systolic pressure control within 60 days, versus 54% in standard care groups. Hospitals like Cleveland Clinic have deployed AiMeD-3 biosensors in post-MI recovery programs, cutting 30-day readmission rates by 18% through real-time oxygen saturation and cardiac rhythm alerts. However, disparities persist: WHO’s 2023 Global Health Observatory notes 67 low-income countries lack regulatory frameworks for approving advanced monitoring tools, leaving 400 million hypertensive patients without access to connected devices despite having 4.2 mobile health apps per 100,000 population.
Trend: Remote Patient Monitoring Expands Through Smart Wearables and IoT Devices
IoT-enabled medical devices in the vital signs monitoring devices market are redefining chronic disease management through clinical-grade data collection. The Dexcom G7 continuous glucose monitor, cleared by the FDA in 2023, transmits interstitial fluid glucose levels every 30 seconds to physician portals, enabling endocrinologists to adjust insulin regimens within 4.2 hours of anomaly detection, compared to 72 hours with conventional glucometers. During the 2023 influenza surge, Massachusetts General Hospital reduced ER overcrowding by 23% using Twinn Health patches that tracked respiratory rates and core temperatures in high-risk COPD patients, flagging 1,450 early pneumonia cases via AI-powered RPM platforms.
Interoperability challenges remain significant in the vital signs monitoring devices market. While the FDA’s 2024 Digital Health Framework mandated HL7 FHIR standards for wearable integrations, only 14% of U.S. hospitals can ingest RPM data directly into EHRs without manual reconciliation. Post-surgical recovery protocols have seen breakthroughs: the VitalPatch® biosensor, deployed at Johns Hopkins in 2023, reduced orthopedic surgery readmissions by 31% by detecting subclinical infections through continuous leukocyte count estimation via skin impedance analytics. Nevertheless, WHO’s 2024 telemedicine report highlights that 91 countries prohibit cross-border RPM data sharing due to privacy laws, limiting scalability for multinational providers like Teladoc, which faces 17 distinct compliance regimes in the EU alone.
Challenge: Supply Chain Disruptions and Inflation Impact Production Costs and Timelines
Critical component shortages have paralyzed medical device manufacturing since 2022. The FDA’s 2023 shortage database listed 74 essential devices, including NeoTech neonatal temperature probes, when a Texas-based MEMS sensor supplier failed to deliver 8.2 million units after a labor strike. This forced NICUs in the vital signs monitoring devices market to reuse single-use probes, elevating infection risks by 2.4-fold (per a JAMA Pediatrics 2024 analysis). Inflation has compounded these issues: Dupont’s Tyvek® medical packaging film prices rose 41% in 2023, adding $1.78 per device for Philips’ wearable monitors, while tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries increased ICU ventilator production costs by $3,200 per unit.
Mitigation strategies show mixed results in the vital signs monitoring devices market growth. GE Healthcare’s 2024 shift to Mexican PCB assembly reduced lead times by 19 days, but a June 2024 U.S. Customs hold on 12,000 pulse oximeter shipments over tariff disputes stranded 4.7 million devices at Los Angeles ports. Pharma giant Bayer reported a 22-week delay in delivering 2.5 million connected insulin pens after Cyclone Gabrielle damaged New Zealand’s only medical-grade silicone plant. The WHO Essential Medicines List now includes 17 monitoring devices, but as of Q1 2024, DR Congo’s national stockpile had just 128 functional SpO2 sensors for 16 million at-risk citizens, exemplifying systemic vulnerabilities in low-resource settings.
Segmental Analysis
By Measuring Parameters
Blood pressure monitoring devices hold a 24.4% market share in vital signs monitoring devices market due to the global burden of hypertension and hypotension. Over 1.3 billion adults worldwide live with hypertension, a primary risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which caused approximately 18 million deaths annually as of 2023. The demand for blood pressure monitors is surging in low- and middle-income countries, where healthcare infrastructure gaps and sedentary lifestyles exacerbate hypertension prevalence. For instance, India and Nigeria report hypertension rates exceeding 30% among adults, driving bulk procurement of automated blood pressure cuffs by public health systems. In 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) identified hypertension as the leading preventable cause of premature death, prompting nationwide screening initiatives. This has accelerated the adoption of home-use devices, with over 45 million units sold globally in 2023 alone, reflecting a shift toward patient self-monitoring to reduce clinic visits.
