Scaffold Technology Market: By Type (Macro-Porous Scaffolds, Micro-Porous Scaffolds, Nano-Porous Scaffolds, Solid Scaffolds, Matrigel Scaffolds, Hydrogel Scaffold (Wound Healing, 3D Bioprinting, Immunomodulation)); Cell Culture Type (2-D Cell Culture and 3-D Cell Culture); Material Type (Synthetic Scaffold and Natural Scaffold (Polysaccharides, Chitosan, Collagen, Fibrin)); Structure (Porous and Non-Porous); Application (Cancer Cell Research, Stem Cell Research, Drug Discovery, Regenerative Medicine); End Users (Hospitals & Clinics, Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Companies, Contract Research Laboratories, Academic Institutes); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: 18-Mar-2025 | | Report ID: AA0124733
Market Scenario
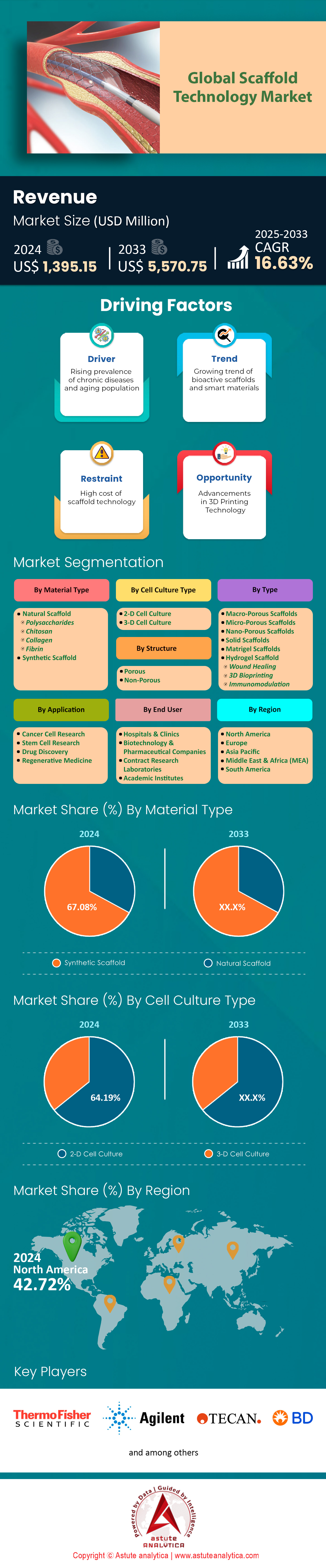
Scaffold technology market was valued at US$ 1,395.15 million in 2024 and is projected to surpass the market size of US$ 5,570.75 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 16.63% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
The growing demand for scaffold technology worldwide is primarily driven by advancements in regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. As the global population ages and the incidence of conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular ailments rises, there is a heightened need for innovative treatment modalities that scaffold technologies can provide. For instance, six in ten Americans now have at least one chronic disease, significantly boosting the demand for regenerative medicine solutions. This demand is further fueled by the expanding biotechnology industry and the rising awareness and acceptance of organ donation. Scaffold technology plays a crucial role in supporting tissue regeneration and repair, making it indispensable in fields such as orthopedics, dental care, and neurology. Notably, over four million bone graft and bone replacement procedures are performed worldwide each year, underscoring the critical role of scaffold technology in modern medicine.

The major types in the scaffold technology market include construction scaffolding and biotechnology scaffolding. Construction scaffolding encompasses frame and brace scaffolding, system scaffolding, rolling scaffold towers, suspended scaffolding, and tube and clamp scaffolding. In the biotechnology sector, scaffold types include hydrogels, polymeric scaffolds, and nanofiber-based scaffolds. Each type serves specific purposes, from providing structural support in construction to facilitating cell growth and tissue regeneration in medical applications. The key applications witnessing the highest growth are stem cell therapy, regenerative medicine, and drug discovery. These areas are experiencing rapid advancement due to the ability of scaffold technology to provide three-dimensional structures that support cell attachment, growth, and differentiation, crucial for developing personalized medicine and more accurate drug testing platforms. Governments worldwide are expected to spend about USD 6 billion on tissue engineering research by 2025, highlighting the significant investment in this field. Moreover, the stem cell therapy, regenerative medicine, and tissue engineering segment held a market share of 66.2% in 2024, reflecting its dominance in the scaffold technology market.
