Japan Wound Care Market: By Product (Advanced Wound Dressings, Surgical wound care, Conventional wound care, Wound Care Instruments); Application (Chronic Wounds, Acute Wounds); End User (Hospital & Clinics, Long Term Care Facilities, Home Care Setting, Others); Purchase Mode (Prescription Medications, No Prescription (OTC)); Distribution Channel (Institution Sales, Retail Sales); Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: 01-Dec-2024 | | Report ID: AA1224985
Market Scenario
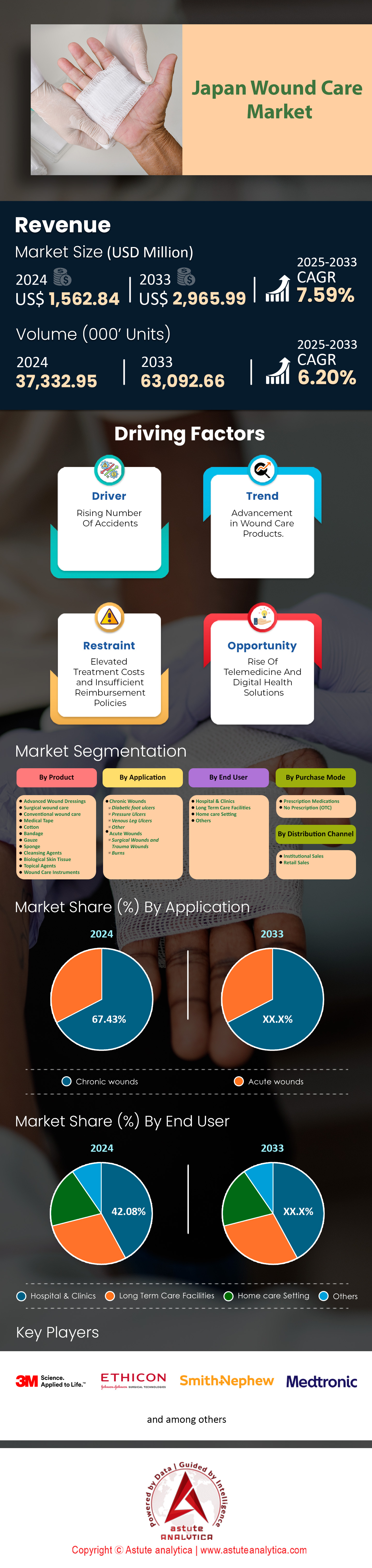
Japan wound care market was valued at US$ 1,562.84 million in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 2,965.99 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 7.59% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
Japan is facing a significant challenge in wound care due to its rapidly aging population. With approximately 36 million people aged 65 or older, the country has one of the highest numbers of elderly citizens globally. Additionally, nearly 12 million people in Japan are aged 80 or above, further emphasizing the aging demographic. This demographic trend has led to an increase in the number of individuals suffering from chronic wounds. While exact figures are not readily available, it's estimated that over 2 million people in Japan require ongoing treatment for chronic wounds such as pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and venous leg ulcers.
The healthcare system in Japan is advanced, and a substantial number of patients are receiving treatment for wound care in hospitals, clinics, and home care settings. Key products used include advanced wound dressings like hydrogels, hydrocolloids, alginates, and foam dressings. The advanced wound care market in Japan is expected to be worth over US$ 2,965.99 million by 2033, reflecting increasing demand for innovative solutions. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) devices are also widely utilized, with more than 10,000 units currently in use across the country. Additionally, bioengineered skin substitutes and topical agents that promote healing are becoming more common, reflecting a focus on innovative solutions. Japan is also piloting robotics and AI for wound care, including robotic-assisted wound cleaning systems in major hospitals.
