Japan Tool Steel Market: By Material (Chromium, Tungsten, Molybdenum, and Vanadium); Product (High Speed Steel, Cold Work Steel, Hot Work Steel, and Others); Process (Rolled and forged); Application (Automotive, Shipbuilding, Aerospace, and Others)—Industry Dynamics, Market Size and Opportunity Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Feb-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0422211 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0422211 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Scenario
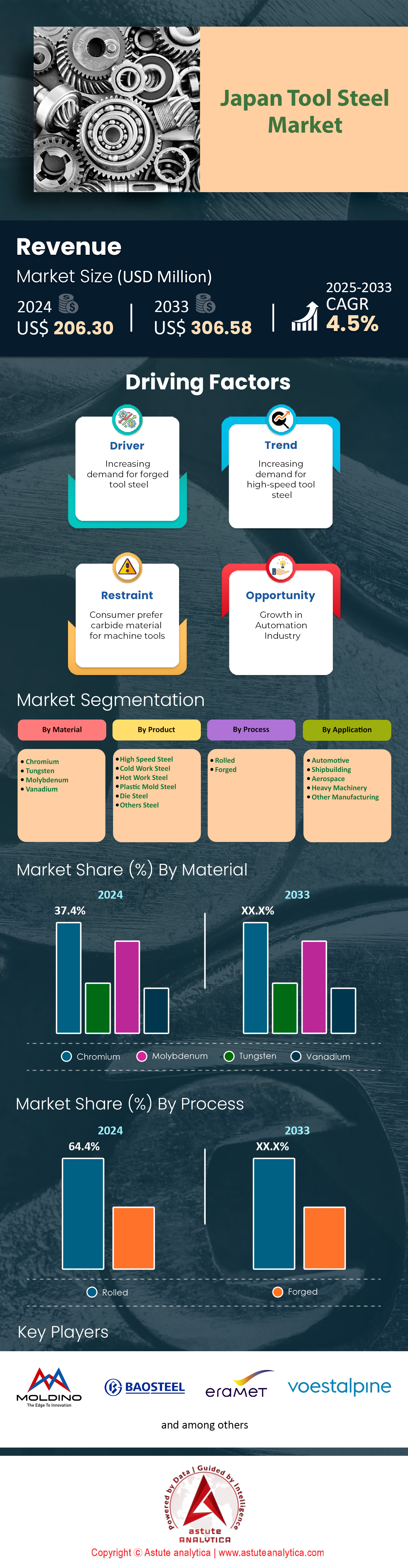
Japan tool steel market was valued at US$ 206.30 million in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 306.58 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
The Japan tool steel market is witnessing heightened demand, primarily spurred by the escalating requirements in automotive, electronics, and aerospace segments. With five tungsten-vanadium steel variants launched by Hitachi Metals in March, manufacturers are focusing heavily on improving hardness and temperature resistance. Automotive companies rely on these advanced steels for critical engine molds and drivetrain components, while aerospace firms favor tool steel with extended fatigue endurance for turbine disks. Meanwhile, three forging laboratories in Osaka are refining their processes to create heat- and wear-resistant solutions for small-scale robotic parts. Growing interest from consumer electronics producers further drives uptake, as more compact devices call for steel with tighter dimensional accuracy. These robust performance specifications indicate a thriving market landscape poised for continued expansion.
Among the most prominent materials in this tool steel market are chromium-based hot-work and cold-work steels, prized for their durability and adaptability across multiple industries. In response to surging demand, Daido Steel announced eight forging expansions, which highlights the appetite for larger production volumes and customized compositions. Additionally, Nippon Koshuha Steel introduced two new vacuum heat treatment lines to cater to the heightened need for distortion-free outputs. Sumitomo has unveiled six advanced forging dies tailored for microcomponents, reflecting a push toward precision engineering for electronics and miniaturized manufacturing. This surge is further supported by eleven major electronics companies embracing specialized cold-work steels with superior wear characteristics. Overall, the forward momentum appears unrelenting, fueled by both domestic innovation and growing export opportunities.
