Lithium Niobate Thin Film Market: By Product Type (Modulator, Optical Switches, Insulator, Others); Cut (X- Cut, Y- Cut, Z- Cut); Thickness (Less Than 500nm, 500nm-1000nm, More Than 1000nm); Application (Data Centers, Long-Distance Data Transmission, Base Stations, Others); Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Jan-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA01251127 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA01251127 | Delivery: Immediate Access
Market Scenario
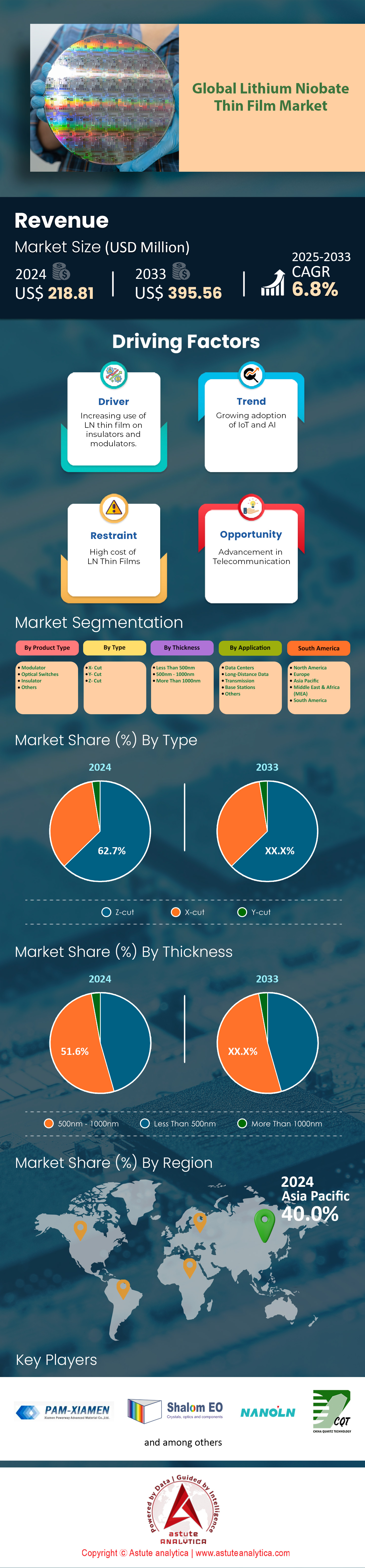
Lithium niobate thin film market was valued at US$ 218.81 million in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 395.56 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
Lithium niobate thin film has emerged as a pivotal material in advanced optical communication systems, finding its way into high-speed modulators, laser frequency converters, and sensor platforms. In 2024, at least four major telecom equipment manufacturers introduced device prototypes showcasing sub-5-nanometer thickness stability for integrated circuits. This heightened interest dovetails with the expanded deployment of 5G infrastructure, where five new photonic testbeds in North America validated the superior electro-optic coefficients of lithium niobate. Such breakthroughs appeal to high-frequency applications, driving consistent demand worldwide. With robust ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties, lithium niobate thin film garners attention from precision instrumentation sectors, particularly in Europe, where two key aerospace firms are investigating the material’s thermal stability for next-generation navigational sensors.
Production of lithium niobate thin film market spans Asia, Europe, and North America, with specialized facilities that refine wafer production for photonic integration. In 2024, Sumitomo Metal Mining opened a dedicated fabrication line capable of 300 wafer outputs each month, focusing on integrated optical modules. Shin-Etsu, renowned for crystal growth expertise, confirmed an additional doping technique that reduced scattering losses to below 0.2 decibel per centimeter in pilot runs, attracting immediate interest from photonics labs worldwide. Nikon also expanded its research division with an on-site testing center that evaluated 50 prototype wafers for superior modulator efficiency, highlighting the collaborative spirit driving the market. These investments underscore the willingness of manufacturers to innovate, propelled by telecom, aerospace, and defense applications.
