Pea Protein Ingredients Market: By Type (Pea Protein Isolates, Pea Protein Concentrates, Textured Pea Protein, Pea Protein Hydrolysate, and Others); Source (Yellow Pea and Green Pea); Form (Dry and Liquid); Application (Nutrition and Health Supplements, Alternative Meat Products, Bakery & Confectionery Products, and Others); and Region—Industry Dynamics, Market Size, Opportunity and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Jan-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0622259 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0622259 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Snapshot
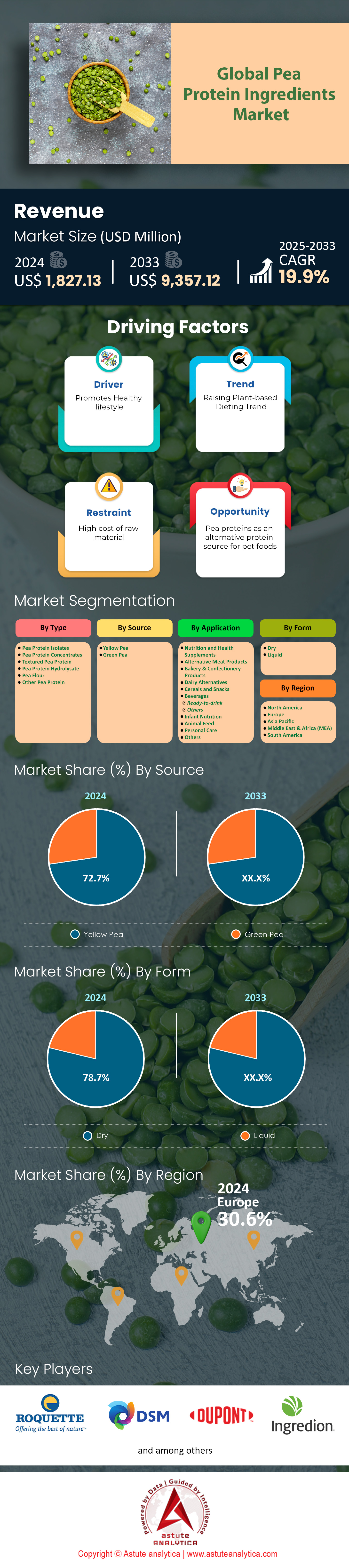
Pea protein ingredients market is experiencing significant growth, with revenue projected to increase from US$ 1,827.13 million in 2024 to US$ 9,357.12 million by 2033 at an estimated CAGR of 19.9% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
Pea protein ingredients market continues to gain traction among health-forward consumers who yearn for clean-label formulations and minimally processed alternatives. This steady rise is reinforced by major producers unveiling advanced variants with refined textures and neutral flavor profiles. Archer Daniels Midland introduced three specialized pea concentrates in early 2024, aiming to improve solubility for sports beverages. By mid-2024, Roquette added six innovative protein solutions designed for plant-based frozen desserts, while Cargill collaborated with two large bakery chains to incorporate pea isolates into artisan breads. These strategic moves underscore growing confidence in pea-based products across diverse consumption patterns, extending from the fitness crowd to casual snackers seeking guilt-free indulgences.
Production levels reflect unpredictable yet expanding demand in the pea protein ingredients market, spurred by technological breakthroughs that deliver better mouthfeel and easier blending characteristics. In late 2023, Kerry Group launched nine functional recipes for pea-infused burger patties, showcasing improved binding capacity and reduced cooking times. Ingredion worked with five beverage startups to tailor pea proteins fit for shelf-stable smoothies in early 2024, illustrating the push toward widespread adoption in convenience-focused formats. Meanwhile, Emsland Group installed a pilot plant that handles seven dedicated blending trials daily, expediting product tests for brands eager to capture niche market segments and tap into consumer curiosity.