The key trends shaping this tool steel market in Japan include collaboration between tool steel producers and robotics integrators, a shift toward sustainable steelmaking, and expanded usage of multi-alloy compositions for lightweight but long-lasting components. Demand is significantly emanating from automotive OEMs like Toyota and Honda, who seek safer and more efficient mold designs, as well as from four leading consumer electronics manufacturers requesting high-wear forged steels for housings and connectors. One additive manufacturing center for specialized dies has been established in Nagoya, enabling faster prototyping and shorter lead times. Kobe Steel has introduced nine multi-material injection mold solutions, emphasizing the market’s collective drive toward customization. Recent developments also point to cross-industry projects, ensuring that Japan’s tool steel segment remains a global leader in both innovation and output. In another notable development, Mitsubishi Materials has established a specialized forging center in Aichi to bolster advanced aerospace tooling.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Expanding adoption of modern automated high-hardness steel forging processes for intricate industrial manufacturing tasks
Expanding adoption of modern automated high-hardness steel forging processes for intricate industrial manufacturing tasks is emerging as a pivotal driver in Japan’s tool steel market. As factories aim to boost output quality, five robotic forging arms have been installed in a Yokohama facility dedicated to automotive engine components. This aligns with the industry’s shift toward real-time monitoring and proactive maintenance, exemplified by one advanced automation line from Fuji Electric that uses sensor-based analytics to prevent die wear. High-hardness steel forging is particularly relevant for aerospace assemblies, where precision is vital for landing gear segments and connector housings. Achieving such accuracy necessitates minimal dimensional deviation, prompting three automated lines for high-hardness steel forging to be launched in Ibaraki. The outcome is better consistency, improved turnaround, and stronger synergy between machine intelligence and robust alloy compositions.
In parallel, advanced lubrication for automated forging procedures has seen remarkable progress, with eight specialized lubricants introduced by Sanko for high-temperature applicators. These solutions in the Japan tool steel market diminish friction during forging and extend die life, making them indispensable for aerospace and heavy machinery tooling. Furthermore, seven new servo-press forging machines were tested in a Nagoya pilot program, demonstrating improved forging speed and reduced downtime, ultimately cutting production bottlenecks. Meanwhile, eleven forging research institutions across Japan are focusing on sensor-integrated die designs that detect microfractures before they escalate. This focus on continuous monitoring and quick intervention bolsters the competitiveness of Japan’s tool steel sector, as clients from electronics and powertrain manufacturing gain steady access to top-quality parts. Through targeted R&D and steady adoption of intelligent forging, the market appears well-positioned for continuous expansion.
Trend: Growing emphasis on multi-alloy compositions to enhance thermal conductivity and product longevity in tooling
Growing emphasis on multi-alloy compositions to enhance thermal conductivity and product longevity in tooling has become a significant trend within Japan’s tool steel market. End users increasingly request robust steel grades that maintain stable properties under extreme heat, especially in press-forming for specialized components. This shift is evident in four newly developed cobalt-chromium alloys deployed for high-temperature forging, offering greater hardness retention and improved wear resistance. Multi-alloy forging expansions by Aichi Steel, which include three separate pilot lines, underscore the push for materials that dissipate heat more effectively. Electronics manufacturers also benefit from these alloys, as they safeguard delicate circuit housings during soldering processes. This strategic move toward varied compositions reflects an ongoing endeavor to tackle tooling fatigue issues, resulting in a noticeable uptick in reliability across automotive, machined parts, and aerospace applications.
To further test these emerging materials in the tool steel market, five advanced thermal analysis labs in Kobe are collaborating with tool steel producers to refine forging temperatures and optimize preheating cycles. Meanwhile, two hybrid steels introduced by Daido combine nickel-alloy cores with carbide-reinforced surfaces, enabling extended use in multi-stage forging processes. Machine builders who cater to micro-turbine manufacturers are also adopting nine specialized tungsten-copper tool solutions that resist cracking under repetitive stress. These new compositions allow for more intricate designs, supporting the trend toward smaller yet more powerful components. In a decisive push, one pilot project in Shizuoka is exploring multi-alloy forging blanks for complex industrial molds, aiming to expedite production steps and ease final assembly. As a result, multi-alloy innovation is cementing Japan’s reputation as a formidable hub for cutting-edge tool steel applications.
