Laser Communication Market: By Type (Ground Terminal, Airborne Terminal, and Space Terminal); Solution (Space-to-space and Space-to-ground Station); Range (Short Range, Medium Range, and Long Range); Component (Transmitter, Receiver, Laser, and Others); Application (Technology Development, Earth Observation & Remote Sensing, Communication, and Others); End Users (Satellite Communications, Transportation, Military, and Others); Region—Industry Dynamics, Market Size, Opportunity and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Feb-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0622275 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0622275 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Snapshot
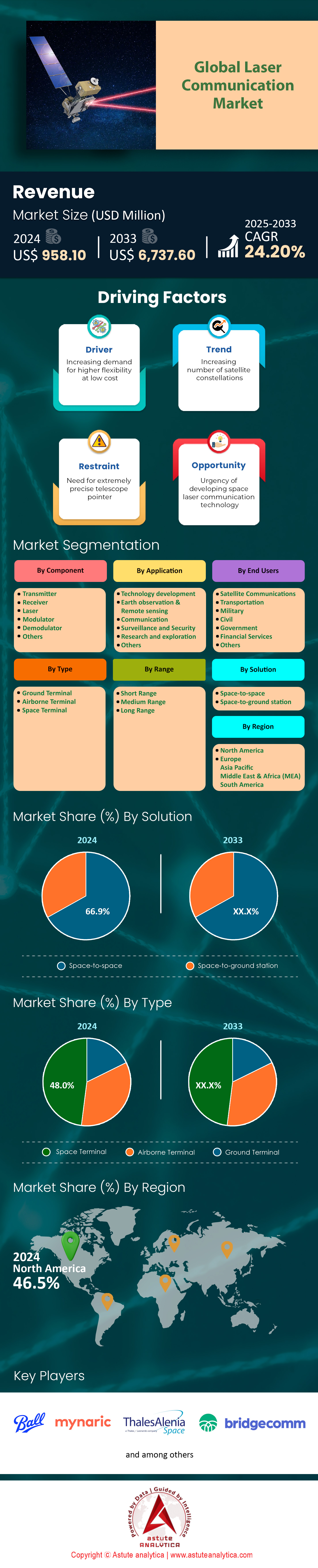
Laser communication market was valued at US$ 958.10 million in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 6,737.60 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 24.20% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
Laser communication technology has evolved rapidly, driven by advances in optics and signal processing. Modern systems now achieve data transfer speeds reaching 100 Gbps and maintain beam divergence measurements as low as 0.1 mrad. Leading aerospace and defense companies develop systems with round-trip latencies below 1 microsecond and bit error rates as low as 10^-9. Laboratory experiments have demonstrated effective free-space operation over distances exceeding 500 kilometers, ensuring robust performance under challenging conditions. The systems typically operate using wavelengths between 1550 nm and 1625 nm, which optimize signal integrity in various environments. In addition, laser modulators are capable of switching at frequencies up to 50 GHz, enabling rapid data modulation for high-throughput applications. Precision tracking methods now achieve alignment controls within 0.05 mrad, further enhancing link stability. Continuous operation tests have recorded reliable performance for periods exceeding 100 hours. These technical achievements highlight the significant improvements over previous communication methods and underscore the collaborative efforts between academic research, government projects, and industry innovation. Such breakthroughs represent a transformative step toward building next-generation global communication networks.
Applications of laser communication market span deep-space missions, inter-satellite links, and secure terrestrial networks. Precision beam steering and adaptive optics combine to reduce signal degradation and improve overall transmission clarity. High signal-to-noise ratios reaching values above 40 dB ensure that optical links remain robust even amid environmental disturbances. Research laboratories continue to refine error correction protocols and modulation techniques to further enhance system reliability. Collaboration among defense contractors, space agencies, and technology innovators advances the practical deployment of these systems into networks that require dynamic, high-speed, and secure connectivity. The integration of laser communication in satellite constellations and data centers marks a shift from conventional radio-frequency systems to advanced optical methods. As ongoing tests validate performance metrics and operational durability, the technology is poised to replace legacy communication methods in critical applications. The steady progress in data throughput, optical precision, and system endurance confirms laser communication as a key enabler for future connectivity solutions, setting the stage for a new era in global networks. These remarkable advancements continue to redefine the boundaries of modern communication technology.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: High bandwidth transmission capabilities enabling faster data transfer rates.
