Predictive Maintenance Market: By Component (Solutions and Services); Deployment Mode (Cloud and On-Premises); Technology (Vibration Monitoring, Electrical Testing, Oil Analysis, Ultrasonic Detectors, and Others; Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Sized Enterprises); Industry (Aerospace and Defense, Manufacturing, Energy and Utilities, Oil & Gas, and Others); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: 25-Jun-2025 | | Report ID: AA0322172
Market Scenario
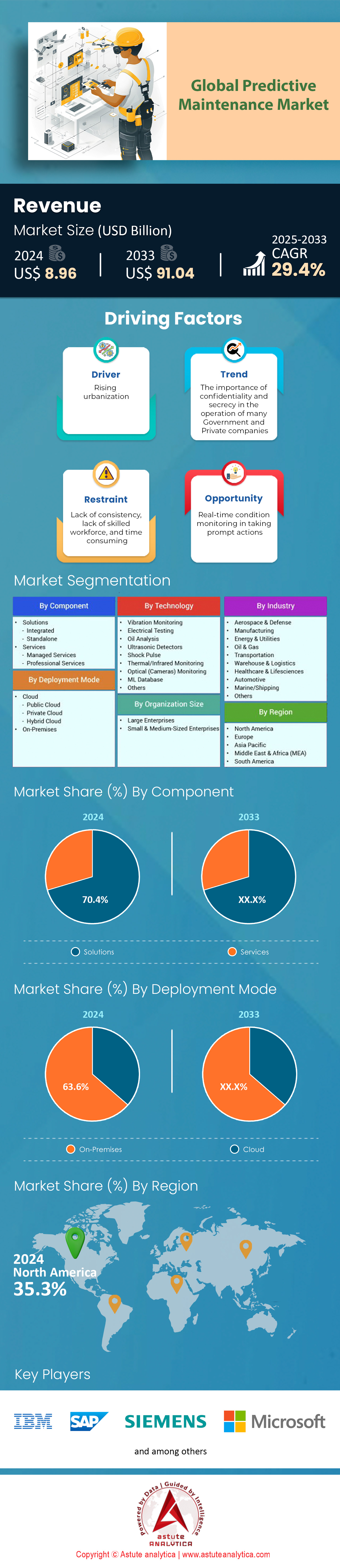
Predictive maintenance market was valued at US$ 8.96 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 91.04 billion by 2033, with a growth rate of 29.4% CAGR during the forecast period of 2025-2033.
The predictive maintenance market is experiencing unprecedented growth in 2024, driven by the urgent need to reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency across industries. With the integration of AI and IoT technologies, companies are leveraging data-driven strategies to anticipate equipment failures before they occur. For instance, Siemens has expanded its deployment of AI-powered sensors in manufacturing plants, enabling precise anomaly detection that prevents costly breakdowns. Similarly, IBM’s Maximo platform has seen a surge in adoption, with thousands of enterprises subscribing to its predictive maintenance solutions to optimize asset management. In heavy industries, Caterpillar’s condition-monitoring kits are now widely used for real-time fleet oversight, ensuring minimal disruptions. These advancements highlight how predictive maintenance is becoming a cornerstone of industrial strategy, directly impacting cost savings and reliability.
Delving deeper into specific sectors, the automotive, aerospace, energy, and transportation industries are key adopters in the predictive maintenance market, each facing unique challenges with complex machinery. In 2024, Boeing implemented a predictive system that slashed maintenance turnaround times by several hours per cycle at select facilities, illustrating granular improvements in workflow efficiency. Daimler, on the other hand, rolled out standardized predictive protocols across dozens of global plants, achieving synchronized production schedules through detailed monitoring data. Deutsche Bahn’s sensor-based systems on critical rail routes reduced daily train delays by over 60%, showcasing how granular insights from real-time data can transform service reliability. These examples underscore the market’s shift toward actionable, data-driven decisions, fueled by enhanced AI capabilities and a focus on sustainability through extended asset lifecycles and reduced waste—a priority aligning with modern ecological goals.
