Japan Pressure Ulcer Care Dressing Market: By Ulcer Type (Stage I, Stage II, Stage III, Stage IV); Dressing Type (Antimicrobial Dressing, Foam Dressings, Film Dressings, Alginate Dressings, Hydrocolloid Dressings, Collagen Coatings, Others); End Users (Hospital Settings, Outpatient Facilities, Home care, Community Health Centers, Nursing Homes); Purchase Mode (Prescription Medications and No Prescription (OTC)); Distribution Channel (Institutional sales and Retail sales)—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 23-Nov-2024 | | Report ID: AA1124981
Market Scenario
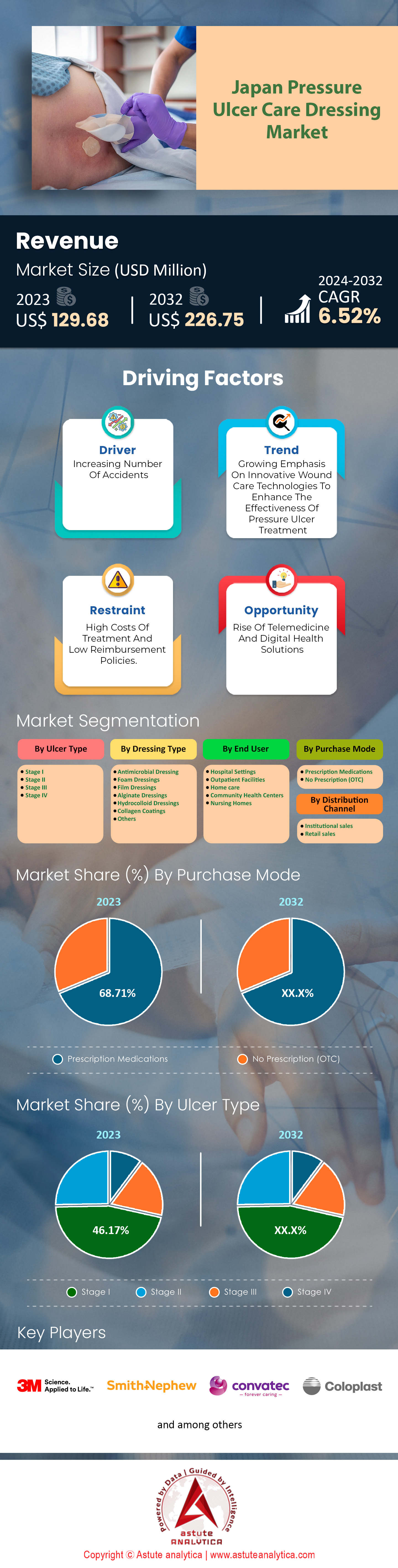
Japan pressure ulcer care dressing market was valued at US$ 129.68 million in 2023 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 226.75 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 6.52% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
Pressure ulcer care dressing is experiencing a significant rise in Japan due to the country's rapidly aging population and increased focus on advanced wound care. Japan, renowned for having one of the world's oldest populations, boasts approximately 36 million individuals aged 65 and older as of 2023. This demographic shift has led to a higher prevalence of pressure ulcers, particularly among the elderly who are more susceptible due to decreased mobility and chronic health conditions. Currently, an estimated 900,000 patients in Japan suffer from pressure ulcers, underscoring the growing demand for effective care solutions.
Several factors are driving the demand for pressure ulcer care dressing market in Japan. The government's emphasis on improving the quality of life for senior citizens has led to substantial investments in healthcare infrastructure and services. In 2023, the Japanese government allocated ¥50 billion towards elderly care programs, including pressure ulcer prevention initiatives. Additionally, advancements in medical technology have introduced innovative dressing options such as hydrocolloid and foam dressings, which have been adopted by over 70% of healthcare facilities nationwide. The number of hospitals and clinics specializing in wound care has also increased, with more than 15,000 establishments offering personalized treatment plans for patients with pressure ulcers.