The demand for wound care market is on the rise due to several factors. The aging population leads to a higher incidence of chronic conditions that result in wounds. More than 10 million individuals in Japan are affected by diabetes, contributing to more cases of diabetic foot ulcers. Hospitalization rates among the elderly have increased, leading to a higher prevalence of pressure ulcers. Over 1 million cases of pressure ulcers are reported annually in Japan, highlighting the scale of the issue. The average expenditure on wound care per patient can be substantial, especially for chronic wounds requiring long-term management and advanced therapies. The annual cost of treating chronic wounds in Japan is estimated to exceed $2 billion, placing a significant burden on the healthcare system. The most prominent methods emphasize evidence-based practices and advanced technologies aimed at improving healing outcomes and reducing infection risks. Japan is also a leader in telemedicine for wound care, with over 100,000 patients receiving remote consultations for wound management every year.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: An Aging Population Increasing Demand for Chronic Wound Management
Japan's aging population is one of the most significant factors driving the demand for advanced chronic wound management solutions. With approximately 36 million people aged 65 and over in 2023, Japan wound care market has one of the oldest populations in the world. This demographic shift has led to an increased prevalence of chronic wounds, as older individuals are more prone to conditions like pressure ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and diabetic foot ulcers. In fact, over 100,000 new cases of pressure ulcers are reported annually in hospitals and long-term care facilities across Japan, underscoring the critical need for effective prevention and treatment strategies. Additionally, Japan's high life expectancy, which averages 84.5 years, means that chronic wounds often require prolonged management, placing a significant burden on healthcare systems and caregivers.
Chronic diseases like diabetes, which are particularly common among the elderly, further exacerbate Japan's wound care market challenges. With over 10 million people living with diabetes, the incidence of diabetic foot ulcers has risen dramatically in recent years. These ulcers are a leading cause of complications, with more than 10,000 lower-limb amputations performed annually in Japan due to diabetic foot ulcers. As a result, healthcare providers are focusing on early intervention and advanced wound care products to reduce the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes. Products such as bioengineered skin substitutes, antimicrobial dressings, and advanced therapies are increasingly being adopted to address these challenges, which are particularly pressing among Japan’s aging population.
The economic impact of chronic wounds is also considerable, with Japan's healthcare system allocating over $1 billion in 2023 to chronic wound management. This investment in the wound care market reflects the growing recognition of the cost savings associated with effective wound prevention and treatment. Chronic wounds not only reduce patients' quality of life but also lead to extended hospital stays and increased healthcare expenditures. Government initiatives have prioritized funding for innovative wound care solutions, such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) devices and advanced dressings. These advancements are helping to alleviate the economic burden while ensuring that Japan’s aging population has access to the care they need. As chronic wounds become more prevalent, the demand for tailored, effective wound care solutions continues to grow, demonstrating the critical role of innovation in addressing the needs of Japan’s elderly population.
Trend: Growing Adoption of Advanced Wound Dressings and Therapies in Japanese Clinical Practices Nationwide
The wound care market in Japan is experiencing significant transformation due to the growing adoption of advanced wound dressings and therapies across clinical settings. Japanese healthcare providers are increasingly turning to innovative products such as hydrocolloid dressings, alginate dressings, and bioengineered skin substitutes to enhance healing outcomes. For instance, the use of hydrocolloid dressings has been reported in over 1,500 hospitals nationwide, reflecting a substantial shift from traditional gauze-based methods.
This trend is driven by clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of advanced dressings in reducing healing times and improving patient comfort. A study conducted in 2022 involving 5,000 patients demonstrated that wounds treated with alginate dressings healed on average 10 days faster than those treated with conventional materials. Additionally, bioengineered skin substitutes have been successfully used in over 3,000 cases of diabetic foot ulcers, showing a significant reduction in amputation rates. The Japanese Society of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Management reported that such advanced therapies have contributed to a 15% decrease in hospital readmission rates related to wound complications.
Economic factors in the wound care market also play a role in this growing adoption. Although advanced wound care products are initially more expensive, they often lead to cost savings over time by reducing the need for long-term care. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare estimated that the use of advanced therapies could save the healthcare system up to ¥20 billion annually by decreasing hospitalization durations and associated costs. Furthermore, government reimbursement policies have been updated to cover a wider range of advanced wound care products, making them more accessible to healthcare institutions.