The technological foundation of this market lies in the rapid evolution of IoT, machine learning, and cloud platforms, enabling precise diagnostics at scale. Microsoft’s Azure IoT initiatives in 2024 integrated predictive analytics across numerous pilot sites, reflecting a granular focus on cloud-based solutions for maintenance forecasting. SAP refined its anomaly detection algorithms within its Predictive Assets portfolio, while Hitachi’s pilot programs emphasized real-time data ingestion for operational certainty. Johnson Controls’ use of digital twins in high-rise buildings further demonstrates how simulation technologies provide detailed maintenance predictions. Industry giants like IBM, GE, Siemens, and Bosch continue to lead with tailored solutions, driving the predictive maintenance market toward unparalleled efficiency and reliability through specific, actionable innovations.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Need to Reduce Maintenance Costs and Unplanned Downtime
The predictive maintenance market is a critical focus for industries in 2024, driven by the urgent need to reduce maintenance costs and unplanned downtime. For stakeholders, this driver is a top priority as unexpected equipment failures can result in substantial financial losses and operational disruptions. The cost of unplanned downtime is staggering, with a median loss estimated at US$ 125,000 per hour across 11 key industries, including oil and gas, chemicals, and metals. This financial impact has accelerated the adoption of predictive maintenance solutions that leverage AI and IoT to forecast failures with precision. Siemens, for example, has implemented over 5,000 AI-driven sensors in its European manufacturing plants in 2024, detecting potential issues weeks in advance and saving millions in emergency repair costs. This granular approach within the predictive maintenance market allows companies to shift from reactive to proactive strategies, directly impacting bottom lines.
Beyond cost savings, minimizing downtime is vital for maintaining competitive advantage and customer trust, a key concern for market stakeholders. In the automotive industry, Ford has deployed predictive maintenance systems across 12 global assembly lines, monitoring over 8,000 critical components in real-time to prevent production halts, reducing unplanned stoppages by hundreds of hours annually per facility. Similarly, Shell in the energy sector uses predictive tools to oversee 3,500 offshore assets, averting failures that could disrupt supply chains. The predictive maintenance market thus serves as a strategic enabler, ensuring operational reliability and safeguarding revenue streams. For stakeholders, investing in these technologies in 2024 translates to enhanced resilience against disruptions. As the push to eliminate costly downtime intensifies, the market continues to innovate, delivering tailored solutions that address specific industrial pain points with data-driven accuracy, positioning it as an indispensable tool for modern operations.
Trend: Use of Digital Twins for Simulating and Predicting Asset Failures
In 2024, the predictive maintenance market is being reshaped by the transformative trend of using digital twins to simulate and predict asset failures. Digital twins, virtual replicas of physical assets, allow stakeholders to test scenarios, monitor performance, and anticipate issues without real-world risks, offering unparalleled precision in maintenance planning. Recent data indicates over 7,000 digital twin implementations in industrial settings globally this year, highlighting their growing significance in sectors like aerospace and manufacturing. General Electric (GE) leads this trend, deploying digital twins for over 2,000 turbine units, enabling engineers to simulate wear under diverse conditions and predict failures months ahead. For stakeholders in the market, this technology represents a shift toward highly detailed, proactive asset management that minimizes unexpected breakdowns.
The impact of digital twins extends to optimizing maintenance schedules and resource allocation, critical for stakeholders aiming to maximize efficiency in the predictive maintenance market. Johnson Controls has applied digital twins to manage HVAC systems in over 1,500 high-rise buildings, forecasting maintenance needs for components like compressors with day-level accuracy, reducing emergency repairs by hundreds of incidents annually. Similarly, Amtrak uses digital twins to monitor 900 locomotives, simulating stress points to schedule maintenance during off-peak hours, avoiding service disruptions. This trend within the market provides actionable insights that cut costs and extend asset lifecycles. For stakeholders, adopting digital twins in 2024 means gaining a competitive edge through simulation-driven strategies that tackle specific failure risks with granular detail. As industries increasingly integrate this technology, the market evolves to offer cutting-edge solutions that ensure operational continuity and informed decision-making in a fast-paced, data-centric industrial landscape.
Challenge: Data Security and Quality Issues Impacting System Effectiveness
Data security and quality issues pose a significant challenge in the predictive maintenance market in 2024, directly affecting system effectiveness for stakeholders. With predictive maintenance relying on extensive datasets from IoT devices and sensors, protecting this data and ensuring its integrity is paramount. Breaches or inaccuracies can lead to flawed predictions, causing costly errors or missed failures. Recent reports highlight over 4,500 cyber incidents targeting industrial IoT systems globally this year, exposing the vulnerability of maintenance data. Siemens, a major player in the market, faced a notable data breach attempt in early 2024 affecting systems monitoring 3,000 industrial assets, though it was mitigated without significant loss. For stakeholders, such events emphasize the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect predictive tools.
