Trade Finance Market: By Offerings Type (Trade Credit, Letter of Credit, Cash Advance, Purchase Order (PO) Finance, Receivables Discounting, Term Loans, Bill of Lading, Insurance, Others); Trade Type (Export Finance and Import Finance); Operation Model (Traditional and Digital); Providers (Banks, Trade Finance Houses, Insurance Companies, Others); Application (Domestic and International); End Users (SMEs, Large Enterprises); Industry (Manufacturing, Retail and E-Commerce, Construction, Others); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Dec-2024 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA12241037 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA12241037 | Delivery: Immediate Access
Market Scenario
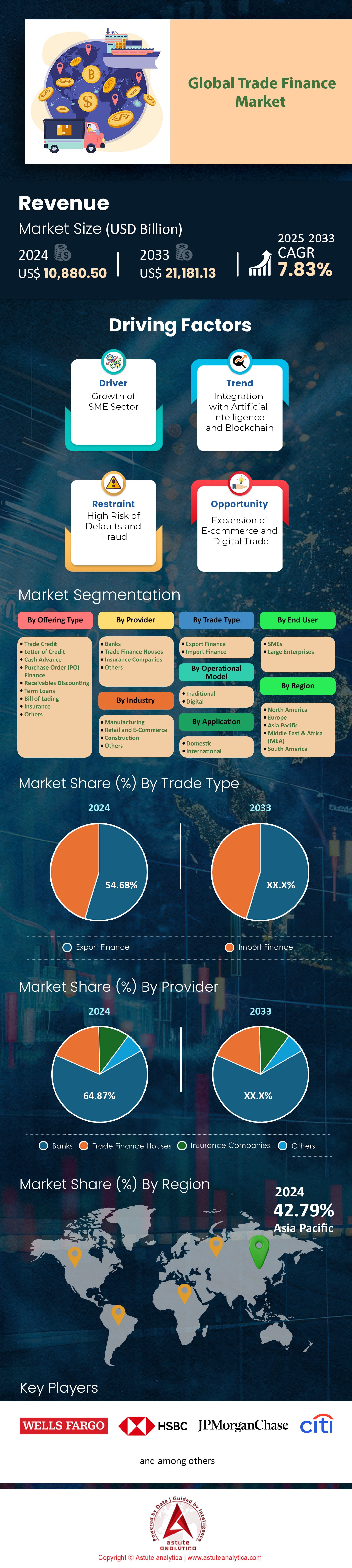
Trade finance market was valued at US$ 10,880.50 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 21,181.13 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 7.83% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
The global trade finance market landscape has witnessed unprecedented momentum in 2023, propelled by expanding cross-border transactions and innovative trading platforms that cater to both institutional and retail participants. Average daily forex turnover has surged to 7.5 trillion US dollars this year, reflecting heightened currency volatility and active hedging requirements. Cross-border payment flows now stand at 156 trillion US dollars, indicating robust import-export activities and remittance inflows. Institutional investors have intensified their presence in sustainable finance, with Europe reporting 650 billion US dollars worth of ESG-focused deals. Derivatives trading remains strong, as the United States averages 30 million contracts daily across options and futures.
Major financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, and Citigroup are reinforcing their technological capabilities to meet the growing demand for fast execution and diversified asset classes in the trade finance market. The New York Stock Exchange, featuring an average daily trade volume of 90 billion US dollars, continues to attract global liquidity. This vibrant setting has inspired more than 4,500 fintech firms to expand digital brokerage solutions tailored to multi-asset portfolios. Meanwhile, exchange-traded funds command an impressive 10 trillion US dollars in global assets under management, illustrating investors’ increasing appetite for cost-efficient, liquid, and transparent products. Around 130 countries are exploring central bank digital currencies, unveiling a future where financial trade may incorporate tokenized fiat.