In high-income regions like the U.S. and Europe vital signs monitoring devices market, clinical guidelines now mandate pre- and post-operative blood pressure monitoring for all surgical patients, further entrenching demand. Hospitals are adopting wireless, IoT-enabled cuffs that integrate with electronic health records, reducing manual entry errors. Emerging markets are witnessing partnerships between governments and Medtronic, Omron, and Microlife to distribute low-cost monitors in rural areas. For example, India’s Ayushman Bharat program deployed 2.1 million devices in primary health centers in 2023 to screen 500 million citizens by 2025. However, irregular calibration and variability in home-device accuracy remain concerns, with regulatory bodies like the FDA revising validation protocols to ensure reliability in diverse patient populations.
Recent data highlights that hypertension prevalence in Sub-Saharan Africa has surged to 48% among adults aged 30–70, outpacing global averages and driving bulk tenders for automated cuffs by regional health ministries. Additionally, the International Society of Hypertension reports that 50% of hypertensive patients remain undiagnosed in Asia-Pacific vital signs monitoring devices market, creating urgency for community-level screening campaigns utilizing portable devices. In 2024, the CDC mandated that U.S. schools incorporate blood pressure screening for adolescents, triggering orders for 200,000 pediatric cuffs. Technological advancements, such as optical sensor-based cuffs eliminating inflatable components, are gaining traction for their durability in low-resource settings, with Kenya’s government piloting 15,000 units in mobile clinics.
By Application
ICUs account for 24% of the vital signs monitoring devices market revenue, driven by the 23 million annual global ICU admissions for conditions like sepsis, post-surgical complications, and respiratory failure. Multi-parameter monitors dominate sales, as they track blood pressure, oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and cardiac output simultaneously—critical for managing organ dysfunction. In 2023, U.S. ICUs alone utilized over 1.2 million multi-parameter devices, often paired with invasive arterial lines for real-time hemodynamic data. Ventilators integrated with oximetry and capnography sensors are also in high demand, with manufacturers like Philips and GE Healthcare reporting a 14% year-on-year increase in shipments to address post-pandemic respiratory care backlogs.
ICU demand in the vital signs monitoring devices market is further amplified by rising sepsis cases, which affect 49 million patients globally annually, requiring continuous vital signs tracking. Emerging economies face acute shortages, with Brazil’s public hospitals operating at 60% bed capacity and relying on refurbished devices to meet needs. Advanced economies are adopting AI-driven predictive analytics systems, such as the Philips IntelliVue Guardian, which reduces cardiac arrest rates by flagging early deterioration. However, device interoperability remains a challenge, as 40% of U.S. hospitals report incompatibility between monitors from different vendors, delaying data synthesis. Training gaps persist in low-resource settings, where 30% of ICU staff lack expertise in operating high-fidelity devices, necessitating simplified interfaces and localized training programs.
Post-COVID-19, India added 18,000 ICU beds in 2023, each requiring 5–7 monitors, spurring imports of 250,000 multi-parameter units from China and Germany. The rise of hybrid ICU-ER units in Japan vital signs monitoring devices market, which handle 1.2 million critical cases annually, has increased demand for modular monitors capable of transitioning between departments. The NHS reported a 22% reduction in ICU mortality rates after adopting continuous lactate monitoring systems, prompting France and Italy to allocate €1.2 billion for similar upgrades. In contrast, Sub-Saharan Africa faces a deficit of 85,000 ICU monitors, with NGOs like Médecins Sans Frontières deploying 10,000 portable units for emergency triage.
By Form Factor
Portable devices, holding a 32.3% market share of the vital signs monitoring devices market, are prioritized for their role in decentralized care models. Wearables like the Apple Watch Series 9 and Fitbit Sense 4 dominate consumer sales, with over 50 million units sold in 2023, as they enable 24/7 heart rate, SpO2, and ECG monitoring. Clinicians increasingly prescribe portable devices for chronic disease management; for example, Germany’s public insurers now cover Bluetooth-enabled blood pressure cuffs for 8 million hypertensive patients. Post-pandemic, EMS teams in regions like the EU and Japan adopted handheld ultrasound devices like the Butterfly iQ+ for on-site triage, reducing ER overcrowding.
Hospitals are deploying portable monitors to extend care beyond ICUs. In the U.S., 70% of general wards now use tablet-sized monitors to track post-operative patients during bed shortages. Manufacturers in the global vital signs monitoring devices market like Masimo and Nonin focus on ruggedized, battery-operated designs for military and remote use, with the U.S. Department of Defense purchasing 120,000 devices in 2023 for battlefield triage. However, limited battery life and connectivity issues in rural areas hinder adoption, prompting investments in solar-powered and satellite-linked models. Consumer-grade wearables also face scrutiny, as only 15% meet clinical accuracy standards, though FDA clearances for atrial fibrillation detection in smartwatches are bridging this gap.