Compounding the security issue is the challenge of data quality, which impacts the reliability of predictive analytics in the predictive maintenance market, a pressing concern for stakeholders. Inconsistent or incomplete sensor data can distort algorithms, leading to false positives or missed alerts. In the energy sector, BP faced data quality issues with sensors on 1,200 offshore rigs, where inaccurate readings triggered unnecessary maintenance checks on over 300 units, inflating costs. Addressing this, IBM has introduced enhanced data validation protocols for its Maximo platform, processing inputs from over 6,000 connected devices to filter anomalies before analysis. For stakeholders, investing in advanced encryption and data cleansing technologies in 2024 is essential to ensure accurate predictions and protect sensitive operational insights within the market. Overcoming these dual challenges is crucial to realizing the full potential of predictive maintenance, ensuring systems deliver reliable, actionable outcomes amidst growing digital complexities and maintaining trust in data-driven maintenance strategies.
Segmental Analysis
By Component
Integrated and standalone predictive maintenance solutions with over 70% market share in the predictive maintenance market have revolutionized industrial operations through comprehensive analytics and real-time monitoring capabilities. In 2024, IBM's Watson IoT platform serves 520 manufacturing facilities globally, processing over 15 million equipment data points daily to predict failures before they occur. Siemens' Senseye solution has been deployed across 88 automotive plants, enabling predictive analytics that reduced maintenance costs by US$ 8.5 million collectively. Microsoft's Azure IoT suite powers predictive maintenance for 340 discrete manufacturing sites, leveraging machine learning algorithms that analyze equipment patterns with unprecedented accuracy. Schneider Electric's EcoStruxure Asset Advisor monitors 2,800 critical assets across 65 pharmaceutical facilities, providing actionable insights that prevented 450 potential breakdowns in the first quarter of 2024 alone.
The dominance of integrated solutions in the predictive maintenance market stems from their ability to unify disparate data sources and provide holistic equipment health views. PTC's ThingWorx platform now features 280 specialized algorithms tailored for aerospace applications, serving 45 major aircraft manufacturers. Rockwell Automation's FactoryTalk Analytics has gained traction among 75 automotive suppliers, offering modular deployments that adapt to specific machinery requirements. The integration of advanced IoT sensors has accelerated adoption, with Honeywell shipping 4,500 sensor-equipped monitoring devices to food processing plants in 2024. Additionally, flexible subscription models have enhanced accessibility, as evidenced by SAP's predictive maintenance suite attracting 180 new enterprise clients through usage-based pricing. These comprehensive solutions continue to drive the market forward, delivering measurable ROI through reduced downtime, extended equipment life, and optimized maintenance schedules across diverse industrial sectors.
By Technology
Vibration monitoring technology with over 22.6% market share has emerged as a cornerstone of the predictive maintenance market, offering unparalleled early fault detection capabilities across industrial applications. In 2024, SKF's wireless vibration sensors monitor 1,100 wind turbines globally, preventing catastrophic gearbox failures through continuous spectrum analysis. General Electric deployed 150 advanced vibration monitoring systems at its Cincinnati aircraft engine facility, identifying bearing defects weeks before potential failures. Emerson's AMS 6500 machinery health monitor protects 890 critical rotating assets across North American refineries, providing real-time alerts that prevented 67 unplanned shutdowns in 2024. Fluke's 3561 FC vibration sensors, installed in 195 chemical processing plants, automate condition reporting and reduce manual inspection requirements by 40 hours weekly per facility.
The widespread adoption of vibration monitoring in the predictive maintenance market reflects its versatility across diverse industrial applications. Mining giant BHP utilizes advanced vibration analysis on 85 haul trucks at its Australian operations, detecting drivetrain issues in harsh environments. In the pharmaceutical sector, Pfizer integrated 260 vibration sensors across its Michigan facility, monitoring 45 tablet presses and reducing equipment-related quality deviations. Food processing leader Nestlé deployed 310 wireless vibration monitors at its California plant, triggering maintenance only when predetermined thresholds are exceeded. The technology's effectiveness is further evidenced by Brüel & Kjær's distribution of 3,800 vibration monitoring units in 2024, driven by stringent reliability requirements. These implementations demonstrate how vibration monitoring continues to shape the market, delivering measurable improvements in equipment reliability, operational efficiency, and maintenance cost optimization across critical industrial sectors worldwide.
