Machine Tools Market: By Product (Milling Machines; Lathe Machines, Laser Machines, Drilling Machines, Turning Machines, Grinding Machines, EDMs, Machining Centers); Industry (Automotive, Aerospace, Construction, Energy, Industrial); Automation (CNC Machine, Conventional Machines); Distribution Channel (Dealers & Distributors, Events & Exhibitions); Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, Middle East & Africa) - Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Jan-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0921094 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0921094 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Scenario
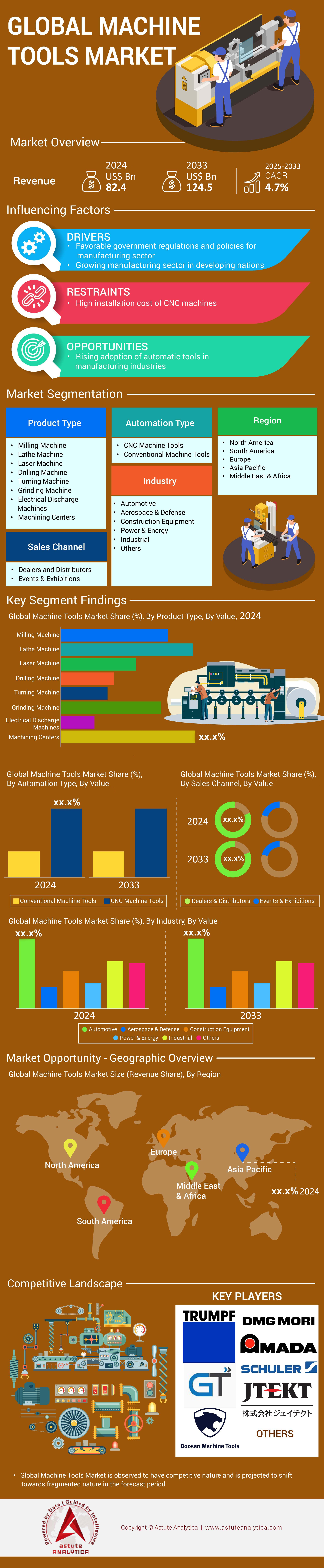
Machine tools market is estimated to generate a revenue of US$ 124.5 billion by 2033 from US$ 82.4 billion in 2024, registering a CAGR of 4.7% over the period 2025-2033.
Machine tools are precision mechanical devices used to cut, shape, and form metals or other rigid materials, employed heavily across industries for activities like milling, drilling, turning, and grinding. In 2024, over 480 new CNC milling models are poised for commercial release worldwide, reflecting strong innovation in product types such as lathes, milling machines, and grinders. On the automation front, CNC platforms remain popular; while emerging robotic arms are rapidly finding their way into machine tool setups. End users span the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical equipment sectors, each requiring varying degrees of customization and productivity. Some advanced 5-axis milling centers weigh around 25 tons for large aerospace components, demonstrating the complexity and scale that meets specific industry demands.
A vibrant outlook of machine tools market is fueled by growing industrial production and heightened emphasis on precision. The automotive sector alone invests in nearly 14 new machining lines specialized in EV components each quarter, indicating robust demand for advanced machining solutions. Meanwhile, in 2023, over 200 aerospace companies in the Asia-Pacific region expanded their machining capabilities to cater to lightweight aerospace materials, highlighting cross-industry uptake. Industry experts foresee rising interest in adaptive machining, where integrated sensors fine-tune cutting conditions mid-process. In line with that, the US witnessed 35 pilot programs implementing AI-driven machine monitoring in large factories, signaling a steady pivot toward smart technologies.