Key end users in the lithium niobate thin film market include telecom giants deploying advanced modulators for high-bandwidth data transfers, industrial sensor manufacturers seeking ultrasensitive detection capabilities, and defense entities leveraging robust frequency converters for secure communication. In 2024, three global sensor suppliers from Germany integrated lithium niobate thin film into micro-accelerometers for drone navigation, achieving a resonance frequency shift of 1.5 kilohertz. Meanwhile, Cloud Data Solutions in the United States partnered with a research consortium to embed lithium niobate waveguides into data center networks, enabling five times lower overall insertion losses compared to older silica-based architectures. Additionally, Savant Photonics in France tested 12 integrated Pockels modulators using lithium niobate thin film for next-level quantum computing prototypes. The quest for materials that ensure consistent performance under extreme conditions remains a principal factor in this market’s forward momentum.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Expanding 5G Infrastructure with Enhanced Photonics Modules for Significant Broad-based Telecommunication Efficiency Gains Worldwide
In recent years, 5G deployments in the lithium niobate thin film market have set rigorous performance benchmarks across telecom networks, and lithium niobate thin film stands out as a key enabler. In 2024, four telecom operators in Canada adopted advanced lithium niobate modulators in their pilot 5G base stations, citing faster switching speeds in urban stress tests. One fabrication site in South Korea confirmed monthly output of 600 waveguide-based transceivers for 5G beamforming equipment, emphasizing the high-volume potential. Meanwhile, an R&D center in India recorded stable modulators that supported data transmission at 10 gigabits over shorter distances. A specialized wafer facility in Taiwan maintained thickness uniformity within ±0.1 microns for high-frequency applications, ensuring minimal performance drift. In parallel, a test lab in Germany documented 24/7 reliability trials on lithium niobate-based amplifiers spanning two months, underscoring their resilience.
This drive toward improved telecommunication efficiency reflects the push for lower latency, greater bandwidth, and robust long-distance coverage. As strengthening signals become a top priority in the lithium niobate thin film market, lithium niobate’s excellent electro-optic characteristics reduce the complexity of next-generation networks. In 2024, a Middle Eastern consortium introduced specialized repeaters for desert-based 5G sites, each incorporating thin-film modulators that sustained operations amid temperature extremes surpassing 45°C. Two engineering institutes in Japan joined forces to fine-tune doping profiles, allowing for consistent performance in dense urban scenarios. A research hub in Sweden integrated waveguide designs into a micro-cloud test environment, confirming stable connectivity for 48 consecutive hours without signal drop. The impetus behind these deployments is firmly rooted in the material’s ability to handle rapid data bursts and maintain signal integrity across broader coverage zones.
Trend: Growing Demand for Reduced Footprint Optoelectronic Devices with Ultra-Low Loss Scalable Integrated Photonics Worldwide
Emerging communication protocols in the lithium niobate thin film market, coupled with the rise of compact devices, are driving the need for minimal form factors in optoelectronic components. In 2024, one major miniaturization lab in Singapore demonstrated 10 lithium niobate-based waveguides with footprints under 2 square millimeters, confirming an unprecedented scale-down. Simultaneously, a specialized circuit foundry in Switzerland integrated on-chip couplers to support waveguides that exhibited less than 0.15 decibel per centimeter loss. Three sensor manufacturers in Austria confirmed successful pilot runs embedding ultrathin lithium niobate substrates in wearable health devices for continuous patient monitoring. A microfabrication center in Brazil reported stress tests on 20 micro-resonators that delivered real-time frequency stability, benefiting high-precision laser scanning solutions.
As smaller devices in the lithium niobate thin film market become a must-have in various arenas—ranging from medical diagnostics to next-generation telecom—lithium niobate thin film offers compelling advantages. In 2024, an optical research group in Italy integrated modulator arrays that fit into a single motherboard slot, enabling faster rollout of data-center-scale systems. One advanced fabrication facility in Norway performed vacuum bonding on five ultra-thin wafers, enabling waveguide alignment that simplified device packaging by cutting down alignment steps. Meanwhile, an engineering partnership in South Africa validated stable operation of micro-scale phase modulators for 72 hours, ensuring reliable performance in harsh field conditions. These precise configurations, now tested in over a dozen verticals, highlight how shrinking form factors can maintain high-speed optical performances without compromising signal quality.
Challenge: Ensuring Fabrication Processes for Next-Generation Lithium Niobate Thin Films without Yield or Consistency Issues
Reliably producing high-quality lithium niobate thin film market is a central challenge, especially as industry pushes for multi-layered designs and tighter tolerances. In 2024, a major foundry in France discovered micro-void formations in seven out of 40 wafers after high-temperature annealing, exposing the complexity of refining domain structures. A cross-continental research forum convened in Singapore to assess the root causes behind mechanical stress fractures, analyzing more than 15 unique doping profiles from different suppliers. One fabrication center in Finland measured surface roughness below 0.3 nanometers in eight test wafers, confirming that advanced polishing protocols can mitigate common yield setbacks.