Recent innovations underscore a rising emphasis on speed, security, and sustainable practices. New retail brokerage accounts in Asia trade finance market climbed to 7 million during the first half of 2023, demonstrating a wave of digitally savvy buyers and sellers. Partnerships between major exchanges and fintech startups have advanced blockchain-based settlements, cutting clearance times from days to hours. Ongoing research into AI-driven risk models is fostering greater confidence among institutional players who seek to mitigate volatility in real time. Altogether, these developments confirm that global financial trade is on a promising trajectory, with scalable technology and investor-driven sustainability goals shaping a resilient market outlook.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver Exploration: Emerging Crypto-Based Clearance Solutions Rapidly Accelerate Instantaneous Global Settlement Processes For Broader Liquidity Gains
The adoption of crypto-based clearance mechanisms in 2023 has opened new frontiers for real-time settlement, allowing banks and large-scale asset managers in the trade finance market to address the inefficiencies of legacy systems. Industry watchers estimate that on-chain stablecoin transactions surpassed 11 trillion US dollars globally this year, reflecting significant appetite for near-instant cross-border settlement. Financial conglomerates, including multiple G20 banks, have collaborated on pilot programs to integrate crypto-based clearing, and at least 50 million cross-border transfers utilized stablecoins during the second quarter alone. These large-scale, blockchain-enabled processes reduce reliance on intermediaries, thereby lowering transaction errors and drastically shortening reconciliation cycles.
Traditional payment networks, while historically robust, often require extended periods for fund settlement, especially across different jurisdictions in the trade finance market. Crypto-based solutions circumvent these delays by enabling direct asset exchange without multiple clearinghouses. Observers note that approximately 11 international central banks entered partnerships in 2023 to test distributed ledger frameworks for wholesale settlements, underscoring increased institutional recognition of digital currency-based architectures. Concurrently, more than 30 digital asset custodians emerged with specialized clearance solutions, reflecting the market’s drive to bolster trust and regulatory compliance in this space. These custodians rely on cryptographic protocols, ensuring the safety of transaction records even in high-volume trading conditions.
As adoption widens, technology providers are striving to integrate risk management capabilities and compliance features directly into blockchain platforms. Over 4 leading blockchain consortia have pooled resources this year to establish standardized protocols for settlement finality, custody frameworks, and identity verification. Such advancements promote clarity in a nascent sector often burdened by legal uncertainties in the trade finance market. By merging cryptographic assets with automated clearing processes, market participants aim to address global liquidity friction. Not only does this innovation foster interconnection among regional markets, but it also streamlines trading hours by offering 24/7 operational capabilities, ultimately stimulating a new era of fluid capital mobility.
Trend: Surging Sustainability-Linked Derivatives Gain Popularity Among ESG-Conscious Market Participants Globally For Responsible Investment Incentives
Sustainability-linked derivatives have captured heightened interest in 2023 as corporations and investors align portfolios with environmental and social objectives. Rough estimates indicate that these specialized contracts have reached US$ 280 billion in notional value, reflecting demand from firms seeking ways to hedge financial exposure while simultaneously meeting sustainability benchmarks. Several global investment banks in the trade finance market launched new product lines this year, tailoring derivatives that integrate key performance indicators related to carbon intensity or labor practices. This approach aligns trading outcomes with measurable progress on ESG goals, incentivizing positive corporate behavior across multiple industries.
To accommodate this growing trend, stock exchanges in Asia and Europe have introduced specialized listing segments for sustainability-driven instruments. Analysts estimate at least 85 newly listed sustainability-linked bonds gained derivatives overlays in 2023, demonstrating the coupling of fixed-income and derivatives markets for cohesive ESG strategies. Institutional portfolios in the trade finance market monitor such instruments, with over 60 pension funds globally adopting standardized ESG metrics in derivatives contracts for the first time. Notably, green finance hubs like Singapore and Luxembourg are refining regulatory guidelines to promote transparency and uniform disclosure, ensuring that sustainability-linked products remain credible and verifiable.
Market participants have also introduced technology-driven solutions to track performance data in real time. Software platforms now include automated dashboards that measure carbon offsets, social impact factors, and third-party audits. Recent data suggests that 15 major asset managers expanded their sustainability-linked coverage to commodity trades, bridging the gap between responsible finance and raw materials procurement. As corporate boards increasingly tie executive incentives to ESG performance, these derivatives provide a tangible mechanism to align profitability with ethical and ecological targets. Ultimately, the growing acceptance of sustainability-linked derivatives underscores a wider movement in global finance, highlighting socially conscious strategies as a mainstream and profitable dimension of modern trading.