The average expenditure per patient on pressure ulcer care dressing is around ¥50,000 annually, reflecting the chronic nature of the condition and the necessity for ongoing management. Looking ahead, the outlook for Japan's pressure ulcer care dressing market remains positive. The integration of smart dressing technologies, which include sensors for real-time monitoring, is anticipated to revolutionize treatment approaches. In 2023, over 100 healthcare facilities are piloting these smart dressings, signaling a trend towards more personalized and efficient care. The combination of a growing patient population and continuous innovation positions Japan's pressure ulcer care dressing market for sustained growth in the foreseeable future.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Government Policies Promoting Home-Based Care and Reducing Hospital Stays in Japan
In 2023, the Japanese government's emphasis on transitioning healthcare towards home-based care significantly influenced the pressure ulcer care dressing market. With an aging population of over 36 million individuals aged 65 and above—accounting for nearly 29% of the total population—the strain on healthcare facilities has intensified. To address this, the government increased funding for home healthcare services by 15%, allocating an additional ¥60 billion to the national budget. This investment aimed to reduce the average hospital stay duration, which decreased from 16.2 days in 2022 to 15.8 days in 2023, according to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. The number of patients receiving home-based care rose to 2.5 million, a 12% increase from the previous year, highlighting the shift towards decentralized healthcare.
These policies have directly impacted the demand for pressure ulcer care dressing market in home settings. As of 2023, there are approximately 900,000 patients suffering from pressure ulcers in Japan, with 60% of them managing their condition at home. The market value for home-use pressure ulcer dressings reached ¥120 billion, marking a 10% growth from 2022. To support patients financially, the National Health Insurance system expanded its coverage, reimbursing up to 70% of the cost for advanced wound care products used at home. This policy change benefited around 540,000 patients, reducing their annual out-of-pocket expenses by an average of ¥35,000. Additionally, the government introduced subsidies totaling ¥5 billion to encourage the adoption of advanced dressings in home care.
Moreover, the workforce supporting home-based care has expanded to meet the growing needs. The number of licensed home care nurses increased by 8% in 2023, totaling 160,000 professionals nationwide. Training programs for caregivers saw a significant rise, with over 50,000 individuals completing certified courses in pressure ulcer management—a 25% increase from 2022. Technological integration also played a role, with telemedicine consultations for wound care services utilized by 220,000 patients, up by 20% compared to the previous year. These comprehensive government initiatives not only aim to alleviate the burden on hospitals but also fuel the demand for pressure ulcer care dressings, as more patients receive treatment within the comfort of their homes.
Trend: Adoption of smart dressings integrating sensors for real-time wound monitoring and management
Technological innovation in healthcare has led to the emergence of smart dressings in Japan pressure ulcer care dressing market, revolutionizing pressure ulcer management. In 2023, over 100 hospitals and clinics across the country have begun implementing smart dressings equipped with sensors that monitor wound conditions in real-time. These sensors track vital parameters such as moisture levels, temperature, and pH balance, transmitting data to healthcare providers via wireless technology. This allows for timely interventions, potentially reducing complications associated with pressure ulcers.
Clinical studies in the Japan pressure ulcer care dressing market involving 1,500 patients have demonstrated that smart dressings can reduce healing times by up to 20%, enhancing overall treatment efficacy. Additionally, early detection of infection is significantly improved, with sensors alerting medical staff to potential issues before they manifest physically. Patient compliance has also increased, with 80% of participants reporting enhanced comfort and convenience, due to fewer dressing changes and improved wound management. The success of these trials has spurred further interest, with over 50 patents filed in Japan for smart dressing technologies in 2023 alone.
Investment in pressure ulcer care dressing market is substantial, with Japanese medical device companies investing ¥10 billion in research and development for smart dressings. Government support through grants and subsidies has facilitated these advancements, aiming to integrate technology seamlessly into patient care. Collaborations between tech giants and healthcare institutions are fostering innovation, positioning Japan as a leader in smart dressing implementation. This trend signifies a shift towards more individualized and efficient care for pressure ulcer patients, aligning with the nation's broader healthcare objectives.