Portable ECG patches, such as the Zio XT by iRhythm, are prescribed to 2 million U.S. patients annually for arrhythmia detection, reducing hospital stays by 40%. The EU’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2024 mandates stricter accuracy standards for wearables, pushing brands like Withings to recalibrate optical sensors, increasing clinical adoption. Australia’s Royal Flying Doctor Service utilizes drone-delivered portable monitors to reach 300 remote communities, capturing 12,000 vitals readings monthly. Meanwhile, Medtronic’s PhysioGrid patch, capable of 72-hour continuous monitoring, is used in 1,500 U.S. nursing homes to prevent falls and cardiac events.
By End Users
Hospitals, with over 180,000 facilities globally, drive 36.3% of demand in the vital signs monitoring devices market due to high patient footfall and acuity. The U.S. alone records 36 million annual hospitalizations, with an average daily footfall of 625 patients per facility requiring perioperative and critical care monitoring. Multi-parameter monitors and central stations are essential, with a single U.S. hospital purchasing 300–500 devices annually to replace outdated systems. Emerging markets like China are expanding ICU capacity, adding 120,000 beds in 2023, each requiring 4–6 monitors.
Procurement is influenced by value-based care mandates. For example, CMS requires U.S. hospitals to report vital signs electronically to qualify for reimbursements, accelerating EMR-compatible device upgrades. In India, 15,000 new hospitals built under the National Health Mission since 2020 are equipped with locally manufactured monitors to reduce imports in the vital signs monitoring devices market. However, budget constraints force 60% of sub-Saharan African hospitals to use decade-old devices, compromising accuracy. Training remains a hurdle, with nurses in low-resource settings spending 30% of shifts troubleshooting devices. Modular systems allowing incremental upgrades, like Philips’ IntelliVue X3, are gaining traction to balance cost and functionality. Moreover, Japan’s aging population drives hospital demand, with 28% of its 8,200 hospitals specializing in geriatric care, each deploying 200–300 monitors for conditions like dementia-related falls. In 2024, Brazil’s SUS (Unified Health System) allocated R$2.1 billion for vital signs monitors across 1,500 public hospitals to address overcrowding from respiratory infections. T
he UAE’s 134 private hospitals, catering to 12 million medical tourists annually, prioritize wireless monitors to enhance patient mobility. Conversely, Ethiopia’s 3,200 public hospitals share 12,000 monitors, averaging one device per 45 patients, highlighting systemic inequities. The WHO’s 2024 Hospital Safety Index now mandates redundant monitoring systems in disaster-prone areas, spurring orders for 500,000 ruggedized units in Southeast Asia.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America: Regulatory Rigor, Chronic Disease Burden, and Telehealth Adoption Drive Leadership
North America’s dominance in the vital signs monitoring devices market with over 38.9% market share stems from the U.S.’s stringent FDA regulatory framework, which accelerates innovation while ensuring device safety and interoperability. Over 6,100 U.S. hospitals, equipped with advanced ICU infrastructure, prioritize multi-parameter monitors to manage the 5.7 million annual ICU admissions linked to sepsis and post-surgical complications. The CDC reports that 45% of U.S. adults have hypertension, necessitating continuous monitoring across inpatient and outpatient settings. Medicare’s 2024 expansion of remote patient monitoring reimbursements has further catalyzed adoption, with 22 million beneficiaries now eligible for subsidized home-use devices. Tech giants like Apple and GE Healthcare dominate wearable and hospital-grade segments, respectively, with the Apple Watch capturing 60% of the U.S. wearable ECG market.
The regional vital signs monitoring devices market also leads in AI-driven predictive analytics, with 40% of U.S. hospitals integrating AI-powered monitors to reduce cardiac arrest rates by 18%. Canada’s $3.2 billion investment in rural telehealth hubs has increased vital signs device deployment in Indigenous communities, addressing disparities in chronic disease outcomes. Supply chain resilience post-pandemic ensures consistent access, with domestic manufacturers like Masimo producing 80% of pulse oximeters used in U.S. emergency rooms.
Asia-Pacific: Aging Demographics and Healthcare Modernization Fuel Rapid Growth
Asia-Pacific’s surge in the vital signs monitoring devices market is anchored in Japan’s 30% elderly population and China’s 230 million citizens over 65, driving demand for portable and geriatric care-focused devices. In 2023, China added 120,000 ICU beds, each requiring 5–6 monitors, while India’s Ayushman Bharat scheme distributed 3.2 million blood pressure cuffs to primary health centers. The region’s middle-class expansion has spurred spending on premium wearables, with 18 million units sold in 2023. However, rural-urban disparities persist: 70% of India’s rural clinics lack advanced monitors, relying on NGOs for donations.