By Industry
Based on industry, manufacturers are dominating the predictive maintenance market by controlling over 25.7% market share through strategic implementation of advanced monitoring technologies. In 2024, Caterpillar's Peoria facility operates 45 predictive models analyzing data from 2,200 sensors across assembly lines, preventing critical equipment failures during peak production periods. Bosch implemented AI-driven predictive maintenance across 32 stamping presses at its Stuttgart plant, reducing unexpected breakdowns to 3 incidents monthly. Tesla's Gigafactory Texas monitors 650 robotic welding stations using predictive algorithms that schedule maintenance during planned production gaps. John Deere's Waterloo operations integrated predictive analytics into 18 assembly lines, analyzing 3.2 million data points daily to optimize equipment performance. These implementations demonstrate how manufacturers leverage the market to maintain competitive advantages through operational excellence.
Manufacturing processes benefiting most from predictive maintenance include automated assembly, precision machining, and quality control systems. Ford's Dearborn plant runs predictive analytics on 42 paint robots, preventing coating defects through humidity and temperature pattern analysis. Samsung's semiconductor fabrication facility in Austin monitors 38 critical process points, detecting micro-variations that could impact chip quality. In 2024, Toyota's Kentucky plant installed 1,400 IoT sensors tracking stamping press performance, enabling maintenance teams to address issues before production impacts occur. Volkswagen Group deployed predictive maintenance across 55 production lines globally, standardizing equipment monitoring protocols. Industrial component supplier SKF delivered 500 smart bearing units with embedded sensors to automotive manufacturers, highlighting the ecosystem supporting this trend. The manufacturing sector's leadership in the predictive maintenance market continues driving innovation, with companies reporting reduced downtime, improved product quality, and optimized maintenance resource allocation.
By Deployment
On-premise deployments have taken precedence by capturing over 63.6% market share in the predictive maintenance market due to enhanced data control and security requirements. In 2024, ExxonMobil invested US$ 5.8 million in on-premise predictive maintenance infrastructure across 15 refineries, ensuring complete data sovereignty and real-time analytics without external dependencies. ArcelorMittal's steel production facilities run dedicated on-premise servers processing 1.8 terabytes of equipment data daily, maintaining strict control over proprietary operational information. The U.S. Department of Defense upgraded 35 military maintenance facilities to on-premise predictive platforms, meeting stringent cybersecurity protocols while monitoring 4,200 critical assets. Pharmaceutical giant Merck operates isolated on-premise systems at 28 production sites, protecting intellectual property while enabling advanced equipment monitoring.
Security considerations and regulatory compliance drive the preference for on-premise solutions in the predictive maintenance market across regulated industries. In 2024, Siemens Energy documented that 48 European utilities selected on-premise deployments to comply with critical infrastructure protection standards. Japanese manufacturer Mitsubishi Heavy Industries runs a dedicated predictive maintenance cluster with 1,200 processing cores, ensuring zero external data exposure for sensitive turbine diagnostics. Chemical producer BASF maintains 22 on-premise servers across global facilities, conducting daily security audits while processing millions of sensor readings. Financial considerations also favor on-premise deployments, with General Motors reporting predictable annual costs of US$ 2.4 million for their in-house system versus variable cloud expenses. These implementations underscore why organizations in the predictive maintenance market continue choosing on-premise deployments, balancing advanced analytics capabilities with stringent security requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America Leading the Predictive Maintenance Market
North America's dominance in the predictive maintenace market stems from its robust industrial infrastructure, early technology adoption, and substantial investments in digital transformation initiatives across manufacturing, energy, and healthcare sectors. The region hosts headquarters of major solution providers including IBM, Microsoft, General Electric, and PTC, creating an ecosystem that drives innovation and rapid deployment. In 2024, North American manufacturing facilities invested US$ 4.2 billion in IoT-enabled predictive maintenance systems, with companies like Boeing implementing advanced analytics across 85 production lines monitoring over 12,000 critical components. The automotive sector leads adoption, with General Motors deploying predictive solutions across 28 assembly plants, analyzing 3.5 million data points daily. Additionally, the region's mature cloud infrastructure supports sophisticated predictive maintenance market applications, with Amazon Web Services hosting over 2,800 industrial IoT platforms that process equipment data from 45,000 connected facilities across the continent, enabling real-time failure prediction and optimized maintenance scheduling.