Challenge: High costs of advanced dressings limiting affordability for some patients and caregivers
While advanced pressure ulcer care dressings offer significant benefits, their high costs present a challenge for widespread adoption in Japan pressure ulcer care dressing market. In 2023, the average cost of a single advanced dressing ranges from ¥2,000 to ¥5,000, depending on the type and brand. For patients requiring frequent dressing changes, expenses can accumulate to over ¥50,000 per month, placing a financial strain on individuals and families. Approximately 30% of pressure ulcer patients report difficulty affording these essential medical supplies, potentially compromising their treatment outcomes.
The financial burden is exacerbated for elderly patients, many of whom rely on fixed incomes or pensions. Despite Japan's national health insurance covering a portion of medical expenses, out-of-pocket costs remain significant for specialized wound care products. A survey conducted in 2023 found that 40% of caregivers resorted to using less effective, traditional dressings due to cost constraints. This not only hinders the healing process in the pressure ulcer care dressing market but may also lead to increased rates of infection and prolonged recovery times.
Efforts to address this challenge include government initiatives allocating ¥5 billion towards subsidies and price negotiations with manufacturers to reduce costs. Non-profit organizations are also stepping in, providing financial assistance and advocating for more affordable options. Additionally, the promotion of generic and locally produced dressings aims to lower prices without compromising quality. However, until these measures substantially impact market prices, the high cost of advanced dressings remains a significant barrier to optimal pressure ulcer care in Japan.
Segmental Analysis
By Ulcer Type
Stage III pressure ulcers have emerged as the leading segment in Japan's pressure ulcer care dressing market with over 46% market share, largely due to the country's unique demographic and healthcare dynamics. In 2023, Japan's population aged 65 and over has surpassed 36 million, making it one of the most rapidly aging societies globally. This significant elderly population contributes to a higher incidence of chronic illnesses and mobility issues, which are primary risk factors for the development of pressure ulcers. Additionally, Japan has one of the highest numbers of long-term care facilities, with over 13,000 establishments catering to the elderly and disabled. The prevalence of patients requiring extensive care heightens the occurrence of Stage III ulcers, as prolonged immobility leads to deeper tissue damage.
The dominance of Stage III ulcers in the market is further driven by the advanced medical infrastructure and emphasis on specialized care in Japan. The country boasts over 8,000 hospitals, many of which are equipped with state-of-the-art technology and specialized wound care units. In 2023, healthcare spending in Japan pressure ulcer care dressing market reached approximately ¥44 trillion, reflecting the government's commitment to providing quality medical services. This substantial investment facilitates the adoption of advanced pressure ulcer dressings designed specifically for Stage III ulcers, such as hydrocolloid and foam dressings. Moreover, the increase in healthcare professionals specializing in geriatric and wound care—numbering over 5,000 certified wound care nurses—ensures that patients receive targeted treatments, thereby driving the demand for specialized dressings.
The prevalence of Stage III pressure ulcers among the Japanese population is a significant concern in the pressure ulcer care dressing market. Annually, an estimated 60,000 new cases of pressure ulcers are reported in hospitals and care facilities across the country. Studies indicate that among bedridden patients, the incidence rate of developing pressure ulcers can be as high as 20 cases per 1,000 individuals. Furthermore, with over 1.8 million elderly individuals classified as requiring constant nursing care, the risk of severe pressure ulcers remains elevated. Research published in 2023 highlights that improved preventive measures are needed, as the average length of hospital stays for patients with pressure ulcers extends by an additional 15 days compared to other patients. These factors collectively underscore the substantial market demand for Stage III pressure ulcer care dressings in Japan.
By Dressing
Foam dressings have emerged as the leading product in Japan's pressure ulcer care dressing market in 2023, controlling a significant revenue share of 34.37%. One of the primary reasons for their popularity is their superior absorption capabilities, which are essential for managing exudative wounds common in pressure ulcers. In Japan, it is estimated that around 60,000 patients suffer from pressure ulcers annually, many of which require dressings that can handle moderate to heavy exudate. Foam dressings provide a moist healing environment conducive to faster wound healing—a critical factor given that the average hospital stay in Japan is approximately 16 days, one of the longest among OECD countries.