The demand for scaffold technology market is taking shape in the market through continuous innovation and integration with other cutting-edge technologies. For instance, the development of smart scaffolding systems incorporating IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of structural integrity and environmental conditions is enhancing safety and efficiency in construction. In the biomedical field, the integration of 3D bioprinting with scaffold technology is revolutionizing tissue engineering, allowing for the creation of patient-specific scaffolds with unprecedented precision. This evolution is supported by significant research and development investments, with companies reinvesting approximately 15% of their revenue into R&D, focusing on improving scaffold materials and 3D printing technologies. CytoNest Inc. recently launched the CytoSurge 3D fiber scaffold to enhance tissue engineering and cell production, showcasing the industry's commitment to innovation. Additionally, the orthopedics, musculoskeletal, and spine segment accounts for a significant portion of the scaffold technology market, driven by advancements in material science such as bioactive ceramics and biodegradable polymers. The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies is also revolutionizing scaffolding design and management, further propelling the market forward. North America held the largest market share in scaffold technology in 2023, reflecting its leadership in both construction and biomedical applications.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Increasing Demand for 3D Cellular Models in Biological Studies
The increasing demand for 3D cellular models in biological studies is a significant driver of scaffold technology market growth. Traditional 2D cell cultures have limitations in mimicking the complex three-dimensional environment of human tissues, leading to less accurate results in drug testing and disease modeling. Scaffold technology provides a 3D structure that closely resembles the extracellular matrix, allowing cells to grow and interact in a more natural environment. This has led to a surge in the use of 3D cellular models in research, particularly in areas like cancer biology, where understanding tumor behavior in a realistic setting is crucial. For instance, researchers are now using 3D scaffolds to study how cancer cells metastasize, providing insights that were previously unattainable with 2D models.
Moreover, the pharmaceutical industry is increasingly adopting 3D cellular models for drug discovery and toxicity testing. These models in the scaffold technology market offer a more accurate prediction of how drugs will behave in the human body, reducing the risk of late-stage clinical trial failures. According to recent data, the use of 3D cellular models has reduced drug development costs by up to 30%, making them an attractive option for pharmaceutical companies. Additionally, the rise of personalized medicine has further fueled the demand for 3D models, as they allow for the testing of treatments on patient-specific cells. This trend is expected to continue, with the global pharmaceutical industry investing heavily in 3D cellular model technologies to improve drug efficacy and safety.
Trend: Increased Use of Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering
The increased use of electrospun nanofiber scaffolds in tissue engineering is a prominent trend shaping the scaffold technology market. Electrospinning is a technique that produces nanofibers with diameters ranging from nanometers to micrometers, creating scaffolds with high surface area-to-volume ratios. These scaffolds are particularly effective in promoting cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation, making them ideal for tissue engineering applications. For example, electrospun nanofiber scaffolds are being used to regenerate skin, bone, and cartilage, offering a promising solution for patients with severe injuries or degenerative diseases. Recent studies have shown that these scaffolds can enhance the healing process by up to 40% compared to traditional methods.
Another key advantage of electrospun nanofiber scaffolds is their versatility in terms of material composition. Researchers can tailor the mechanical and biological properties of the scaffolds by using different polymers, such as biodegradable polyesters or natural proteins like collagen. This flexibility allows for the development of scaffolds that are specifically designed for different types of tissues in the scaffold technology market. For instance, electrospun scaffolds made from bioactive ceramics are being used in bone regeneration, while those made from biodegradable polymers are being used in soft tissue engineering. The global research community is increasingly focusing on optimizing electrospinning techniques to produce scaffolds with enhanced properties, such as improved mechanical strength and controlled degradation rates. This trend is expected to drive further innovation in the field of tissue engineering, with electrospun nanofiber scaffolds playing a central role.
