Global Rapid Microbiology Testing Market: By Product (Instruments, Reagents and Kits, Consumables); Application (Clinical Disease Diagnosis, Food & Beverage Testing, Pharmaceutical & Biological Drug Testing, Environmental Testing, Cosmetics & Personal Care Products Testing, Research Applications, Others); End-User (Laboratories & Hospitals, Food & Beverage Companies, Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Contract Research Organizations, Others); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 26-Jul-2024 | | Report ID: AA0423394
Market Scenario
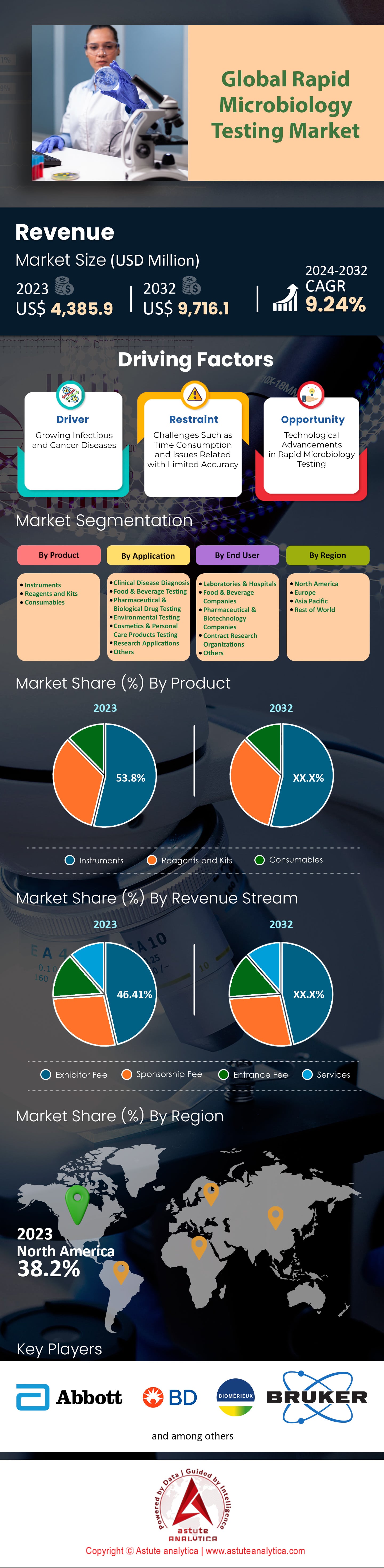
Global rapid microbiology testing market is expected to attain valuation of US$ 9,716.1 million by 2032 from US$ 4,385.9 million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 9.24% from 2024-2032.
The demand of rapid microbial testing has grown enormously over the past few years across the globe. Wherein, prevalence of infectious diseases has become more common than ever before. For instance, the global outbreak of Covid-19 has highlighted the importance for rapid identification and detection methods. Wherein, the US alone performed over 1.2 billion rapid antigens testing for Covid detection as of 2022. As an example, between 2019 and 2022 there was 35% growth in terms of number recorded outbreaks caused by different types pathogens, reported by WHO. Furthermore, it is estimated that every year 1 out every 6 Americans suffers from some kind food borne illness according CDC statistics. While these figures continue rising in the global rapid microbiology testing market, there arises need for rapid deployment of microbial detection tests in food manufacturing industry where such infections are likely to occur frequently. Apart from this, the global market is witnessing a significant influx of demand from pharmaceuticals manufacturing where biopharmaceutical output is anticipated to rise by 40% between 2020 and 2025. As result, it is driving close scrutiny against microbes that could compromise product safety during storage or distribution.