Challenge: Regulatory Fragmentation Complicates Unified Compliance For Cross-Border Digital Trading Activities Amid Divergent Oversight Norms
Geographically disjointed regulations present a formidable challenge to digital trading ecosystems in 2023, particularly for institutions operating across multiple jurisdictions across the trade finance market. Recent reports suggest that 130 different regulatory frameworks are currently in effect worldwide, each imposing distinct requirements on Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols and capital adequacy. As a result, multinational finance entities often grapple with complex licensing processes, which limit their ability to scale offerings or launch new digital trading services seamlessly. In an environment where daily cross-border finance transactions exceed US$ 156 trillion, conflicting norms introduce inefficiencies that can hinder growth and innovation.
Technology providers have sought to address this fragmentation by developing compliance software that automates region-specific reporting obligations. At least 40 major banks have invested in integrated platforms that claim to reduce manual compliance work by merging data analysis with real-time updates on new regulations. Although these tools alleviate some burdens, observers highlight that digital trading instruments—ranging from security tokens to complex crypto derivatives—fall into regulatory grey zones in certain emerging markets. In more established jurisdictions, strict interpretations often loop in multiple oversight bodies, resulting in overlapping audits and extended dispute resolution timelines in the trade finance market.
In response, international standard-setting groups have begun coordinating to harmonize digital trading rules. Over 25 cross-border memorandums of understanding have been signed this year, aiming to streamline supervisory procedures and align definitions for blockchain-based instruments. However, progress remains uneven, and many critical areas, such as consumer protection and data privacy, continue to vary dramatically between regions. Financial institutions that cannot adapt to such mosaic-like oversight risk operational slowdowns, especially if mandated to halt specific trading activities pending regulatory clarifications.
Segmental Analysis
By Offerings
Letter of credit remains a dominant trade finance tool, holding nearly 39% share of the trade finance market. This leadership reflects its capacity to mitigate counterparty risk while guaranteeing prompt payment in cross-border deals Micro-economically, traditional bank intermediation ensures exporters receive funds once shipping documents are validated. Macroeconomically, volatile exchange rates and shifting global credit dynamics amplify reliance on LCs In 2023, TFG’s Letters of Credit Ultimate Guide reported over four million new LC issuances worldwide, signaling strong demand for document-backed settlements. The average transaction value climbed to US$ 2.7 million, confirming its prominence in high-value trade. HSBC supported US$ 60 billion worth of LC-based transactions this year, revealing the scale of global banks’ involvement Asia-Pacific alone initiated around 450,000 issuance requests, reflecting emergent economies’ rising preference for secure instruments. Meanwhile, more than 200,000 SMEs adopted LCs to lower payment risk in overseas ventures.
Banks, large exporters, and importers remain the principal end users, though smaller firms are increasingly embracing LCs to safeguard revenue streams In practice, exporters rely on guaranteed disbursement once evidence of shipment is verified, ensuring consistent cash flow. On the other side, importers in the trade finance market leverage LCs to confirm product quality and timely shipment before releasing funds. This alignment of interests enhances trust within global supply chains, where logistical disruptions and regulatory hurdles can create costly delays Additionally, heightened compliance requisites in cross-border commerce drive the popularity of letters of credit, as involved banks scrutinize every relevant document. On a broader scale, stabilized trade policies across emerging and developed nations encourage LCs for large-scale infrastructure projects and complex capital investments As digitization and blockchain-based solutions mature, letters of credit are poised to maintain their lead, offering unmatched security, minimized dispute risk, and operational efficiency in an evolving international trade environment.