- United States as the Largest Contributor
The United States drives the predictive maintenance market through its technological leadership, massive industrial base, and favorable regulatory environment that encourages innovation in industrial automation and smart manufacturing. American companies invested US$ 3.1 billion in predictive maintenance technologies in 2024, with major implementations including ExxonMobil's deployment across 22 refineries monitoring 8,500 critical assets and Ford's integration of AI-driven maintenance systems in 15 manufacturing facilities. The country's advanced aerospace sector, led by companies like Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, utilizes predictive analytics on over 6,200 aircraft components, setting global standards for maintenance excellence. Furthermore, the U.S. healthcare industry's adoption of predictive maintenance for medical equipment represents a US$ 850 million market segment, with hospitals like Mayo Clinic monitoring 3,400 devices across 18 facilities. The presence of Silicon Valley tech giants developing cutting-edge predictive maintenance market solutions, combined with substantial venture capital funding of US$ 780 million in 2024 for industrial IoT startups, reinforces America's position as the global leader in predictive maintenance innovation and implementation.
Europe as the Second Largest Market
Europe secures its position as the second-largest predictive maintenance market through stringent industrial safety regulations, strong manufacturing heritage, and commitment to Industry 4.0 initiatives across member states. Germany leads regional adoption with automotive giants like Volkswagen and BMW implementing predictive analytics across 42 production facilities, monitoring 15,000 robots and assembly systems. The United Kingdom follows with significant deployments in aerospace, where Rolls-Royce monitors 9,800 aircraft engines using advanced predictive algorithms. France's energy sector drives demand through EDF's implementation across 58 nuclear reactors, analyzing 2.2 million sensor readings daily. Italy's manufacturing base contributes substantially, with companies like Ferrari and Pirelli investing US$ 125 million collectively in predictive maintenance systems for 28 production lines. These four countries account for US$ 2.8 billion in market investments, supported by EU funding programs allocating US$ 450 million for industrial digitalization projects that prioritize predictive maintenance as a key component of sustainable manufacturing practices.
Key Developments in Predictive Maintenance Market
- In February 2025, IBM completed the acquisition of HashiCorp for US$ 6.4 billion, strengthening its multicloud offerings and predictive maintenance solutions through integration with the Red Hat portfolio.
- In March 2025, Siemens launched its next-generation predictive maintenance platform incorporating generative AI capabilities to enhance equipment failure prediction and address maintenance sector skill shortages.
- In June 2025, C3 AI received a US$ 13 million task order from the U.S. Air Force Rapid Sustainment Office to expand its AI-enabled predictive maintenance system across additional aircraft platforms.
- In February 2024, Novity Inc. secured US$ 7.8 million in funding led by WERU Investment to expand its TruPrognostics AI platform across chemicals, manufacturing, and water industries.
- In March 2024, KBR was awarded a significant contract by Petro Rabigh to provide comprehensive predictive maintenance services for optimizing asset lifecycle and machinery performance.
- In May 2023, Infinite Uptime secured US$ 18.85 million in Series B3 funding led by Tiger Global to enhance its industrial IoT-based predictive maintenance solutions.
- In June 2024, Nvidia acquired Shoreline.io for US$ 100 million to enhance its DGX Cloud business and integrate automated data center issue resolution capabilities into its AI Enterprise software suite for predictive maintenance of GPU clusters.
- In August 2024, Aiomatic raised US$ 2.2 million (€2 million) in funding backed by EIT Manufacturing to expand its AI-driven predictive maintenance platform across Europe.
Top Players in the Predictive Maintenance Market:
- Fujitsu Limited
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Toshiba Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Google Llc
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- SAP Se
- Software Ag
- Onyx Insight
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- SAS Institute
- Hakunamatata Solutions
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Component:
- Solutions
- Integrated
- Standalone
- Services
- Managed Services
- Professional Services
By Deployment Mode:
- Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- On-Premises
By Technology:
- Vibration Monitoring
- Electrical Testing
- Oil Analysis
- Ultrasonic Detectors
- Shock Pulse
- Thermal/Infrared Monitoring
- Optical (cameras) Monitoring
- ML Database
- Others
By Organization Size:
- Large Enterprises
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
By Industry:
- Aerospace and Defense
- Manufacturing
- Energy and Utilities
- Oil & Gas
- Transportation
- Warehouse & Logistics
- Healthcare and Lifesciences
- Automotive
- Marine/ Shipping
- Others
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Poland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 8.96 Bn |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 91.04 Bn |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Bn) |
| CAGR | 29.4% |
| Segments covered | By Component, By Deployment Mode, By Technology, By Organization Size, By Region |
| Key Companies | Fujitsu Limited, Hitachi, Ltd., Toshiba Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Google Llc, IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Oracle Corporation, SAP Se, Software Ag, Onyx Insight, Amazon Web Services, Inc., SAS Institute, Hakunamatata Solutions, Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)