End users of the pea protein ingredients market span beyond standard grocery shoppers, branching into specialized categories like infant nutrition and clinical diets. Burcon set up one new facility in 2024 focusing on enzymatic modifications of pea protein for sensitive digestive systems. Nestlé partnered on a pilot study that placed pea-based dairy alternatives in three corporate cafeterias, sparking important data about on-the-spot consumer preferences. Beyond Meat tested pea formulations in two quick-service restaurants to gauge acceptance of new patty compositions, while Danone deployed pea isolates in six trial yogurt recipes to boost protein content without introducing common allergens. These concerted efforts signal a robust surge in application areas, from comfort meals to specialized health solutions, as pea protein cements its reputation as a reliable, appealing plant-derived ingredient.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Mainstream acceptance of advanced pea protein solutions for everyday culinary convenience across multiple regions
An escalating driver for pea protein ingredients market is its seamless integration into daily meal routines. Archer Daniels Midland reported steady requests from six ready-to-eat soup manufacturers eager to replace common allergens with readily digestible pea formulas. This shift is fueled by appetites for balanced nutrition, with fewer concerns over dairy or soy sensitivities. Specialty grocers now stock more than five varieties of pea-enriched nut butter spreads, reflecting widespread consumer enthusiasm for new tastes and approachable textures. In 2024, Cargill established pilot programs with three nutrient bar brands hoping to streamline product consistency while retaining essential amino acids. Meanwhile, health coaches increasingly champion pea-based solutions for busy individuals who need protein-rich snacks without complicated ingredient lists. Practical applications span from creamy sauces to simple on-the-go shakes, driving relentless interest across multiple continents.
Producers respond by fine-tuning flavor and structural characteristics to meet diverse gastronomic needs in the pea protein ingredients markets. Ingredion collaborated with two gastronomic institutes to create spice-infused pea flour recipes designed for rapid cooking. In addition, Emsland Group deployed four lab-scale fermentation studies focused on achieving mellower flavor while keeping robust nutritional densities. Increased awareness of natural food claims prompts major retailers to highlight pea protein as a front-of-package highlight, reinforcing its everyday appeal. In parallel, smaller regional brands incorporate pea isolates into condiments, preserving the sense of familiar home-cooking while trimming out allergens. This continued interplay between production ingenuity and consumer receptiveness cements pea protein’s role as a driver for inclusive, hassle-free diets that blend nourishment with day-to-day meal enjoyment.
Trend: High-profile scientific collaborations forging novel cross-category pea protein expansions among creative, globally health-driven innovators
Pea protein ingredients market players increasingly unite to push the boundaries of inventive pea protein usage. Danone joined forces with three flavor-lab specialists in 2024 to explore tropical fruit pairings for pea-based yogurts, injecting bolder taste profiles into the health-focused dairy aisle. Such synergy is echoed by Kerry Group’s partnership with a global culinary school that introduced five newly curated pea marinade concepts, catering to food service clients seeking plant-driven entrée solutions. By leveraging the expertise of multiple stakeholders, brands rapidly test cutting-edge techniques like enzymatic protein enhancement or vacuum infusion for improved texture. Another noteworthy alliance involves Beyond Meat deploying two specialized feeding trials in university cafeterias to gauge real-time responses to redesigned pea patties. These cross-sector experiments highlight how collaborative projects unravel fresh possibilities in flavor, consistency, and overall palatability.
Technological leaps also emerge from these alliances, as specialists exchange research and pilot-scale findings in the pea protein ingredients market. Burcon launched a cooperative project with three institutes focused on customizing pea protein for infant cereal, emphasizing gentler digestion and dense micronutrient profiles. Cargill capitalized on open-innovation hubs to test eight advanced formulations spanning soups, pastries, and functional bars, forging knowledge chains that accelerate product readiness. Meanwhile, Emsland Group tested dual-phase processing methods with one specialized start-up, targeting higher nitrogen retention as well as smoother mouthfeel in final goods. Notably, consumer-facing campaigns underscore the co-creation angle, reinforcing brand trust formed through transparent, multi-party collaborations. Shoppers become part of the story, intrigued by ground-breaking ingredients forged in flexitarian test kitchens worldwide. This evolving trend empowers pea protein to transcend its early limitations and mature into a champion of flavor diversity, eco-friendly production, and wide-ranging nutritional appeal.