By Trade Type
Export finance accounts for the lion’s share of global trade finance market, with more than 54.68% of cross-border transactions falling under its umbrella This prominence is rooted in a combination of supplier expansion, government-backed export credit schemes, and the proliferation of emerging markets as production hubs. Exporters gain access to pre- and post-shipment credit lines that stabilize cash flow during lengthy shipping cycles. According to an analysis by the International Chamber of Commerce, banks extended export financing support worth US$ 2.3 trillion worldwide this year, indicating robust institutional backing. In the same period, Export-Import Bank of China recorded over US$ 180 billion dedicated to export finance, emphasizing the role of policy banks in fueling outbound trade. An industry survey highlighted more than 70,000 export financing deals across Southeast Asia alone, underscoring the region’s increasing trade volumes. Commodity traders secured average loans exceeding US$ 1.2 billion for large-scale shipments in 2023.
This sustained growth emerges from key drivers, including heightened competition among exporters and evolving regulatory frameworks designed to reduce trade barriers Notably, advanced economies such as the United States and Germany trade finance market offer export credit guarantees to encourage local manufacturers to expand into untapped foreign markets. Simultaneously, emerging nations like Vietnam and India witness a steady increase in export-related credit demand, propelled by infrastructure upgrades and diversified production bases. Government subsidies and lower interest rates on export credit also attract companies looking to scale globally without straining their working capital. As a result, both large multinational corporates and small-scale producers can access sophisticated financing structures tailored to their operational timelines. Coupled with the rise of digital platforms that expedite documentation and reduce manual processes, export finance is set for further expansion in the coming years. Its flexibility in bridging payment gaps fosters cross-border collaboration among businesses of varying sizes.
By Providers
Banks dominate the trade finance market with 64.87% market share owing to their extensive global networks, regulatory influence, and deep capital reserves. As major intermediaries, they underwrite and facilitate a wide range of instruments—letters of credit, guarantees, and supply chain finance solutions—ensuring both liquidity and risk mitigation. In 2023, a consolidated study by the Bank for International Settlements revealed that commercial banks collectively issued trade finance products valued at over US$ 10 trillion, reflecting continued faith in banking institutions. JPMorgan Chase alone supported trade transactions exceeding US$ 1.5 trillion, underscoring the scale of top-tier providers. HSBC expanded its trade finance segment by onboarding around 8,000 new corporate clients this year, driven by demand for bundled financing services. Average processing time for documentary compliance dropped to 24 hours at major banks, highlighting technological improvements in transaction workflows. In emerging economies, local banks formed more than 500 cross-border alliances, bolstering credit distribution worldwide.
A key factor behind banks’ leadership in the trade finance market is their ability to offer end-to-end services, from factoring and invoice discounting to export credit insurance Their compliance infrastructure also reassures regulators and trading partners, as robust know-your-customer and anti-money-laundering procedures lower the risk of fraudulent transactions. Moreover, leading institutions such as Citibank and Standard Chartered invest heavily in digitization, utilizing blockchain-based platforms to speed up settlement cycles and cut operational costs. These initiatives resonate with corporations that value streamlined documentation and near-instant credit approvals. Another advantage is the global brand trust banks command, which encourages both small and large businesses to partner for cross-border transactions. By maintaining dedicated trade finance teams and round-the-clock customer support, banks cater to complex supply chain requirements across multiple time zones. As digital platforms and fintech collaborations evolve, banks remain well-positioned to sustain their dominance, offering integrated services that address the growing sophistication of global trade.
By Application
Trade finance sees its most prevalent use in international trade finance market, reflecting the complexities of cross-border commerce, currency fluctuations, and multi-jurisdictional risks. The international application holds over 67.55% market share. In 2023, global cross-border trade transactions under trade finance instruments surpassed US$ 14 trillion, according to data compiled by Swift and ICC. Banks in Asia processed around seven million international trade finance applications this year, illustrating the region’s central role in manufacturing and export-led growth. Meanwhile, the World Trade Organization recorded over 29 million shipping documents electronically verified through banking channels, signaling increasing adoption of digitized trade finance processes. The Export-Import Bank of India extended nearly US$ 45 billion in trade finance support for outbound transactions, further highlighting the emphasis on overseas project financing. Leading container lines and logistics providers collaborated on over 300 digitization initiatives to align shipping processes with trade finance functionalities, reducing paperwork backlogs.