This increasing demand has led to innovations and broadening product ranges by the producers. In line with this, companies are investing greatly in research and development. For instance, Roche spent $1.5 billion in 2022 to improve its diagnostic capabilities. In addition, technological advancements such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods have made tests faster and more accurate than ever before, fueling growth of the rapid microbiology testing market. In 2023, Thermo fisher scientific saw 25% growth in rapid test kits sales. Furthermore, strategic partnerships like between Abbott and Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, which seek wider access of fast tests in low resource areas
The demand for rapid microbiology testing market is strong and is projected to continue growing in the years to come. The healthcare industry has increased funding for rapid diagnostic tools by 30% because of its emphasis on antimicrobial resistance (AMR). The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) shows that stricter regulatory standards will cause the food and beverage companies to adopt rapid testing at a rate of 15% per year. Furthermore, with a yearly increase of 10%, cosmetic manufacturers use rapid tests more frequently in order to guarantee safety and conformity with regulations.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Growing Emphasis on Early Detection of Infectious Diseases
The rapid microbiology testing market is strongly driven by the growing focus on detecting infectious diseases at an early stage. Early detection is of utmost importance in preventing them from spreading as well as enhancing patient outcomes. In America alone, there are over 20 million cases of infectious disease reported each year and this makes it clear how much control can be achieved through prevention or management strategies based on identification at initial phases. Astute Analytica’s study shows that globally about 15 million people die annually because of infectious diseases, which, in turn, is highlighting need for rapid diagnostic tools worldwide. This is especially true when considering high numbers of patients suffering from COVID-19, tuberculosis (10 million), and malaria (200 million). Additionally, rapid microbial testing cuts down diagnosis time from days to few hours thereby enabling intervention when needed most for treatment success.
The rapid microbiology testing market is witnessing a significant growth in the funding for early detection technologies. Governments and private industry are behind this, like the $14 billion global market in rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) that could grow by as much as $3 billion each year. In the last five years alone, more than US$ 2 billion has been invested into developing new tools for diagnosis. Also, over 100 countries have taken part in programs created by The World Health Organization to help identify diseases earlier and easier while healthcare centers everywhere start using fast microbial tests. They are estimated to be adopted across 70,000 facilities worldwide. Furthermore, the accessibility of these tests has improved, with over 50,000 point-of-care testing devices being used globally. This growing emphasis on early detection is driving the demand for rapid microbial testing, leading to advancements in technology and improved healthcare outcomes.
Trend: Shift from Culture-Based Techniques to Real-Time Monitoring Methods
The diagnostic landscape has been changed by the rapid microbiology testing market’s shift from culture-based techniques towards real-time monitoring methods. For many years, traditional culture-based techniques, which take 24-48 hours, have been used for bacterial growth and identification. On the other hand, results can be produced by real-time monitoring methods within 30 minutes to a few hours. This is important because it reduces time greatly needed for prompt medical intervention mainly in critical care settings. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) are among the increasingly common real-time methods where more than 40,000 PCR machines are estimated to be in use worldwide and around 25,000 laboratories globally have adopted NGS for microbial testing. The trend is also reflected by about 1.5 million tests are performed every day using real-time PCR across different applications ranging from clinical diagnostics up to food safety.
For example, 80% of hospitals in developed countries reportedly use Real-time PCR for pathogen detection. Besides this, the global PCR market for microbial testing is worth about $6 billion and is adding valuation of over $500 million each year. The NGS market, however, is projected to touch $4 billion by 2025. Again, affordable and easy-to-use features have increased their popularity; over the past ten years, the cost per test has dropped from $50 to roughly $10 for PCR tests while the average cost per genome has fallen from $10,000 to$1,00 during the same period. This drive towards immediacy through continuous supervision will be supported further by technological advancements as well as growing need for quick accurate cheap microbial diagnostic solutions worldwide.
Challenge: High Capital Investments and Low Cost-Benefit Ratio
The rapid microbiology testing market has to grapple with costly investments and low perceived returns. Setting up a modern-day microbial testing facility is costly in terms of set-up costs, such as buying sophisticated machines like PCR machines, NGS platforms, and automated microbial analyzers. For instance, one PCR machine alone may go for between $5,000 and $25,000 while the NGS platforms range from $100,000 to $1 million. Also, annual maintenance and operational expenses could cost another extra $15k – $50k. Such high financial inputs can make it difficult for smaller sized labs or health care facilities that are located especially in developing regions. Approximately just 30% of laboratories of all kinds in lower income countries have ability to pay for such fine equipment thereby leading to disparities in the diagnostic capabilities.