Laser communication market is revolutionizing data transfer by offering unparalleled bandwidth capabilities. Traditional radio frequency (RF) systems are limited in their data transmission speeds, often maxing out at gigabits per second. In contrast, laser communication systems, such as NASA’s Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), have demonstrated data rates exceeding terabits per second. This is particularly crucial for applications like satellite-to-ground communication, where large volumes of data need to be transmitted quickly. For instance, the European Space Agency’s (ESA) EDRS-C satellite uses laser communication to transmit Earth observation data at speeds up to 1.8 gigabits per second, significantly faster than RF systems.
The demand for high-speed data transfer is further amplified by the growing need for real-time data in sectors like defense, autonomous vehicles, and space exploration. The U.S. Department of Defense’s Space Development Agency (SDA) has been actively investing in laser communication for its National Defense Space Architecture (NDSA), aiming to achieve secure, high-speed data links between satellites. Similarly, companies like SpaceX are leveraging laser communication in their Starlink satellites to enable faster internet speeds globally. The ability to transmit large datasets, such as high-resolution images or real-time video feeds, without latency is a key driver for the adoption of laser communication technologies.
Trend: Development of interoperable mesh networks for scalable communication systems.
The laser communication market is witnessing a significant shift toward the development of interoperable mesh networks, which allow multiple nodes to communicate seamlessly. This trend is particularly evident in satellite constellations, where laser communication links between satellites create a robust, scalable network. For example, SpaceX’s Starlink satellites use laser inter-satellite links to form a mesh network, enabling data to be routed through multiple satellites without relying on ground stations. This not only reduces latency but also enhances the overall reliability of the network. Similarly, the European Union’s IRIS² satellite constellation project aims to deploy laser-based mesh networks for secure and resilient communication across Europe.
Interoperable mesh networks are also gaining traction in terrestrial applications, such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Companies like Luminar are exploring the use of laser communication to create vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) networks, enabling real-time data exchange for safer and more efficient transportation. The U.S. Army’s Tactical Space Layer (TSL) program is another example, where laser communication is being used to create a mesh network for battlefield communication. The ability to scale these networks without compromising on speed or security is a key trend driving innovation in the laser communication market.
Challenge: Atmospheric interference affecting signal reliability in free-space optical communication.
One of the most significant challenges in laser communication is atmospheric interference, which can degrade signal reliability in free-space optical communication (FSO). Factors like fog, rain, and turbulence can scatter or absorb laser beams, leading to signal loss. For instance, the European Space Agency’s Alphasat mission experienced signal degradation due to atmospheric turbulence, despite using advanced adaptive optics to mitigate the effects. Similarly, the U.S. Navy’s Maritime Laser Communication (MLC) system faced challenges in maintaining stable communication links over long distances due to weather conditions.
To address this issue, researchers in the global laser communication market are developing advanced techniques like adaptive optics and wavelength diversity. Adaptive optics, used in NASA’s LCRD, can correct for atmospheric distortions in real-time, improving signal reliability. Wavelength diversity, on the other hand, involves using multiple wavelengths to transmit data, reducing the impact of atmospheric interference. For example, the German Aerospace Center (DLR) has successfully tested wavelength diversity in its Terabit Optical Link (TOL) project, achieving stable communication links even in adverse weather conditions. Despite these advancements, atmospheric interference remains a persistent challenge, particularly for long-distance communication in terrestrial and space-based applications.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Space terminals with over 48% market share dominate the laser communication market due to their unparalleled ability to facilitate high-speed, secure, and efficient data transmission across vast distances in space. This dominance is driven by the increasing demand for high-bandwidth communication in satellite networks, deep-space missions, and inter-satellite links. Space terminals offer data rates exceeding 10 Gbps, which is significantly higher than traditional radio frequency systems, making them indispensable for modern space missions. Key end users include government space agencies like NASA and ESA, as well as private space companies such as SpaceX and OneWeb, which rely on laser communication for real-time data transfer and mission control. The growing deployment of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, which require high-speed inter-satellite links, has further accelerated the adoption of space terminals. NASA’s LCOT (Low-Cost Optical Terminal) has successfully demonstrated uplink speeds of 1.2 Gbps, showcasing the reliability of space terminals. Additionally, the increasing number of satellite constellations and deep-space exploration missions has driven the demand for space terminals, with the global space-based laser communication market projected to grow significantly.