Challenge: Deep-rooted culinary hesitations often significantly hampering universal integration of pea proteins in heritage cuisine
Certain culinary traditions in the global pea protein ingredients market cling to time-honored methods and distinctive flavor foundations, making it challenging to incorporate contemporary ingredients. Roquette’s chefs documented at least two cultural events in 2024 where pea-infused noodles faced lukewarm reactions due to novel aromas. Such feedback echoes the experience of smaller artisan bakers who tested six pilot recipes merging ancient grains with pea flour, only to find that local customers preferred customary, grain-only alternatives. This inertia can slow global expansion, especially in regions where taste expectations remain closely tied to generational cooking methods. Even when health attributes are apparent, gastronomic authenticity often dictates acceptance or rejection of new elements. Consequently, brand managers tread cautiously, fine-tuning recipes to maintain a comfortable link to tradition.
Bridging classic flavors with pea protein solutions calls for meticulous innovation. Archer Daniels Midland guided one heritage-themed restaurant chain through blending trials that allowed minor pea additions in soups without overpowering traditional spices. Ingredion, one of the key participants in the pea protein ingredients market, collaborated with respected local chefs, formulating three stepwise substitution methods in popular sauces, helping communities adapt bit by bit rather than through sudden overhauls. Kerry Group has also run region-specific tasting surveys, capturing direct feedback before rolling out menu updates. These efforts underscore the delicate balance producers must strike: highlight nutritional gains while honoring recognized tastes and textures. Cultural acceptance hinges on incremental adaptation, open dialogue, and measured integration, ensuring that pea proteins can thrive within ancestral cuisines without undermining hallmark flavors. As such, surmounting deep-rooted culinary hesitations remains a pivotal challenge that demands constant refinement and mindful collaboration.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Pea protein isolates are dominating the pea protein ingredients market by capturing over 42% market share primarily due to their exceptional purity levels, versatile functionality, and low allergenicity. The high concentration of protein, often exceeding 80 grams per 100 grams of product, sets isolates apart. This composition suits applications requiring a neutral flavor, such as protein shakes and dairy analogs. Additionally, pea protein isolates exhibit excellent foam stability, retaining about 90% volume for 15 minutes, ideal for aerated baked goods. Their capacity to emulsify approximately 300 milliliters of oil per gram of protein boosts texture in sauces and dressings. With sodium levels generally under 400 milligrams per 100 grams, these ingredients meet clean-label needs. Because they lack most common allergens, including gluten and soy, many vegan and hypoallergenic product lines increasingly prioritize pea protein isolates. Additionally, the isolate’s modest flavor profile can be masked, suiting both sweet and savory recipes.
Pea protein ingredients market growth is also driven by their essential amino acid profile, delivering roughly 3.6 grams of BCAAs in a 20-gram serving, supporting muscle recovery. Notably, their water-holding capacity averages around 2.5 grams of water per gram of protein, enhancing moisture retention in final formulations. In sports nutrition and dietary products, formulators value pea protein isolate’s balanced macronutrient ratio. They are also widely used in dairy-free yogurts, cheese alternatives, and ice creams, thanks to a mild taste and creamy mouthfeel. A single 25-gram scoop can assist with satiety, aligning with weight management goals. Battered coatings incorporating pea isolate show a 10-gram reduction in oil uptake compared to wheat-based coatings, offering a healthier profile. Supported by robust functionality and easy digestibility, pea protein isolates remain at the forefront of plant-based protein innovations. Such highly beneficial attributes explain why isolates dominate the market.
By Source
Over 72% of pea protein ingredients market originate from yellow peas because these varieties typically yield a higher protein content than green peas. Yellow peas often contain around 24 grams of protein per 100 grams, while green peas generally hover near 20 grams, giving yellow peas a nutritional edge. Their lower chlorophyll content, measured at roughly 2 milligrams per 100 grams, contributes to a milder taste and lighter color. Such neutrality in flavor is especially valued in dairy analogs, where bright hues or strong earthy notes could be off-putting. In terms of processing efficiency, yellow peas have a denser starch structure, allowing quicker isolation steps and reduced energy consumption by about 15% compared to green pea processing. Additionally, the relatively subdued pea flavor of yellow varieties has only about 5 detectable off-flavor compounds, whereas green peas may contain up to 10.