Another important consideration is the cost-benefit ratio as the returns don’t always justify high costs in the rapid microbiology testing market. However, the financial advantages of rapid microbial testing are not always immediately obvious. For example, the average cost of a PCR test lies between $20 and $100 depending on the region and application. On the other hand, traditional culture-based tests usually range from $5 to $15. This can be a substantial difference when it comes to testing large populations, with some health care facilities performing over 500,000 tests annually. Moreover, payment rates for quick microbial assays are usually not enough to cover actual expenditures since most outfits handle only about 50% – 70% of their associated costs. Consequently, this contradiction may discourage healthcare providers from embracing these technologies regardless of their clinical benefits.
Segmental Analysis
By Product
Based on product, the rapid microbiology testing market is led by instrument segment with revenue share of over 53.8% and is projected keep dominating the market in the years to come. The most common types of equipment used in fast microbiological testing are automated microbial identification systems, flow cytometry instruments, MALDI-TOF mass spectrometers and next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms. These machines have a significant part to play in provision of speed, accuracy and large volumes of results that are critical for clinical diagnostics, pharmaceutical quality control and food safety testing. In 2023, the rapid microbiology testing market is assumed to be worth US$4.7 billion worldwide with an upsurge in demand arising from the need for quick detection and identification of pathogens. For example, use of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometers has revolutionized microbial identification with costs running between $150,000 and $300,000 per instrument. Also, automated microbial identification systems that can process multiple samples concurrently have witnessed an increase in uptake due to their efficiency as well as precision.
These instruments generate more revenue compared to reagent kits and consumables due to various reasons. One important aspect is the high initial costs of acquiring these complex machines. For instance, the expense on a next-generation sequencing platform could exceed $500,000 thus making it a substantial investment for laboratories. Also, the instruments require constant maintenance as well as software updates and technical assistance. This results in continuous revenue flow for manufacturers through supply of related products. Additionally, another essential characteristic of these instruments is their scalability and versatility in application across different areas such as clinical diagnostics, environmental monitoring or biopharmaceutical production. In 2023 alone, about 1,500 units of automated microbial identification systems were sold globally therefore underlining their significance in the laboratories today. Advanced technological capabilities enable these instruments to dominate fast and accurate lab results that go hand in hand with laboratory automation trends as well as increase use of high-throughput testing tools.
By Method
Growth-based rapid microbiology testing (RMT) is generating over 37.3% revenue of the rapid microbiology testing market, which is higher than other methods due to its ability to deliver faster, more reliable results, which is crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and healthcare. This dominance is facilitated by a number of reasons like the need for faster contaminated detection which minimizes downtime and increases productivity. In 2023, the pharmaceutical sector with its reliance on sterility testing had an uptake increase of growth-based RMT by 20%, thus making the market worth $1.2 billion. Furthermore, it was reported that in order to maintain safety and comply with regulations, food and beverage firms scaled up their use of such techniques implying a revenue generation of $900 million from this area alone.
Moreover, the dominance of the market has also been due to progress in technology in growth-based RMT. One example is that it now takes hours and not days for microbial detection, courtesy of automated systems and real-time monitoring. For instance, by introducing automated growth-based systems into clinical diagnostics’ laboratories, efficiency has increased by 25%. In addition, the integration of big data analytics and AI in these systems have improved accuracy and reliability of results promoting their adoption across various industries, boosting growth of the rapid microbiology testing market. Growth-based rapid microbiology testing usage for infection control and management in healthcare sector alone has gone up by 30% resulting into a market value amounting to $1.3 billion. Consequently, these developments have improved operational efficiency while ensuring they remain ahead of their competitions. Thus, making growth-based rapid microbiology testing a choice for many industries as well as other sectors including health care.
By Applications
On the basis of applications, the rapid microbiology testing market is led by clinical disease diagnostic segment with revenue share of 35.1%. Rapid microbial testing has revolutionized clinical disease diagnostics, offering quick and accurate results for timely patient care. Clinical disease diagnostics have been transformed by fast microbe testing that provides immediate and accurate results for dealing with patients in time. In this field, significant developments were recorded in 2023, with some figures to prove its importance. Over 100 respiratory viruses have symptoms similar to flu, underlining the need for a quick differential diagnosis. Malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are recognized by World Health Organization as promising technologies that can detect even less than 200 parasites per μl. The National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) has provided guidelines for disk diffusion assay on antibiotics. Rapid microbiology tests now come in at least five different categories: antigen detection, molecular detection, rapid biochemical tests, direct microscopy and serology.