Challenge: Complexity in Designing Scaffolds Mimicking Natural Tissue Microstructures
Complexity involved in designing scaffolds that accurately mimic the microstructures of natural tissues is one of the most significant challenges in the scaffold technology market. Human tissues have intricate architectures that vary significantly depending on their location and function. For example, bone tissue has a highly organized, porous structure that provides both strength and flexibility, while cartilage has a dense, fibrous matrix that absorbs shock. Replicating these complex microstructures in synthetic scaffolds is a daunting task that requires advanced manufacturing techniques and a deep understanding of tissue biology. Despite significant progress in 3D printing and electrospinning, achieving the level of detail needed to replicate natural tissues remains a major hurdle.
Another aspect of this challenge is the need to balance mechanical properties with biological functionality. Scaffolds must be strong enough to support tissue growth while also being biocompatible and biodegradable. Achieving this balance often involves trade-offs, as materials that are mechanically robust may not be ideal for cell attachment and growth. For instance, while metals like titanium are excellent for load-bearing applications, they are not biodegradable and can cause long-term complications in the body. On the other hand, biodegradable polymers may not provide the necessary mechanical support for certain tissues. Researchers are exploring hybrid materials and composite scaffolds to address this issue, but the development process is time-consuming and costly. This complexity in scaffold design is a major barrier to the widespread adoption of scaffold technology, particularly in clinical applications where precision and reliability are paramount.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Hydrogel scaffold segment of the scaffold technology market is set to continue leading the market with a robust market share of over 34.28% in 2024. This dominance is attributed to their exceptional water retention, biocompatibility, and natural extracellular matrix-like structure, which collectively foster reliable cell growth and tissue regeneration. Today, hydrogel scaffolds are widely utilized in areas such as wound healing, drug delivery, and tissue engineering. Their polymeric networks can integrate cells and active molecules without damaging biological functionality, allowing for more effective therapeutic interventions. In recent years, innovative research on hydrogel modifications has driven the creation of stimuli-responsive variants capable of adapting to changes in temperature, pH, or mechanical stress. These next-generation hydrogels broaden the scope of regenerative applications, offering potential breakthroughs in organoid cultivation and targeted drug release. Furthermore, hydrogel scaffolds’ compatibility with emerging 3D bioprinting techniques enhances precision and patient-specific design, reinforcing their status as a cornerstone in modern regenerative medicine.
Despite the current leadership of hydrogel scaffolds in the scaffold technology market, the nanofiber scaffold segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate, recording a CAGR of 17.36% in upcoming forecasts. Nanofiber scaffolds feature a densely woven architecture that significantly elevates surface area, supporting cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation. Their electrospun fibers replicate the intricate meshwork found within natural tissues, thereby improving interactive signals between cells. This intricate environment is invaluable for procedures like advanced wound care and nerve regeneration. The rising appeal of nanofiber scaffolds aligns with continuous investments in nanotechnology, promoting ever more refined fiber production methods. Ongoing research also explores hybrid scaffolds combining nanofibers and hydrogels for synergistic benefits, such as enhanced mechanical strength and controlled biodegradability. By offering a supportive matrix conducive to natural healing, both hydrogel and nanofiber scaffolds remain vital components of this evolving market. These advancements collectively drive heightened interest among clinicians and researchers worldwide.
By Material Type
Based on material type, synthetic scaffolds continue to dominate the global scaffold technology market, holding an impressive 67.08% share. Their success stems from the precise control manufacturers can exert over chemical composition, mechanical integrity, and degradation profiles. This rigorous consistency streamlines mass production, ensuring scalability for broader clinical use. Synthetic options, including polylactic acid (PLA) and polyglycolic acid (PGA), provide reliable support for tissue regeneration, while also allowing researchers to embed growth factors, peptides, or stem cells, thereby optimizing therapeutic outcomes. One crucial factor fueling this segment’s growth is the high level of customization that synthetic scaffolds allow. Parameters like pore size, molecular weight, and crosslinking density can be tailored to match different tissue types, from bone and cartilage to vascular grafts. Researchers exploit these adjustable properties to optimize cell adhesion and nutrient diffusion. As a result, synthetic scaffolds have emerged as a highly adaptable platform across a diverse spectrum of biomedical applications.