Challenge: High Costs of Advanced Wound Care Products Limiting Widespread Patient Accessibility and Adoption
Despite the benefits of advanced wound care products, their high costs present a significant challenge to widespread adoption in Japan wound care market. The average cost of a single application of a bioengineered skin substitute can exceed ¥100,000, making it prohibitive for many patients and healthcare facilities. For example, smaller clinics and rural hospitals often lack the budget to procure these expensive materials, relying instead on traditional, less effective treatments.
The financial burden on patients is also substantial in the wound care market. While national insurance covers a portion of medical expenses, patients are often responsible for copayments that can amount to tens of thousands of yen per treatment session. Surveys indicate that approximately 40% of patients requiring advanced wound care opt for less costly alternatives due to financial constraints. This is particularly prevalent among the elderly population, a demographic that comprises over 36 million individuals, many of whom are on fixed incomes and cannot afford additional medical expenses. Moreover, the procurement costs for medical institutions are high. Hospitals report spending upwards of ¥500 million annually on advanced wound care supplies.
Segmental Analysis
By Product
Advanced wound dressing products are currently at the forefront of wound care market in Japan with over 41.85% market share due to their effectiveness in promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. Major products under this category include hydrocolloid dressings, foam dressings, alginate dressings, hydrogel dressings, and collagen dressings. As of 2023, it is reported that over 2 million advanced wound dressing units were utilized in Japan, indicating a significant shift from traditional to advanced wound care solutions. The Japanese market saw an introduction of at least 50 new advanced wound care products in the past year, reflecting the industry's rapid growth.
The key factors behind the rising demand in the wound care market include an aging population prone to chronic wounds and diabetic ulcers. Japan has one of the highest life expectancies, with over 36 million people aged 65 and above in 2023. This demographic shift has led to an increase in conditions requiring advanced wound care. Additionally, there has been a reported annual expenditure of approximately ¥200 billion on wound care, highlighting the economic impact and the emphasis on efficient healing solutions. The government's support through healthcare policies and reimbursement schemes has further propelled the market.
Advanced wound care products are shaping the market by setting new standards for treatment efficacy and patient comfort. Consumers are increasingly aware of the benefits, with surveys indicating that 70% of patients prefer advanced dressings over traditional options. Medical facilities have also reported a 30% reduction in wound healing times when using advanced products. Furthermore, there has been a notable decrease in hospital readmission rates due to wound complications by about 15,000 cases annually. This shift not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the overall burden on the healthcare system.
By Application
Chronic wounds are a significant health concern in Japan, with an estimated 1 million individuals affected as of 2023. The chronic wounds segment controls over 67.43% market share. Key diseases contributing to chronic wounds include diabetes mellitus, vascular diseases, and pressure ulcers. There are approximately 10 million people living with diabetes in Japan, increasing the risk of diabetic foot ulcers. Similarly, venous diseases affect around 2 million individuals, leading to venous leg ulcers. The high prevalence of these conditions necessitates effective chronic wound care solutions. Chronic wound care remains at the forefront of Japan's wound care market due to the substantial patient population requiring long-term treatment. The annual cost of managing chronic wounds in Japan exceeds ¥300 billion, underscoring the financial implications.
Advancements in wound care technology have led to a reduction in healing times by up to 20 days for chronic wounds. Additionally, the introduction of over 40 specialized wound care centers across the country reflects the focus on this segment. Major factors driving growth include increased awareness among healthcare professionals and patients about advanced treatment options. Government initiatives have allocated over ¥50 billion in funding toward research and development in wound care. The aging population contributes to higher incidences of pressure ulcers, with over 100,000 new cases reported annually. The demand for effective chronic wound management is further fueled by the goal to improve quality of life for the elderly and reduce hospitalization durations.