End users in the pea protein ingredients market opt for yellow pea because they provide consistent texture control in high-moisture extrusion for alternative meats, cereals, and protein bars. When forming dough for baked goods, incorporating 10 grams of yellow pea flour per 100 grams of total flour can enhance crumb structure while improving protein levels. In beverage formulations, powdered yellow pea extracts show better solubility, taking around 20 seconds to disperse under standard mixing conditions. Furthermore, yellow peas deliver around 5 grams of dietary fiber per 100 grams, promoting benefits in finished foods. Their amino acid composition supports balanced nutrition, offering nearly 2.3 grams of lysine per 100 grams. Given these functional advantages, many manufacturers prioritize yellow peas to maintain consistent quality, reduce production downtime, and satisfy taste profiles.
By Application
Based on application, pea protein ingredients market witnesses over 21.1% of the market share coming from alternative meat product applications, largely because consumers are gravitating toward plant-based diets to support health, environmental sustainability, and animal welfare concerns. Many of these alternative meat offerings closely mimic conventional products in taste and texture, and pea protein is integral to achieving that outcome. It can deliver up to 17 grams of protein per 100 grams of finished meat analog, a figure comparable to certain lean meats. In the texturization process, temperatures can reach nearly 150°C, at which point pea protein develops fibrous structures that resemble the bite of cooked muscle. Furthermore, its relatively neutral flavor profile, with fewer strong off-notes than some soy-based proteins, makes it easier to season and adapt to various cuisines.
One reason for pea protein ingredients market’s popularity in meat substitutes is its strong functional performance during extrusion. Equipment throughput can process around 800 kilograms per hour of hydrated pea protein, indicating a scalable solution for high-volume producers. Also, because pea protein has a lower allergen risk than wheat or soy, manufacturers can address a wider audience and meet strict label demands. Many companies find that including roughly 10–15 grams of pea protein in a single serving of an alternative burger offers both satiety and robust mouthfeel, reducing cooking time by as much as 10 minutes compared to traditional meat patties. The result is a product that replicates up to 80% of the texture of real meat, driving broader consumer acceptance. Given its balance of nutrition, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, pea protein consistently remains the primary choice for innovators striving to deliver realistic, sustainable meat alternatives.
By Form
Today, an estimated 78.7% of pea protein ingredients are offered in dry form. One chief reason behind this wide adoption is the prolonged shelf life that dry formats deliver, frequently lasting up to 18 months when stored properly. The moisture content in the pea protein ingredients market is typically maintained below 6%, which helps curb microbial growth and preserve product integrity over time. Another practical benefit is packaging convenience: dry pea protein is commonly shipped in 25-kilogram bags that are easy to stack and transport. In contrast, liquid forms demand more specialized containers and can incur higher logistics costs. Dry forms also tend to simplify formulation steps, since powders can be readily weighed and mixed with other dry ingredients in large-scale food processes.
Product developers across the global pea protein ingredients market favor the dry version because it disperses more quickly in many applications. Under high-shear mixing conditions, pea protein powder can fully dissolve in under 10 seconds, easing the production of protein-fortified beverages, soups, or sauces. Additionally, controlling viscosity becomes more manageable with dry inputs, as manufacturers can precisely calibrate how much powder is added to their recipe. For instance, adding 15 grams of dry pea protein to a 200-gram dough mix can bolster nutritional content without overly thickening the batter. Processing equipment also benefits from reduced clogging issues during blending, cutting down on downtime. Dry pea protein’s stable nutrient profile—retaining its amino acid density and functional properties without refrigeration—further cements its status as the preferred format. By offering reliable performance, cost-effectiveness, and simplified logistics, dry forms remain the industry standard for pea protein ingredient delivery.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
Europe’s Leadership to Stay Strong with Over 30% Market Share
Europe, holding around 30.6% of the pea protein ingredients market, has emerged as the foremost producer and consumer of this plant-based resource for several compelling reasons. Among the top four countries driving this dominance are Germany, France, the Netherlands, and Italy. Each contributes significantly to research, raw material cultivation, and end-use innovation. Germany invests heavily in technology that refines the quality of pea protein concentrates and isolates, allowing manufacturers to produce formulations with uniform taste and texture. France has long been a hub for agricultural cultivation, and its well-established pea-farming cooperatives ensure steady supplies of high-grade raw materials. The Netherlands, known for its logistical infrastructure, facilitates swift exports and imports of intermediate pea protein ingredients, thereby supporting continuous cross-border collaboration among food tech companies. Italy’s culinary tradition fosters a prime market for novel plant-based dishes, motivating companies to develop more sophisticated pea protein–based products tailored to Mediterranean palates.