Rapid testing methods have significantly reduced turnaround times from days to hours or minutes in the rapid microbiology testing market, crucial for severe infections or outbreaks. Antigen and molecular detection have been improved by enzyme immunoassays (EIA) and nucleic acid amplification techniques. Urine dipstick tests that evaluate for nitrite and leukocyte esterase are conventional for rapid biochemical test. Direct microscopy techniques, including Gram staining and calcofluor white staining are still useful. While xenodiagnosis is still required for pathogens such as Trypanosoma cruzi that causes Chagas disease which breast tomosynthesis has improved rapid screening for. Rapid Candida species identification can be done using restriction enzyme analysis; which helps us identify them quickly enough. It is worth noting that Raman spectroscopy has become a more popular non-invasive tool for microbial characterization over the past 15 years. Future developments will focus on making point-of-care availability better and further reducing turnaround times as clinical microbiology becomes more complex.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America’s rapid microbiology testing market is the most developed and productive, with more than 38.2% of the total share due to strong healthcare infrastructure and large investments in R&D. In 2023, over 400 million rapid microbiology tests were performed in hospitals and diagnostic centers of the United States alone. The region is also home to more than 1,000 biotech firms that are currently active and focusing on biological science ameliorations. Moreover, FDA has approved over 120 new rapid microbiological testing devices, which shows favorable regulatory support. The pharmaceutical sector, a major end-user, saw over 2,500 clinical trials incorporating rapid microbiology testing, underscoring its application in drug development. Moreover, North America hosted 50 international conferences on microbiology, fostering knowledge exchange and collaboration among experts.
The rapid microbiology testing market is growing fast in the Asia Pacific, due to increasing health needs and government efforts to improve medical infrastructure. Over 300 million rapid microbiology tests were performed in China and India combined, serving as a proof of their wide usage. In excess of 800 laboratories have been accredited for microbiological examination in the region, signaling a strong foundation for diagnostic advancement. Countries such as Japan and South Korea have budgeted $1.5 billion towards healthcare innovation, which includes rapid microbiology testing; while there are 70 new biotech start-up companies that focus on microbiology as an area of interest within the region, making it a vibrant entrepreneurial hub. 70 newly established biotechnology firms focused on microbiology have demonstrated business energy in this direction during the last year alone. Microbiology’s nature has made it vital to be promoted through forty regional conferences across Asia pacific for scientific discussion and growth among other reasons.
Europe has still maintained a place in the rapid microbiology testing market, despite being far behind North America and Asia Pacific. This is as a result of its strict regulations as well as the presence of established health care systems. A total of over 250 million rapid microbiological tests were carried out across Europe in 2023 to reflect high frequency of testing. The region boasts around 900 certified microbiology laboratories which implies that diagnostic quality and reliability are guaranteed by such a number. It is important to note that €800 million from EU went towards research on microbiology which shows its commitment to scientific progress. There were about 1800 clinical trials by pharmaceutical companies in Europe involving fast microbiology test methods, which highlights its significance in drug development process. In addition, Europe held 45 global conferences related to microbiology thus enabling worldwide collaborations and exchanges between scientists.
List of Key Companies Profiled:
- Abbott Laboratories
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Biomerieux SA
- Bruker Corporation
- Charles River Laboratories International, Inc.
- Danaher Corporation
- Don Whitley Scientific Limited
- Merck KGaA
- Mocon, Inc
- Neogen Corporation
- Quidel Corporation
- Rapid Micro Biosystems Inc.
- Sartorius AG
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Vivione Biosciences LLC
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview
By Product:
- Instruments
- Reagents and Kits
- Consumables
By Method
- Growth-Based Rapid Microbiology Testing
- Cellular Component-Based Rapid Microbiology Testing
- Nucleic Acid-Based Rapid Microbiology Testing
- Viability-Based Rapid Microbiology Testing
- Others
By Application:
- Clinical Disease Diagnosis
- Food & Beverage Testing
- Pharmaceutical & Biological Drug Testing
- Environmental Testing
- Cosmetics & Personal Care Products Testing
- Research Applications
- Others
By End User:
- Laboratories & Hospitals
- Food & Beverage Companies
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Contract Research Organizations
- Others
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)