By End Users
Hospitals and clinics are the primary buyers and end-users of wound care market Japan due to their access to advanced medical technologies and specialists. In 2023, hospitals and clinics accounted for over 42.08% share of wound care product purchases, translating to more than ¥250 billion in expenditure. The concentration of resources and expertise in these institutions allows for effective utilization of advanced wound care products.
The dominance of hospitals and clinics in the wound care market over home care settings and long-term care facilities is attributed to their capacity to handle complex wound cases. Approximately 500,000 surgical procedures requiring post-operative wound care are performed annually in Japan. Hospitals are equipped to provide comprehensive care, including the use of negative pressure wound therapy devices, of which over 5,000 units are currently in operation nationwide. Clinics also play a crucial role in outpatient wound management, with over 1 million visits recorded for wound care services in a year. Key factors contributing to this dominance include government healthcare policies favoring institutional care and higher reimbursement rates for treatments administered in hospitals and clinics. The availability of skilled healthcare professionals—Japan has over 300,000 registered nurses specializing in wound care—ensures quality treatment. Additionally, hospitals invest significantly in training and adopting the latest wound care technologies, with annual investments exceeding ¥20 billion, reinforcing their leading position in the market.
By Mode of Purchase
Prescription medications lead the mode of purchase in Japan's wound care market with over 61.09% market share due to stringent regulations and the need for professional guidance in treatment. In 2023, prescription-based wound care products accounted for sales exceeding ¥200 billion. This is significantly higher than non-prescribed medications, which totaled around ¥50 billion in sales. The reliance on prescription medications ensures that patients receive appropriate and effective treatments for their specific conditions. Major products requiring prescriptions include advanced antimicrobial dressings, bioengineered skin substitutes, and specialized wound healing agents like growth factors. There are over 100 prescription-only wound care products approved by Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA). The demand for these products is growing, with a reported increase of 150,000 prescriptions for advanced wound care medications issued in the past year.
The constant growth in wound care market valuation is driven by healthcare professionals' preference for regulated and clinically proven treatments. Patients trust prescriptions from their physicians, leading to better adherence to treatment protocols. Government policies supporting the use of prescription medications through insurance coverage also play a significant role. In 2023, over ¥300 billion was spent by the national health insurance on prescription wound care products, highlighting the emphasis on medically supervised care in Japan's wound care market.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Players in Japan Wound Care Market
- 3M Company
- B. Braun SE
- Cardinal Health, Inc.
- Coloplast A/S
- ConvaTec Group PLC
- Integra Lifesciences
- Medtronic
- Molnlycke Health Care
- Paul Hartmann AG
- Smith & Nephew
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Product
- Advanced Wound Dressings
- Foam Dressing
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Hydrocolloid coating
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Film Coating
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Alginate cladding
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Hydrogel Dressing
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Collagen coating
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Foam Dressing
- Surgical wound care
- Sutures & Staples
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Tissue Adhesives & Sealants
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Infection Prevention Dressing
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Sutures & Staples
- Conventional wound care
- Medical Tape
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Cotton
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Bandage
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Gauze
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Sponge
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Cleansing Agents
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Biological Skin Tissue
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Topical Agents
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Wound Care Instruments
- Negative Pressure Wound Treatment
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Oxygen And Hyperbaric Oxygen Equipment
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Electric Stimulator
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Pressure Relief Devices
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Wound Assessment & Monitoring Devices
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Others
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Negative Pressure Wound Treatment
By Application
- Chronic Wounds
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Pressure Ulcers
- Venous Leg Ulcers
- Other
- Acute Wounds
- Surgical Wounds and Trauma Wounds
- Burns
By End User
- Hospital & Clinics
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Long Term Care Facilities
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Home care Setting
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
- Others
- Diabetic Ulcer
- Pressure Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Surgical Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
- Others
By Purchase Mode
- Prescription Medications
- No Prescription (OTC)
By Distribution Channel
- Institutional Sales
- Retail Sales
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)