Recent trends in the machine tools market center around multi-tasking systems, additive manufacturing integration, and digital twins to optimize production cycles. Japan’s leading manufacturers have established 16 R&D facilities focusing on multi-tasking machines, aiming to reduce operational downtime and manual intervention. Germany recorded 2 major expansions in gear-grinding technology for high-precision automotive parts, underscoring Europe’s commitment to advanced machining. Likewise, China allocated funds to build 9 advanced production lines for additive-enabled machine tools, underscoring Asia’s appetite for next-generation fabrication. In 2023, more than 1,800 training courses on CNC operation were conducted across North American manufacturing hubs, reflecting a focus on workforce development. Such wide-ranging efforts from leading markets illustrate the multifaceted demand shaping the global machine tools landscape.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Proliferation of Next-Level Automotive Electrification and Battery Manufacturing Accelerating Demand For High-Precision Machining Innovations
The automotive industry’s transition to electric vehicle (EV) platforms is sparking an unprecedented appetite for more refined, high-precision machining solutions in the machine tools market. According to a specialized 2023 workshop on e-mobility manufacturing, engineers face exacting requirements when producing copper rotor elements and high-strength steel motor housings, pushing conventional machinery beyond traditional limits. An R&D center in Sweden recently published findings on rotor shaft finishing, showing that ultra-hard cutting inserts improved surface finishes by several microns relative to standard tooling. Additionally, a tier-one automotive supplier in Michigan inaugurated a pilot line in early 2023 that introduced active vibration dampening in multi-axis machining heads, allowing for superior cutting stability in lightweight chassis frames. Such advancements underscore how specialized machine tools now cater to EV components that must meet tight weight and performance targets.
Battery manufacturing also spurs innovation, particularly in milling and drilling processes vital for battery cell casings. A South Korean materials lab in the machine tools market reported verifying a new coolant delivery concept that produced significantly smoother bores in thin-walled aluminum housings, reflecting the industry’s quest for higher cycle times and safer thermal profiles. Meanwhile, a leading Japanese machinery builder documented a notable jump in orders for compact CNC systems that streamline the milling of complex battery tray geometries. In parallel, test labs across Europe have validated advanced spindle designs that sustained consistent torque over extended machining cycles, fostering stable production for EV powertrain parts. Another development is the expansion of intelligent control algorithms to monitor voltage levels and tool deflection in real time, ensuring continuous accuracy within EV-specific production lines. Taken together, these exacting needs in the race toward cleaner mobility highlight why automotive electrification and battery manufacturing stand as a powerful driver, compelling machine tool makers to refine designs and adopt forward-thinking technologies at a rapid clip.
Trend: Surging Adoption of AI-Infused Quality Inspection And Predictive Repair Mechanisms In CNC Workshop Operations
Across global machine tools market, artificial intelligence is no longer a fringe experiment but a fully integrated element guiding maintenance and inspection. In 2023, a well-known electronics manufacturer in Taiwan incorporated AI-driven visual systems into its CNC lines for smartphone frame machining, enabling automated flaw detection on high-gloss surfaces. At a symposium in California that same year, a top-tier aerospace supplier revealed its neural-network-based inspection tool that reduced manual checks on turbine discs by a significant margin in real production trials. Another noteworthy milestone came when a Swiss toolmaker validated an adaptive algorithm that performs in-situ tool compensation, lowering the scrap rate for precision watch components dramatically. These examples demonstrate how AI is redefining the speed and accuracy of quality assurance, even for highly specialized parts.
Predictive repair mechanisms further amplify this trend. A major machine tool user in Denmark shared data on sensor-equipped linear guides that flagged an impending bearing malfunction hours before it could disrupt a critical medical device production run. Meanwhile, a large gear manufacturer in South Korea machine tools market tested an AI-based spindle monitoring platform that offered actionable alerts on micro-fractures, allowing service teams to replace components precisely when required. A robotics cluster in Singapore also showcased a proof-of-concept system that harmonizes control signals from multiple CNC stations, achieving unified predictive maintenance scheduling across an entire workshop. Similarly, a custom machine integrator in Canada documented real-time tracking of coolant system performance to prevent abrupt temperature spikes and cavitation. These advances around AI-driven inspection and self-correcting repairs define one of the most transformative trends in modern CNC operations, unlocking higher yields and more consistent quality across various industries.