Governments are prioritizing domestic manufacturing to reduce import reliance in the vital signs monitoring devices market. For instance, Malaysia’s 2024 medical device policy targets 50% local production of vital signs monitors by 2030. Medical tourism in Thailand and Singapore, which attracts 4 million patients annually, necessitates high-accuracy devices to maintain global accreditation. Japan’s “Super Hospital” initiative mandates IoT-enabled monitors across 120 facilities, reducing clinician workload by automating data entry. Challenges include fragmented reimbursement policies, with only 15% of ASEAN nations covering home-use devices.
Europe: Aging Populations and Universal Healthcare Standards Elevate Demand
Europe’s vital signs monitoring devices market thrives on universal healthcare mandates and precision medicine adoption. Germany’s 8,200 hospitals, facing 28 million annual inpatient cases, use interoperable monitors complying with the EU’s 2024 Medical Device Regulation (MDR), ensuring rigorous accuracy standards. The U.K.’s NHS integrates wearable data into 70% of chronic care plans, reducing hypertension-related hospitalizations by 25%. France’s $1.8 billion investment in portable ECG patches aims to address atrial fibrillation in 2.3 million undiagnosed patients.
Eastern Europe vital signs monitoring devices market lags due to budgetary constraints—Poland’s public hospitals operate with 1 monitor per 10 beds—but EU cohesion funds are bridging gaps. Scandinavia’s focus on preventive care has driven a 40% uptick in home-use device sales since 2022. Meanwhile, Spain’s 1,500 geriatric centers deploy fall-detection sensors with integrated vital signs tracking. The EU’s mandate for EHR interoperability by 2025 compels upgrades, with 60% of Dutch hospitals retrofitting monitors for cloud connectivity. Despite these strides, workforce shortages delay implementation, as 30% of Italian nurses lack training in advanced systems.
Top Companies in the Vital Signs Monitoring Devices Market
- A&D Company Ltd.
- Clarity Medical Pvt. Ltd.
- Contec Medical Systems Co. Ltd
- DRE Inc.
- GE Healthcare
- Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc.
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- Masimo Corporation
- Mediaid, Inc.
- Medtronic plc.
- Nihon Kohden Corporation
- Nonin Medical Inc.
- Omron Healthcare
- Smiths Group plc.
- SunTech Medical, Inc.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview
By Measuring Parameters:
- Oxygen
- Blood Pressure
- Temperature
- ECG
- Carbon dioxide
- Respiratory
- Heart Rate
- Blood Glucose
- Cardiac output
- Others
By Application:
- Intensive Care
- Veterinary
- Ambulatory
- Emergency
- Clinical
- Transport
- Anesthesia
- Others
By Form Factor:
- Portable
- Handheld
- Wearable
- Compact (Tabletop)
- Modular
- Floor standing
- Tunnel
By End User:
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Ambulatory Centers
- Home Healthcare
- Veterinary Clinics
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Vital signs monitoring devices provide a quantification of physiological functions that measures the basic medical indicators of health.
Blood pressure cuff, glucometer, pulse oximeter, ECG + Stethoscope, wearables, thermometer, and scale are the common remote patient monitoring devices.
Vital signs are used to measure the basic functions in humans such as pulse rate, body temperature, respiration rate, and blood pressure, it can record and store thousands of pieces of information.
Global vital signs monitoring devices market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period 2023-2031 and is expected to reach US$ 8,592.1 Million.
The Vital signs monitoring devices market is studied from 2018-2031.
Factor such as growth in demand for home care monitoring with the increasing ageing population and increasing incidence rate of chronic diseases drives the growth in the global vital signs monitoring devices market over the forecast period.
The intensive care segment holds the largest CAGR in the Global vital signs monitoring devices market during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific region is growing with the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
Competitive pricing pressure and the presence of counterfeit products is a restraining factor that inhibits the growth of the vital signs monitoring devices market over the forecast period.
China holds the major share in terms of revenue in the Asia Pacific vital signs monitoring devices market.
Technological advancement and innovation of new devices provide a lucrative growth opportunity in the vital signs monitoring devices.
Measuring parameters, application, form factor and end user are the different segments in the global vital signs monitoring devices market.
A&D Company Limited, Clarity Medical, CONTEC Medical Systems Co., Ltd., DRE Medical, Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc., Koninklijke Philips, Masimo Corporation, Nihon Kohden Corporation, Smiths Group plc. and SunTech Medical Inc. among others.
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)