The primary demand originates from exporters and importers who depend on financing structures to navigate extended payment terms, guarantee performance, and safeguard against political uncertainty As companies enter new territories in the trade finance markets, they face unfamiliar regulatory regimes, making instruments like letters of credit and export credit insurance critical for risk mitigation. Industries that rely heavily on complex supply chains—including automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals—drive a substantial portion of this demand, with multi-tiered producers seeking funding to cover raw material import costs and finished goods shipping. Another factor is the increasing role of global value chains: manufacturers in Europe often procure components from Asia, ship to North American markets, and rely on financial instruments to bridge cash flow gaps. This intersecting flow across continents necessitates robust trade finance solutions that can adapt to varied customs protocols and shipping timelines. Consequently, international usage remains the cornerstone of trade finance, facilitating global expansions and fueling new market opportunities.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific has cemented its position as the world’s leading trade finance market with over 42.79% market share by combining massive manufacturing output and extensive cross-border networks. In 2023 alone, it recorded US$560 billion worth of trade finance transactions, outpacing every other region in sheer volume. The International Chamber of Commerce documented over five million letter-of-credit issuances across key economies such as China, Japan, and South Korea in the first quarter of this year, reflecting the region’s robust appetite for structured financial instruments. A World Bank review pinpointed US$150 billion in yuan-denominated cross-border settlements by Chinese exporters, highlighting a growing trend of regional currency usage in trade finance. Singapore’s Networked Trade Platform processed more than 600,000 e-invoices by mid-2023, showcasing how digitalization is expediting credit approvals for importers and exporters alike. Meanwhile, Fintech Asia reported 2,000 new partnerships between banks and technology firms dedicated to enhancing automated documentation processes across Asian ports, reducing human error and accelerating transaction speeds.
This dominance in the trade finance market is underpinned by economic factors such as large-scale infrastructure projects, government-backed incentives, and continued shifts in global supply chains toward Asian markets. The Asian Development Bank has allocated US$4 billion to narrow trade finance gaps in Vietnam and Indonesia, reflecting multilateral commitment to sustaining growth in frontier economies. South Korea’s semiconductor exporters alone secured US$5 billion in supply chain financing this year, reinforcing the region’s capability to nurture high-value sectors. Hong Kong and Shanghai together facilitated US$200 million in short-term credit lines for electronics suppliers in the second quarter, indicating a steady flow of working capital to support advanced manufacturing. Across the region, over 150 banks now offer specialized trade finance solutions that combine traditional letters of credit with cutting-edge digital tools, making Asia Pacific a one-stop platform for diverse trading needs. With China’s Belt and Road Initiative spurring more than 200 infrastructure developments in emerging trade finance markets and e-commerce giants like Alibaba increasing cross-border sales, the region is positioned to sustain its leadership, leveraging innovation, large-scale investment, and progressive policies to maintain a thriving trade finance ecosystem for years to come.
Top Players in Trade Finance Market
- Asian Development Bank
- Barclays Bank
- Wells Fargo & Co.
- Banco Santander SA
- Standard Chartered Bank
- Bank of America Corp.
- Royal Bank of Scotland
- BNP Paribas SA
- Morgan Stanley
- Citigroup Inc.
- Mitsubishi Ufj Financial Group Inc.
- Credit Agricole Group
- JPMorgan Chase & Co
- Allianz Trade
- HSBC Holdings Plc
- HSBC Holdings Plc
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Offering Type
- Trade Credit
- Letter of Credit
- Cash Advance
- Purchase Order (PO) Finance
- Receivables Discounting
- Term Loans
- Bill of Lading
- Insurance
- Others
By Trade Type
- Export Finance
- Import Finance
By Operational Model
- Traditional
- Digital
By Provider
- Banks
- Trade Finance Houses
- Insurance Companies
- Others
By Application
- Domestic
- International
By End User
- SMEs
- Large Enterprises
By Industry
- Manufacturing
- Retail and E-Commerce
- Construction
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA12241037 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA12241037 | Delivery: Immediate Access 
.svg)