Challenge: Intensifying Global Talent Gap In Multi-Axis Programming Consistently Straining Heavily Strategic Automation Investments Everywhere
As machine tools market grow more sophisticated, an acute shortage of qualified personnel proficient in multi-axis programming is casting a long shadow on production timelines and innovation efforts. A German research institute reported that many advanced five-axis systems it surveyed still operate below optimal feed rates because operators lack the specific G-code expertise to push cutting parameters safely. Meanwhile, a renowned apprenticeship academy in Switzerland introduced new curricula in 2023 after local manufacturers highlighted the difficulties of finding staff to handle dual-spindle turning centers. One US-based aerospace giant contends that it is spending increased resources on in-house simulation training, yet the pipeline of skilled recruits remains insufficient to fully staff next-generation machining cells.
Various industry stakeholders in the machine tools market have launched collaborative efforts to bridge this gap. A British machine tool trade association helped introduce specialized courses that align with turning-milling hybrid systems, focusing on post-processing and tool-path optimization. In Italy, a racing engine supplier reported that new hires could not readily handle advanced lathe cycles, prompting the firm to partner with a technical university for tailored instruction on parametric programming. A Canadian CNC consortium published a white paper in 2023 emphasizing the need for standardized certification in multi-axis tool setup, after surveys indicated widespread inconsistency in workforce competencies. Another cluster of manufacturers in India invested in remote learning portals that feature interactive digital twins, aiming to accelerate knowledge transfer across plant locations. These collective efforts highlight how the talent crunch in multi-axis programming continues to challenge the worldwide push toward higher automation. Without a robust pipeline of skilled machinists and programmers, even the most advanced systems risk underutilization, prolonging lead times and undercutting the returns promised by modern machine tool investments.
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type
Machining centers, featuring integrated milling, drilling, and turning capabilities, are dominating the machine tools market by capturing over 20.7% market share due to their high efficiency, versatility, and continuous automation. A newly released engineering study indicates that advanced 6-axis machining centers can conduct up to 50 different operations without manual intervention, drastically reducing production time. In 2023, more than 15 globally recognized automotive manufacturers upgraded at least 30% of their lines to machining centers to accelerate mass production of critical components. The surge is also linked to the proliferation of digital manufacturing solutions, with over 200 newly patented software integrations designed explicitly for multi-tasking machining systems. Additionally, the average lead time for complex part fabrication has decreased from 14 days to seven days when using high-performance machining centers, as recorded in 2023 engineering benchmarks.
In addition, demand is fueled by the aerospace and consumer electronics sectors, which collectively added over 400 new machining centers in 2023 to meet rising demand for precision components and faster prototyping. The flexibility of these systems in the machine tools market drives uptake among medium and small enterprises; reports show that more than 10 advanced machining center models now offer modular expansions for automatic part loading and inspection. Industry experts highlight that the integration of real-time analytics has grown fivefold since 2021, enabling predictive maintenance and improved machine uptime for the majority of machining centers deployed in large-scale facilities. The synergy of reduced labor costs, accelerated cycle times, and minimal material waste underscores their dominant position in metal fabrication lines globally. Notably, one engineering database cites 350 newly accredited training programs focused on machining center operation, reflecting heightened demand for skilled technicians.
By Automation Type
CNC machine tools have emerged as the most sought-after automation option in the machine tools market, primarily due to their repeatable precision, ease of programming, and reduced reliance on manual labor. The CNC machine tools are controlling over 65.2% market share. According to an industrial computation study published this year, more than 20 newly developed CNC systems now feature integrated AI modules that cut average manufacturing time by nearly two hours per production run for complex tasks. The global deployment of CNC lathes, mills, and turning centers has risen by 5,000 new units in key automotive and defense manufacturing hubs, indicative of a robust drive toward digital transformation. Another crucial factor is that modern CNC tools can store up to 10,000 lines of production code, enabling quick adaptation to diverse production batches without hardware modifications. Further, the growing popularity of remote machine monitoring solutions has triggered over 1,000 new installations of sensor-based CNC systems in high-volume plants worldwide.