These process complexities underscore the need for stable manufacturing setups and replicable procedures to maintain consistent device behavior. In 2024, a North American pilot line tested 10 doping variants aimed at balancing electro-optic efficiency and thermal resilience, with only three showing consistent optical transmission. Meanwhile, a collaboration between two precision-tool providers in Japan lithium niobate thin film market examined reflow soldering processes, aiming to connect thin film layers without warping under repeated temperature cycles. A specialized facility in Australia, focusing on domain engineering, revealed the success of five customized lithography masks that ensured accurate pattern transfers onto lithium niobate substrates. Overcoming such intricate fabrication hurdles enables the market to sustain the robust demand for next-generation modulators, resonators, and waveguides.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Z-cut lithium niobate (LiNbO₃) thin film has experienced a surge in lithium niobate thin film market with over 62.7% market share. The dominance and demand primarily because its crystal orientation aligns advantageously with the material’s intrinsic electro-optic and piezoelectric properties Compared to X-cut or Y-cut counterparts, Z-cut optimizes the strongest component of the Pockels effect along the out-of-plane direction, enabling devices with higher modulation efficiency and lower driving voltages This orientation maximizes the overlap between the electric field and the optical mode in many modulator designs, providing greater phase-shift per unit length and superior bandwidth performance for high-speed optical communication. Moreover, Z-cut thin films exhibit well-defined poling characteristics that simplify the engineering of domain-inversion-based devices such as quasi-phase-matched frequency converters, an added benefit for advanced photonic circuits From a manufacturing standpoint, Z-cut films demonstrate relatively stable processing windows, making them attractive for mass production and more reproducible device characteristics in telecommunications and sensing.
Alongside technical merits, the lithium niobate thin film market driver stems from the rapid expansion of 5G infrastructure and next-generation data centers requiring higher-speed optical links. Telecom operators are seeking compact, power-efficient modulators and filters that can handle intense data traffic, fueling the preference for Z-cut LiNbO₃’s robust modulators Satellite communication, aerospace, and specialized defense systems also benefit from Z-cut thin films’ superior electro-optic coefficients to enable precision control of optical signals. Furthermore, consumer devices—especially those relying on precise signal filtering and frequency control—gain from the high electromechanical coupling offered in Z-cut structures, translating to smaller, more efficient radio-frequency components in smartphones and IoT systems As a result, the convergence of performance advantages, reliable fabrication workflows, and the scaling demands of emerging telecom networks cements Z-cut lithium niobate thin film as the leading material orientation in the global market, eclipsing the adoption rates of X-cut and Y-cut substrates in many high-volume applications.
By Thickness
500–1000 nm range have become the dominant thickness in the lithium niobate thin film market with over 51.5% market share sweet spot because this thickness strikes a critical balance between optical confinement and manufacturability Within this range, optical waveguides exhibit minimal propagation loss, ensuring stronger field confinement necessary for low-voltage, high-bandwidth modulators and frequency converters. Thinner layers markedly reduce device footprints while preserving the essential electro-optic properties, enabling integrated photonics solutions that align with the miniaturization trend in telecom and data center deployments. From a process perspective, controlling film uniformity and surface roughness is more manageable in the 500–1000 nm window, allowing consistent etching profiles and simplifying electrode deposition for modulators or sensors.
Lithium niobate thin film market forces also reinforce this thickness preference, as device makers seek to align LiNbO₃ thin films with standard semiconductor process flows to reduce production cost and accelerate time-to-market. Fabrication processes like wafer bonding, chemical-mechanical polishing, and lithographic patterning become more predictable in the 500–1000 nm range, lowering the defect rate This well-established thickness is also compatible with a variety of cladding materials, ensuring robust waveguide confinement while accommodating advanced designs like Mach-Zehnder modulators and ring resonators for next-generation integrated circuits As demand expands for photonic integrated circuits (PICs) in data centers, aerospace, and medical diagnostics, the reliability of device fabrication at these thicknesses garners additional investment and R&D focus. In turn, production volumes have ramped up, driving down costs and further incentivizing end-users to choose the 500–1000 nm thickness range. As a result, the synergy between strong optical performance, ease of fabrication, reduced cost structures, and broad design flexibility explains why 500–1000 nm LiNbO₃ thin films dominate the market and play a pivotal role in unlocking new opportunities in high-speed optical communication, sensing, and signal processing.
By Product Type
Optical modulators based on lithium niobate thin film market with over 62.7% market share have established themselves as the frontrunners with more than 42.6% market share in high-speed data communication, largely because LiNbO₃’s electro-optic properties deliver unparalleled performance in terms of modulation bandwidth and stability By leveraging the crystal’s strong Pockels effect, these modulators can operate at lower voltages while achieving high-frequency response, making them indispensable for applications like long-haul fiber optics and emerging coherent communication standards Lithium niobate modulators further benefit from a mature design ecosystem, where electrode patterns are well-studied, ensuring predictable phase-matching between the optical and RF signals. Manufacturers favor LiNbO₃ in this category over alternative materials, such as silicon photonics with organic polymers, because it combines longevity, reliability, and the ability to sustain consistent performance under demanding environmental conditions demand for these devices is heavily influenced by the exponential growth of data traffic, particularly from streaming platforms, teleconferencing, and data-hungry cloud services.