Challenge: Rising complexities in precision milling requiring advanced specialized coatings and extended heat resistance solutions
Rising complexities in precision milling requiring advanced specialized coatings and extended heat resistance solutions has emerged as a defining challenge for Japan’s tool steel market. Complex gear mechanisms and integrated electronic components demand ultra-fine tolerances that generate high friction and elevated temperatures during machining. To address these issues, eight advanced milling centers in Aichi are experimenting with tungsten-enriched lubrication that mitigates excessive thermal expansion. Furthermore, one specialized coating introduced by OSG relies on nano-structured ceramic layers to reduce tool wear during multi-axis milling, specifically for medical device components. Three novel surface finishing lines launched in Hiroshima target micro-burr formation in aerospace turbine rotors, which is especially problematic in high-heat applications. Despite these progressive solutions, the rapid miniaturization of parts continues to amplify the difficulty of maintaining uniform material removal rates.
To counter these escalating demands, two tungsten-rich PVD coatings were unveiled by a Tokyo-based research consortium, offering improved hardness thresholds for drilling superalloys. However, sustaining consistent surface finishes on small-diameter tools remains problematic, highlighting the need for tailored heat dissipation methods. Five new R&D alliances across Osaka and Yokohama are investigating real-time temperature feedback systems that alert machinists of potential distortion. This synergy between advanced coatings and intelligent process controls helps prevent catastrophic failures in high-precision applications in the Japan’s tool steel market. In another forward-looking step, one pilot test program for diamond-like carbon layers is underway to enhance friction performance on stainless steel molds. Although innovations are steadily emerging, the challenge persists: pushing equipment capabilities to meet ultra-complex milling shapes while ensuring materials and coatings can withstand relentless thermal stresses.
Segmental Analysis
By Material
Chromium’s prominent position in Japan’s tool steel market, holding over 37.5% share, is primarily attributed to its remarkable ability to bolster hardness and durability. By forming stable carbides, chromium-enriched tool steels can deliver a tool lifespan up to 2.5 times longer than those without chromium, an essential trait for high-stress environments such as automotive and aerospace production. This metal also excels at corrosion resistance, producing an oxide layer that reduces rust-related deterioration by around 90% in steels containing 8% or more chromium. In a demanding industrial climate like Japan’s, this resistance translates into fewer replacements, minimized downtime, and improved production throughput. Furthermore, chromium-rich steels can reach a hardness level of up to 66 HRC, allowing them to withstand repeated impacts and abrasive forces with minimal wear.
In comparison to tungsten, chromium demonstrates superior cost efficiency, being roughly 2.3 times more affordable while also contributing robust anti-corrosion properties in Japan tool steel market. Tungsten, which is approximately 3.7 times more expensive, may offer high-temperature stability but lacks the same cost-performance balance. Vanadium and molybdenum each bring added toughness or strength, yet chromium’s blend of hardness, corrosion defense, and overall adaptability makes it the top material choice in Japan’s tool steel sector. Another factor propelling chromium’s popularity is its ability to boost steel hardenability by about 1.5 times, ensuring that even large, complex tool shapes maintain uniform strength. This reliability is particularly significant when manufacturers aim to maximize production efficiency by reducing tool failures, saving both time and money. As a result, chromium’s competitive advantages continue to reinforce its market dominance in Japan’s tool steel industry, securing the metal’s reputation as a highly preferred alloying element.
By Product
Cold work tool steels, holding a substantial 27% share in Japan’s tool steel market, owe their standing to exceptional performance under ambient conditions. These steels achieve impressively low wear rates, measuring around 0.02 mm³/Nm during abrasive testing, making them ideal for demanding industries like automotive manufacturing. Specifically, dies and punches fashioned from these steels can endure over 1 million stamping cycles before experiencing notable wear, which is vital for Japan’s high-volume production environment. Such resilience directly cuts maintenance costs, fueling consistent demand. Additionally, cold work tool steels’ ability to preserve sharp cutting edges for up to 30% longer than standard steels further boosts operational efficiency when producing precision components.
Core applications include creating cutting tools for various industrial segments, where the heightened wear resistance increases productivity and extends tool life. Equally important in the tool steel market is their role in fabricating ultra-precise forming dies for consumer electronics, achieving minimal tolerances of about ±0.005 mm. Automotive companies remain the largest end-user group, accounting for roughly 45% of cold work tool steel usage, requiring an average of 2.5 tons of such steels across multiple tooling stations per vehicle model. Electronics manufacturers follow at about 30%, leveraged by the necessity for small, accurate parts. Industrial machinery producers consume roughly 15%, with the remaining 10% distributed across other sectors. Japan’s flourishing automotive sector, surpassing 7.8 million vehicles produced in 2024, intensifies the appetite for cold work tool steels, as each vehicle’s production involves stamping and shaping operations that demand high-performance alloys. By combining durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness, cold work tool steels continue to anchor themselves as the preferred choice for Japanese industries seeking reliable tooling solutions capable of thriving under strenuous, high-output conditions.