The dominance of space terminals is further fueled by advancements in miniaturization and cost reduction, with terminals now weighing less than 20 kg and costing under $1 million per unit. The ability to transmit data at high speeds with minimal latency has made space terminals the preferred choice for critical applications such as Earth observation, military communication, and global internet coverage. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has also driven the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. NASA’s TBIRD (TeraByte InfraRed Delivery) system has demonstrated downlink speeds of 200 Gbps, highlighting the potential of space terminals in satellite communication. The growing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites, has further accelerated the demand for space terminals. The ability to transmit large volumes of data in real-time has made space terminals the backbone of modern space communication systems. The increasing investment in space exploration and satellite communication by both public and private sectors has also contributed to the dominance of space terminals in the laser communication market.
By Application
Laser communication market is increasingly being used for technology development, driven by the need for advanced communication systems in emerging fields such as Beyond-5G (B5G) networks, quantum communication, and space exploration. The technology development segment is controlling over 26.80% market share. Laser communication is critical for developing high-speed, low-latency networks that can support future technologies like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Key end users include research institutions, technology companies, and government agencies that are investing in next-generation communication infrastructure. The ability to achieve data rates of up to 100 Gbps makes laser communication essential for testing and deploying advanced communication systems. For instance, Japan’s Society 5.0 initiative relies on laser communication to integrate economic growth with technological innovation. The increasing demand for high-speed communication in technology development has driven the adoption of laser communication in various applications, including data centers, industrial automation, and defense systems.
The dominance of technology development in laser communication market is supported by its ability to provide secure and interference-free communication, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data transfer. The increasing adoption of laser communication in data centers is also driving the market, with data centers now accounting for a significant portion of the global laser communication market. The ability to transmit large volumes of data at high speeds with minimal latency has made laser communication the preferred choice for critical applications such as high-frequency trading and industrial automation. The growing investment in next-generation communication infrastructure by both public and private sectors has also contributed to the dominance of laser communication in technology development. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has further accelerated the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. The ability to transmit data at high speeds with minimal latency has made laser communication the backbone of modern communication systems. The growing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites, has further accelerated the demand for laser communication in technology development.
By End User
Satellite communication is the most dominant end user category of laser communication market with over 25.90% market share, driven by the need for high-speed, secure, and reliable communication in satellite networks. Laser communication offers data rates of up to 10 Gbps, which is essential for transmitting large volumes of data from satellites to ground stations. Key end users include satellite operators like SpaceX, OneWeb, and SES, as well as government agencies like NASA and the Department of Defense. The growing deployment of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, which require high-speed inter-satellite links to maintain seamless communication, has accelerated the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. NASA’s TBIRD (TeraByte InfraRed Delivery) system has demonstrated downlink speeds of 200 Gbps, showcasing the potential of laser communication in satellite networks. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has also driven the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks.
The dominance of satellite communication in the laser communication market is further fueled by the increasing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites. The ability to transmit large volumes of data in real-time has made laser communication the backbone of modern satellite communication systems. The growing investment in space exploration and satellite communication by both public and private sectors has also contributed to the dominance of satellite communication in the laser communication market. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has further accelerated the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. The ability to transmit data at high speeds with minimal latency has made laser communication the preferred choice for critical applications such as Earth observation, military communication, and global internet coverage. The growing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites, has further accelerated the demand for laser communication in satellite networks.
By Range
Short-range laser communication with more than 54.90% market share dominates the laser communication market, driven by its applications in secure military communication, data centers, and industrial automation. Short-range laser communication offers high-speed, secure, and interference-free communication, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data transfer. Key end users include defense organizations, data center operators, and industrial automation companies that rely on laser communication for secure and efficient data transmission. The ability to achieve data rates of up to 100 Gbps makes short-range laser communication essential for applications like high-frequency trading and industrial automation. The increasing adoption of laser communication in data centers is also driving the market, with data centers now accounting for a significant portion of the global laser communication market.