Modulators are integral components in advanced optical networks, controlling the phase, amplitude, or polarization of light to encode data with high fidelity. As telecom providers in the lithium niobate thin film market race to accommodate higher data rates and lower latency, LiNbO₃ modulators have become a cornerstone technology, driving widespread interest in LiNbO₃ thin film. Next-generation applications like optical computing, quantum communication, and LiDAR also rely on robust modulation capabilities, pushing developers to refine device size, insertion loss, and power consumption. Given the proven record of LiNbO₃-based modulators in meeting strict industry benchmarks, major players in telecommunications and photonics continue to invest in refining designs and fabrication methods. Consequently, modulators maintain a decisive lead over other device types—like filters or resonators—when it comes to capturing the lion’s share of lithium niobate thin film demand, ensuring continued market prominence and R&D focus on this critical product segment.
By Application
Base station application with over 39.0% market share in the lithium niobate thin film market because modern wireless infrastructure requires ever faster and more reliable signal processing to support high-capacity data transmission. Base stations, essential to cellular networks, rely on both high-frequency filtering and efficient electro-optic modulation to manage data throughput and optimize signal integrity in congested spectrum environments. Lithium niobate’s inherent ability to handle high power levels without sacrificing linearity or reliability makes it the preferred option over competing materials like gallium arsenide, especially as telecom technology transitions to advanced 5G standard deployments Moreover, LiNbO₃’s stable temperature performance ensures consistent operation across varying environmental conditions—a critical requirement for base stations distributed over large geographic zones.
Further fueling this trend in the lithium niobate thin film market are the strategic benefits that LiNbO₃-based components bring to radio frequency (RF) filtering, frequency mixers, and optical links within base station equipment. As data densities scale, operators aim to minimize signal distortion and reduce latency—outcomes best achieved using the robust electro-optic coefficients in LiNbO₃ thin films to achieve precise, low-loss manipulation of signals. The desire for compact, integrable solutions also plays a significant role in LiNbO₃ adoption, as device footprint can be minimized through waveguide integration while maintaining high performance. As 5G evolves toward ultrareliable low-latency communications, the synergy of miniaturized modulator technology and stable, high-frequency operation of LiNbO₃ thin films is poised to play an even bigger role. With telecom giants ramping up base station installations worldwide, contract manufacturers and system integrators are actively standardizing on lithium niobate thin film components to stay competitive. This lasting confidence in LiNbO₃’s reliability, high-speed capability, and thermal robustness explains why network development strategies decisively favor the material, ensuring that base station usage continues to drive significant growth in global demand.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific’s leadership in lithium niobate thin film market in terms of production and consumption stems from the region’s established dominance in semiconductor manufacturing, longstanding expertise in optics, and the significant presence of telecom equipment giants. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea contribute immensely to this market, boosted by substantial investments in photonics research, government-backed industry initiatives, and vast consumer electronics manufacturing bases. Large-scale deployments of 5G infrastructure and the overlap with integrated photonics production accelerate LiNbO₃ adoption, especially in modulators, filters, and advanced sensor technologies. Demand comes predominantly from data communication providers, handset manufacturers, and defense contractors who require precision components for next-generation communication systems. In parallel, academic-industry collaborations within research hubs throughout Asia Pacific catalyze new technology breakthroughs, ensuring ongoing innovation in lithium niobate product design. Consequently, the synergy of strong industrial capacity, high-end research, and the relentless push for cutting-edge telecom solutions cements Asia Pacific’s position as both the largest producer and consumer of lithium niobate thin film for the rapidly evolving global market.
Key Players in Lithium Niobate Thin Film Market
- Hangzhou Shalom Electro-optics Technology Co., Ltd.
- Inno Semiconductor Technology
- NANOLN (Jinan Jingzheng Electronics Co., Ltd.)
- Partow Technologies LLC
- Xiamen Powerway Advanced Material Co., Ltd (PAM-Xiamen)
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Product Type
- Modulator
- Optical Switches
- Insulator
- Others
By Type
- X- Cut
- Y- Cut
- Z- Cut
By Thickness
- Less Than 500nm
- 500nm - 1000nm
- More Than 1000nm
By Application
- Data Centers
- Long-Distance Data Transmission
- Base Stations
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA01251127 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA01251127 | Delivery: Immediate Access 
.svg)