By Process
Rolled tool steel commands over 64% of Japan’s tool steel market, thanks to its reputation for precise dimensional control and enhanced mechanical performance. When subjected to rolling, steel develops a fine, uniform grain size generally spanning 5 to 20 μm—significantly smaller than the 50 to 100 μm range observed in many forged products. This tighter grain structure results in tensile strength gains of 15-20% and fatigue resistance improvements of up to 30%, turning rolled sheet or bar stock into a high-grade option for applications where endurance is non-negotiable. The process also facilitates on-target thickness control, holding variations to around ±0.05 mm, which is integral to the precise manufacturing demands of Japan’s advanced industrial ecosystem.
Another strong advantage of the rolled process is its efficiency and high-volume potential. Certain rolling mills in Japan handle up to 500 tons of tool steel daily, achieving speeds of around 60 meters per minute for thinner gauge strips. This volume capacity, along with a material yield that can exceed 98%, curtails waste and reduces per-unit costs. Automotive manufacturers, predominantly using large panels and complex structural components, benefit immensely from consistent sheets produced through rolling. Typical stamping dies that weigh anywhere from 20 to 40 tons are more efficiently machined from rolled stock, improving throughput. Moreover, carefully controlled cooling at rates as precise as 10°C per second allows engineers to tailor the microstructure of these steels, producing specialized grades optimized for extreme wear resistance or high-impact scenarios. Such refinement cements rolled products as a go-to for various end-users, driving the rolled process’s long-standing preeminence in Japan’s tool steel marketplace.
By Application
The automotive sector’s robust 62.4% share in Japan tool steel market is largely fueled by the country’s extensive vehicle output and unwavering pursuit of quality. In 2024 alone, Japan’s automotive industry manufactured more than 7.8 million vehicles, each demanding around 900 kg of steel, including specialized tool steels used for mold making, stamping, and precision cutting. Since advanced high-strength steels have gained traction in car design—partly to foster fuel efficiency—tool steels must meet higher wear and toughness benchmarks. For example, cutting tools crafted from premium tool steel can hold their edge for up to 300% longer when working with modern steel grades, significantly cutting time lost to sharpening or replacement. These improvements underscore why automotive OEMs in Japan value premium tool steels that consistently deliver superior outcomes, reinforcing the sector’s lead in market revenue.
The surge in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids further amplifies this segment’s influence in the Japan tool steel market. In 2024, EV and hybrid sales in Japan climbed to 1.2 million units, marking a 35% year-on-year jump. Manufacturing EV battery casings and specialized components calls for tool steels capable of enduring over 500,000 stamping cycles—a 25% jump in durability compared to traditional automotive parts. Many automakers demand a 50% enhancement in tool life to minimize interruptions on their production lines. Reinforced by Japan’s solid consumer base, with annual vehicle sales topping 5 million units, the automotive field remains the most significant driver of tool steel demand. As a result, forward-looking R&D efforts and continuous process innovations persist across Japan’s tool steel industry, aiming to meet automakers’ exacting standards and sustain the automotive sector’s commanding share of revenues.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Companies in the Japan Tool Steel Market:
- Baosteel Group
- Buderus Edelstahl GmbH
- Eramet SA
- Hitachi Metals, Ltd.
- Hudson Tool Steel Corporation
- Iwata Bolt Co., Ltd.
- Kosakusho Works
- Mitsubishi Materials Corporation
- Naigai Trans Line Ltd.
- QiLu Special Steel Co., Ltd
- Samuel, Son & Co.
- Schmiedewerke Gröditz
- Takisawa Machine Tool
- Tiangong International Co., Ltd.
- Toa Intersystem Inc.
- Tpr Co., Ltd.
- Transcontainer Ltd.
- Voestalpine AG
- Other Major Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Material
- Chromium
- Tungsten
- Molybdenum
- Vanadium
By Product
- High Speed Steel
- Cold Work Steel
- Hot Work Steel
- Plastic Mold Steel
- Die Steel
- Others Steel
By Process
- Rolled
- Forged
By Application
- Automotive
- Shipbuilding
- Aerospace
- Heavy Machinery
- Other Manufacturing
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0422211 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0422211 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