Additional drivers behind CNC dominance in the machine tools market include the expansion of multi-axis machining capabilities and advanced control software, which allows for highly intricate geometries that are otherwise infeasible with manual machines. A recent study on industrial productivity found that CNC-based setups contributed to a measured drop of 200 metric tons of scrap material monthly in large-scale forging and milling operations, thanks to consistent tool positioning and proactive tool-change alerts. In sectors like aerospace, major OEMs have introduced over 50 newly approved material grades specifically for CNC machining, underscoring the technology’s ability to handle diverse substrates. Furthermore, automation-savvy operators now benefit from real-time data dashboards, with over 900 facilities installing cloud-connected CNC interfaces for tighter process control just this year. Coupled with robust maintenance support—exemplified by a tenfold uptick in CNC service training modules introduced by technical colleges—the future trajectory of CNC machine tools signals sustained leadership in the automation spectrum.
By End Use Industry
The automotive industry has retained the top position among end-users of machine tools market with revenue share of over 29%, largely driven by surging demand for efficient fabrication of engine components, transmission housings, and chassis parts. Industry reports show that modern automotive assembly lines employ up to 40 specialized machine tools per production cell, emphasizing the need for speed and throughput in high-volume manufacturing. This concentration on automation is reflected in more than 8,000 newly commissioned robotic arms designed to integrate seamlessly with CNC milling and turning machines for continuous operation. Additionally, a leading carmaker recently reported that advanced multi-axis machine tools helped reduce gear production steps from 10 procedures to just five, effectively halving the overall process time. Continuous innovation in materials—such as ultra-high-strength steel and lightweight alloys—further boosts this segment’s reliance on flexible machine tools capable of precision milling at micrometer-level tolerances.
The key machine tools deployed are advanced CNC lathes, multi-spindle drilling machines, and 5-axis machining centers, each tailored for complex engine blocks or transmission components. In 2023 alone, at least 20 new lines for electric vehicle powertrain manufacturing in the machine tools market have incorporated precision grinding machines to meet tighter tolerances for battery and motor housings. Automotive-grade machining cells are increasingly equipped with inline measurement systems, confirming that over 600 new setups now feature real-time laser scanning for quality checks. This heightened focus on consistent accuracy addresses the growing complexity of hybrid engine designs, where more than 100 distinct part variations may be milled in a single factory shift. Meanwhile, after-sales support and rapid prototype requirements are accelerating adoption of high-speed milling, with 15 major OEMs reporting a combined 10,000 hours of reduced downtime through predictive tool maintenance in the past year.
By Sales Channel
Dealers and distributors continue to act as the primary gateway for machine tool acquisitions with over 81% market share by connecting end-users with a vast portfolio of cutting-edge technologies while offering localized support. A recent industry distribution report on the machine tools market shows that eight out of every ten machine tool purchases occur through these intermediaries, a ratio sustained by their expansive service networks and product availability. Over 300 authorized distribution centers have been newly established worldwide, ensuring prompt delivery and servicing for businesses venturing into advanced automation systems. A key advantage offered by these distribution channels is comprehensive after-sales support, with some service providers claiming to resolve technical issues within 48 hours by employing remote diagnostics and dedicated spare-parts inventories. Additionally, many dealers now conduct in-house demonstration workshops—more than 600 such events took place in the first half of 2023 alone—enabling prospective buyers to evaluate equipment compatibility before purchase.