Looking ahead, synthetic scaffolds are projected to register the highest CAGR of 16.91% in the near future across the global scaffold technology market. Emerging technologies like 3D bioprinting and robotic assembly augment the production of complex, patient-specific implants. These approaches reduce material wastage and shorten lead times, supporting a more cost-effective manufacturing cycle. In tandem, ongoing efforts to improve biocompatibility and refine mechanical properties open up new avenues for advanced regenerative therapies and precision medicine. In addition, breakthroughs in biodegradable polymers drive interest in synthetic scaffolds that gradually dissolve once tissue regeneration is complete. This feature is particularly compelling in orthopedic and cardiovascular repairs, where temporary support structures reduce the need for secondary surgeries. With researchers consistently exploring novel polymer blends and manufacturing methodologies, synthetic scaffolds remain central to the future of scaffold technology. Their capacity to integrate with gene therapies, bioactive agents, and custom-tailored designs will likely reinforce their market dominance. Collaborations flourish.
By Application
The dominance of regenerative medicine, controlling 38.05% of the scaffold technology market revenue, is driven by the critical role scaffolds play in tissue engineering and stem cell therapies. Synthetic scaffolds have become indispensable in this field due to their superior properties, including biocompatibility, controlled degradation rates, and the ability to mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM). These features are essential for supporting cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation, which are fundamental to successful tissue regeneration. The higher demand for synthetic scaffolds in regenerative medicine is fueled by their versatility and adaptability. Materials such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polycaprolactone (PCL) can be engineered to meet specific mechanical and biological requirements, crucial for applications ranging from musculoskeletal to cardiovascular and neurological therapies.
The expansion of regenerative medicine's market share is further propelled by significant technological advancements and a supportive regulatory environment. Innovations in 3D printing and bioprinting technologies have revolutionized scaffold production, enabling the creation of complex structures with precise control over porosity and mechanical strength. This level of customization is essential for successful tissue integration and regeneration, particularly in personalized medicine applications. Additionally, regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA have established frameworks that facilitate the approval of innovative scaffold technologies, accelerating their market entry. This supportive landscape, coupled with increasing investments in research and development, is driving the synthetic scaffold segment towards significant growth. As of 2024, the global regenerative medicine market is projected to reach $42.18 billion, with expectations to soar to $398.77 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 16.79%. This remarkable growth trajectory underscores the expanding role of synthetic scaffolds in addressing the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the growing demand for personalized therapeutic solutions.
By Cell Culture Type
The 2-D cell culture's commanding 64.19% share of the scaffold technology market is rooted in its long-standing position as the gold standard for biological research and drug development. This dominance is primarily driven by the method's simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reproducibility, which are crucial factors in drug screening, toxicity testing, and disease modeling. The 2-D culture systems offer a straightforward approach by growing cells in a monolayer on flat surfaces, allowing for easier manipulation and observation of cell behavior. This simplicity translates into lower setup and maintenance costs compared to more complex 3D systems, making 2-D cultures particularly attractive for high-throughput screening in drug discovery processes.
Key factors behind the continued dominance of 2-D cell cultures include their established protocols, extensive comparative literature, and compatibility with existing laboratory equipment and imaging techniques. These advantages allow researchers to quickly interpret results and make informed decisions, accelerating the research process and potentially reducing time-to-market for new therapies. Moreover, the pharmaceutical industry's shift towards more personalized and targeted therapies has increased the demand for consistent and reproducible in vitro models, a need that 2-D cultures effectively meet. The market is further bolstered by continuous innovations in biotechnology and bioengineering, enhancing the performance of 2-D cultures through the development of new cell lines, culture media, and surfaces. Strategic collaborations and mergers within the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are also driving market growth, facilitating the rapid introduction of new technologies and methodologies. As of 2024, while 3D culture systems are gaining traction for specific applications, the operational simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of 2-D cultures continue to secure their dominant position in the market, particularly in early-stage drug development and large-scale experiments where high-throughput capabilities are essential.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America Set to Remain the Largest Region, With US is Being the Key Contributor
North America, capturing over 42.72% of the global scaffold technology market as of 2024, remains the most influential region driving this industry forward. A key contributing factor is the advanced healthcare infrastructure that fosters rapid adoption of innovative medical solutions. The United States alone surpasses USD 1 billion in market size, reflecting high research and development activity, which constitutes roughly 40% of global scaffold technology investments. This substantial funding underpins consistent breakthroughs in biomaterials, 3D printing techniques, and tissue engineering strategies.