The dominance of short-range laser communication is further fueled by its ability to provide secure and interference-free communication, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data transfer. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has further accelerated the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. The ability to transmit data at high speeds with minimal latency has made laser communication the preferred choice for critical applications such as high-frequency trading and industrial automation. The growing investment in next-generation communication infrastructure by both public and private sectors has also contributed to the dominance of short-range laser communication in the laser communication market. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has further accelerated the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. The ability to transmit data at high speeds with minimal latency has made laser communication the backbone of modern communication systems. The growing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites, has further accelerated the demand for laser communication in short-range applications.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America is the most dominant region in the laser communication market with over 46.50% market share, driven by the presence of leading space agencies, technology companies, and defense organizations. The region’s dominance is fueled by the increasing demand for high-speed communication in satellite networks, deep-space missions, and military applications. The U.S. is the largest contributor to this regional dominance, with significant investments in space communication and defense technologies. Key organizations in the U.S. that make use of laser communication include NASA, SpaceX, and the Department of Defense. The annual spending on space communication in the U.S. exceeds $50 billion, driven by the increasing number of satellite constellations and deep-space exploration missions. The U.S. space budget, including both public and private funding, is projected to reach $100 billion by 2030, with significant investments in laser communication technologies.
The dominance of North America in the laser communication market is further fueled by the increasing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites. The ability to transmit large volumes of data in real-time has made laser communication the backbone of modern satellite communication systems. The growing investment in space exploration and satellite communication by both public and private sectors has also contributed to the dominance of North America in the market. The increasing demand for high-speed internet in remote areas has further accelerated the adoption of laser communication in satellite networks. The ability to transmit data at high speeds with minimal latency has made laser communication the preferred choice for critical applications such as Earth observation, military communication, and global internet coverage. The growing number of satellite constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb’s LEO satellites, has further accelerated the demand for laser communication in North America.
Recent Development in Laser Communication Market
- In January 2025, Xscape Photonics raised $44.0 million in a Series A funding round led by IAG Capital Partners, with participation from Altair, Cisco Investments, and Fathom Fund. This investment aims to advance their optical interconnect technologies for data centers and AI clusters.
- In 2024, Synopsys, Inc. completed a $33 billion acquisition of ANSYS, Inc., a supplier of engineering simulation software and services, strengthening their position in the photonics sector which includes laser communication technologies.
- In 2024, Hewlett Packard Enterprise acquired Juniper Networks, Inc. for $15 billion, enhancing their capabilities in optical data communications networking equipment crucial for laser communication systems.
- In 2024, Nokia Oyj acquired Infinera Corporation for $2.4 billion, expanding their portfolio in optical access to long-haul networking gear, which is relevant to laser communication technologies.
- In 2024, Lockheed Martin acquired Terran Orbital Corporation, a manufacturer of satellites for aerospace and US defense, including those with laser communication capabilities.
- In November 2024, Sony announced a partnership with Astro Digital to test laser communications from two small satellites, demonstrating high data-rate optical links between satellites and ground stations.
- In January 2024, NASA highlighted its collaboration with Fibertek Inc. to develop the Orion Artemis II Optical Communications System for the Artemis II mission, facilitating high-resolution data transmission from the lunar region to Earth.
- In 2024, the U.S. Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC) awarded contracts to Blue Origin, CACI International, General Atomics, and Viasat as part of a $100 million program to develop space laser communication terminal prototypes.
- In January 2023, Airbus and VDL Group announced their collaboration to develop and manufacture an airborne laser communication terminal called UltraAir, with a prototype demonstration and flight test planned for 2024.
- In 2023, NASA launched the Integrated LCRD Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) as a payload on the International Space Station, aiming to enhance ISS communications and assist future deep space missions through high-speed laser communication capabilities
Top Companies in the Laser Communication Market:
- AAC Clyde Space
- Ball Aerospace and Technologies
- BridgeComm, Inc.
- Fibertek
- General Atomics
- Hensoldt
- Hyperion Technologies
- Mynaric AG
- Mynaric
- ODYSSEUS Space
- Optical Physics Company
- Space Micro
- TESAT Spacecom
- Thales Alenia Space
- Other Prominent players
Market Segmentation Overview
By Type:
- Ground Terminal
- Airborne Terminal
- Space Terminal
By Solution:
- Space-to-space
- Space-to-ground station
By Range:
- Short Range
- Medium Range
- Long Range
By Component:
- Transmitter
- Receiver
- Laser
- Modulator
- Demodulator
- Others
By Application:
- Technology development
- Earth observation & Remote sensing
- Communication
- Surveillance and Security
- Research and exploration
- Others
By End Users:
- Satellite Communications
- Transportation
- Military
- Civil
- Government
- Financial Services
- Others
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0622275 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0622275 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