Several factors bolster the influence of dealers and distributors in the machine tools market. Wherein, reinvestment in technical training has soared, with more than 1,200 newly certified machine tool technicians now employed by distributor-managed service teams in the machine tools market. Financing options tailored by these intermediaries also helped secure equipment upgrades for at least 500 small-to-medium enterprises transitioning from manual to automated solutions. Moreover, the streamlined procurement processes introduced this year enable integrated software licensing, allowing end-users to reduce administrative overhead by eliminating multiple vendor negotiations. Furthermore, real-time parts availability has been enhanced through digital inventory systems, with over 2,000 machine tool components recorded in distributor-managed online catalogs for quick dispatch.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
With more than 54.1% market share, Asia Pacific has emerged as the leading region in the global machine tools market. The dominance of the region is propelled by an extraordinary rise in manufacturing output, infrastructural expansion, and solid demand from various industrial sectors. Within this region, China, Japan, South Korea, and India collectively host over 600 specialized machine tool production facilities, each focusing on high-tech interventions like multi-axis CNC solutions and automated assembly lines. In China alone, more than 100 newly established precision engineering centers have been unveiled this year to support the shift toward high-value manufacturing, including aerospace applications. Meanwhile, Japan has reported a surge in robotics integration, with 2,500 industrial robots installed in new machine tool lines over the last 12 months. This infrastructural deepening is echoed in South Korea, which revised its industrial policy to allocate significant funding for advanced machining hubs, resulting in 40 newly operational CNC training institutes.
These nations are prime consumers of machine tools market for the automotive, construction equipment, and general industrial segments, fueling a dynamic ecosystem of suppliers and end-users. In India, at least 50 new automotive component plants have adopted 5-axis machining centers to enhance part consistency for domestic and export markets. The emphasis on electric and hybrid vehicle manufacturing also drives investment, as more than 200 advanced metal-cutting and forging lines are earmarked for installation throughout the region in the coming year. A strong push into smart factories has boosted demand for high-end CNC lathes, with over 5,000 interconnected machines now tracked via real-time analytics across these four nations. Analysts confirm that multi-tasking machining centers are heavily consumed to support the production of everything from aerospace turbines to electronic components, highlighting the region’s diversified industrial footprint. Coupled with robust government support in research grants—evident from the 80 newly funded collaborative projects for advanced tooling—the Asia Pacific region cements its dominant status in machine tool adoption.
Top Companies in Machine Tools Market:
- Ace Micromatic Group
- Amada Co. Ltd.
- CHIRON Group
- Dalian Machine Tool Group Corporation (DMTG)
- DMG MORI
- Doosan Machine Tools Co. Ltd.
- Electronica Hitech Engineering Pvt. Ltd.
- Georg Fischer Ltd
- Gleason Corporation
- GROB-WERKE GmbH & Co. KG
- Haas Automation Inc.
- Hyundai WIA
- JTKET Corporation
- Komatsu Ltd.
- MAG IAS GmbH
- Makino
- Okuma Corporation
- Schuler AG
- Spinner Machine Tools
- Yamazaki Mazak Corporation
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Product
- Milling Machine
- Lathe Machine
- Laser Machine
- Drilling Machine
- Turning Machine
- Grinding Machine
- Electrical Discharge Machine
- Machining Centers
By Automation Type
- CNC Machine Tools
- Conventional Machine Tools
By Industry
- Automotive
- Aerospace and Defense
- Construction Equipment
- Power and Energy
- Industrial
- Others
By Sales Channel
- Dealers and Distributors
- Events and Exhibitions
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Malaysia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Cambodia
- Vietnam
- Rest of ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Turkey
- Egypt
- South Africa
- Nigeria
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Columbia
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 82.4 Bn |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 124.5 Bn |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (US$ Bn) |
| CAGR | 4.7% |
| Segments covered | By Product, By Automation Type, By Industry, By Sales Channel, By Region |
| Key Companies | Ace Micromatic Group, Amada Co. Ltd., CHIRON Group, Dalian Machine Tool Group Corporation (DMTG), DMG MORI, Doosan Machine Tools Co. Ltd., Electronica Hitech Engineering Pvt. Ltd., Georg Fischer Ltd, Gleason Corporation, GROB-WERKE GmbH & Co. KG, Haas Automation Inc., Hyundai WIA, JTKET Corporation, Komatsu Ltd., MAG IAS GmbH, Makino, Okuma Corporation, Schuler AG, Spinner Machine Tools, Yamazaki Mazak Corporation, Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0921094 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0921094 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