Specific applications in orthopedics and dental implants command 40% of the region’s total usage, demonstrating a focused approach to addressing musculoskeletal disorders, bone regeneration, and robust dental restorations. Another cornerstone propelling the North American market is strong collaboration between academic institutions, private entities, and government agencies. These partnerships streamline clinical trials, expedite regulatory approvals, and ultimately accelerate market penetration. Furthermore, the demand for patient-specific treatments continues to rise, positioning North America as a key innovation hub for scaffold-based therapies.
Europe Holds Second Largest Share in Scaffold Technology Market
Following North America, Europe secures the second-largest market share in scaffold technology, buoyed by well-established healthcare systems and proactive research frameworks. Germany, the United Kingdom, and France spearhead this regional growth, collectively benefiting from a highly educated scientific ecosystem. Germany, in particular, accounts for over 15% of the European market, showcasing strong expertise in biomaterial development and tissue engineering experimentation. Government-funded healthcare institutions and private organizations in Europe allocate increasing resources toward regenerative medicine—up by 20% in funding over recent years. This infusion of capital drives the exploration of next-generation scaffolds designed for specific applications, notably cardiovascular and neurological procedures, which collectively comprise 35% of market usage in Europe. The region’s stringent regulatory environment, though rigorous, enforces product safety and reliability, fostering strong consumer confidence. Academic and commercial partnerships are similarly pivotal across Europe; these collaborations streamline the path from lab discovery to clinical implementation, ensuring continued advancement for scaffold-based medical technologies.
Asia Pacific Poised to Grow at the Robust CAGR
Asia Pacific, while ranking behind North America and Europe in overall scaffold technology market share, is rapidly ascending as a formidable player in scaffold technology. This region’s surge can be attributed to expanding healthcare infrastructures and increasing investments in advanced treatment modalities. China and India lead the pack; China alone claims a 30% share of the regional market, propelled by robust government initiatives and an ever-growing biotech sector. The region’s scaffold market is slated to grow at a CAGR of 16.25%, outpacing many global counterparts and highlighting its potential in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Major focus areas in Asia Pacific center on wound healing and tissue regeneration, together accounting for 30% of market applications. Japan’s emphasis on cutting-edge research, combined with its aging population, sustains a steady demand for innovative treatment approaches. Meanwhile, South Korea’s technologically progressive landscape underpins a swift adoption of medical innovations.
Top Companies in the Scaffold Technology Market
- 3D Biotek LLC
- Agilent Technologies Inc. (Biotek)
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Bico Group
- BioVison Incorporated
- Corning Incorporated
- Merck KGaA (Sigma aldrich)
- Promo Cell GmbH
- Reprocell Incorporation
- Synthecon Incorporated
- Tecan Trading AG
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Material Type
- Natural Scaffold
- Polysaccharides
- Chitosan
- Collagen
- Fibrin
- Synthetic Scaffold
By Type
- Macro-Porous Scaffolds
- Micro-Porous Scaffolds
- Nano-Porous Scaffolds
- Solid Scaffolds
- Matrigel Scaffolds
- Hydrogel Scaffold
- Wound Healing
- 3D Bioprinting
- Immunomodulation
By Cell Culture Type
- 2-D Cell Culture
- 3-D Cell Culture
By Structure
- Porous
- Non-Porous
By Application
- Cancer Cell Research
- Stem Cell Research
- Drug Discovery
- Regenerative Medicine
By End User
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Companies
- Contract Research Laboratories
- Academic Institutes
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 1,395.15 Million |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 5,570.75 Million |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Mn) |
| CAGR | 16.63% |
| Segments covered | By Type, By Material Type, By Structure, By Application, By Industry Verticals, By End-User, By Region |
| Key Companies | 3D Biotek LLC, Agilent Technologies Inc. (Biotek), Becton, Dickinson and Company, Bico Group, BioVison Incorporated, Corning Incorporated, Merck KGaA (Sigma aldrich), Promo Cell GmbH, Reprocell Incorporation, Synthecon Incorporated, Tecan Trading AG, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)