The region’s growth in the pea protein ingredients market is driven by multiple factors including marked consumer shift toward mindful eating, encouraging plant-based diets that align with health and environmental ideals. Apart from this, European regulatory frameworks often endorse or subsidize sustainable protein sources, fostering innovation in fields like cultured meat or pea-derived functional blends. Also, major food brands are investing in dedicated product lines—such as ready-to-eat entrees, dairy alternatives, and snacks—that rely heavily on pea protein’s capabilities for emulsification, texturing, and balanced nutrition.
Europe’s momentum in pea protein ingredients market in terms of production and consumption is further supported by scientific research. Laboratories have measured protein digestibility scores nearing 0.8 for many European-sourced pea isolates, indicating a high-quality nutritional profile that appeals to mainstream consumers and specialized health segments alike. Producers also highlight that extruded products using European pea protein can achieve cooking temperatures around 140°C with minimal off-flavors, streamlining blending processes and yielding a favorable mouthfeel. Industrial-scale facilities operate with throughput rates exceeding one metric ton per hour, meeting the demands of fast-expanding retail channels. Moreover, with recommended protein intakes generally established at 50 grams per day for adults, pea protein–fortified products fit conveniently into daily meal plans without triggering common allergens. Finally, because plant-based foods typically generate a lower carbon footprint, pea protein aligns with Europe’s long-standing emphasis on eco-friendly manufacturing. As a result, key end-use applications such as alternative meats, sports nutrition products, dairy analogs, and health bars continue to exhibit soaring demand, positioning Europe at the forefront of pea protein innovation.
Top Companies in the Pea Protein Ingredients Market:
- A&B Ingredients
- AGT Food and Ingredients Inc.
- Archer Daniels Midland Company
- Axiom Foods Inc
- Burcon NutraScience Corporation
- Cargill Inc.
- Cosucra Groupe Warcoing SA
- DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
- Emsland Group
- Farbest Brands
- Fenchem Inc.
- Glanbia PLC
- Ingredion Inc.
- Nutri-Pea Ltd.
- Puris Foods
- Roquette Freres Le Romarin
- Shandong Jianyuan Foods Co., Ltd.
- The Emsland Group
- The Green Labs LLC.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Type:
- Pea Protein Isolates
- Pea Protein Concentrates
- Textured Pea Protein
- Pea Protein Hydrolysate
- Pea Flour
- Others Pea Protein
By Source:
- Yellow Pea
- Green Pea
By Form:
- Dry
- Liquid
By Application:
- Nutrition and Health Supplements
- Alternative Meat Products
- Bakery & Confectionery Products
- Dairy Alternatives
- Cereals and Snacks
- Beverages
- Ready-to-drink
- Others
- Infant Nutrition
- Animal Feed
- Personal Care
- Others
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 1,827.13 Million |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 9,357.12 Million |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Mn) |
| CAGR | 19.9% |
| Segments covered | By Type, By Source, By Form, By Application, By Region |
| Key Companies | A&B Ingredients, AGT Food and Ingredients Inc., Archer Daniels Midland Company, Axiom Foods Inc, Burcon NutraScience Corporation, Cargill Inc., Cosucra Groupe Warcoing SA, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Emsland Group, Farbest Brands, Fenchem Inc., Glanbia PLC, Ingredion Inc., Nutri-Pea Ltd., Puris Foods, Roquette Freres Le Romarin,Shandong Jianyuan Foods Co., Ltd., The Emsland Group, The Green Labs LLC., Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0622259 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0622259 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