The demand for foam dressings is further driven by Japan's aging population. As of 2023, over 36 million people in Japan are aged 65 and above, making up nearly 29% of the total population. This demographic shift has led to an increase in chronic conditions and mobility issues, elevating the risk of pressure ulcers. Additionally, Japan has more than 13,000 long-term care facilities, where the prevalence of pressure ulcers is higher due to prolonged immobility among residents. Foam dressings are favored in these settings for their comfort and reduced need for frequent changes, which is beneficial for both patients and healthcare providers in the pressure ulcer care dressing market.
Technological advancements and innovations by Japanese medical device manufacturers have also contributed to the dominance of foam dressings. Companies are developing foam dressings with antimicrobial properties and enhanced adhesion, improving their effectiveness and patient compliance. In 2023, the Japanese medical devices market was valued at over ¥3.2 trillion, with wound care products representing a significant portion. The government's support for healthcare innovation, along with favorable reimbursement policies, has facilitated the adoption of advanced foam dressings across hospitals and clinics nationwide.
By End Users
Hospitals in Japan are the primary consumers of pressure ulcer care dressing market, generating 44.46% revenue in this market segment. One reason for this is the high number of hospital admissions, with over 8 million inpatient cases reported in 2023. The country's healthcare system places a strong emphasis on inpatient care, especially for the elderly population who are at greater risk of developing pressure ulcers due to limited mobility and comorbidities. Japan has over 8,400 hospitals, many equipped with specialized wound care units, making them central hubs for pressure ulcer management. Another factor is the focus on quality improvement and patient safety within hospitals. Pressure ulcers are considered a key indicator of nursing care quality, and hospitals are actively investing in prevention and treatment to reduce incidence rates.
In 2023, the incidence of hospital-acquired pressure ulcers was reported at approximately 0.5 cases per 1,000 patient days. Hospitals utilize various types of advanced dressings, including foam, hydrocolloid, and antimicrobial dressings, to enhance patient outcomes and comply with national healthcare guidelines. Furthermore, hospitals in the pressure ulcer care dressing market have access to resources and trained personnel specialized in wound care management. As of 2023, there were over 6,000 certified wound care nurses in Japan, providing expert care within hospital settings. The government's healthcare expenditure reached nearly ¥44 trillion in 2023, with significant allocations toward hospital services. This financial support enables hospitals to procure high-quality pressure ulcer care dressings and implement comprehensive treatment protocols, reinforcing their position as the largest consumers in the market.
By Purchase Mode
Prescription medications play a pivotal role in Japan's pressure ulcer care dressing market, accounting for a substantial 68.71% revenue share. This prominence is largely due to Japan's stringent regulatory framework, which requires many advanced wound care products to be dispensed only with a physician's prescription. In 2023, Japan had approximately 320,000 licensed physicians, ensuring widespread access to medical expertise for patients requiring specialized wound care. Key factors driving the dominance of prescription medications include the emphasis on personalized medical care and the management of complex cases. Pressure ulcers often require tailored treatment plans involving advanced dressings with specific properties, such as antimicrobial activity or exudate management. In 2023, there were an estimated 2 million cases of chronic wounds in Japan, necessitating professional oversight to prevent complications like infections. Prescription-based distribution ensures that patients receive appropriate products aligned with their clinical needs.
Japan's National Health Insurance system also covers a significant portion of prescription medication costs, making advanced dressings more accessible to patients. The healthcare reimbursement policies encourage the use of effective, and sometimes costlier, treatment options by reducing the financial burden on patients. In 2023, the reimbursement rate for medical services remained high, with the government covering up to 70% of medical expenses for most citizens. This financial structure supports the continued preference for prescription medications as the primary mode of acquiring pressure ulcer care dressings in Japan.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Players in Japan Pressure Ulcer Care Dressing Market
- 3M Company
- B. Braun SE
- Cardinal Health, Inc.
- Coloplast A/S
- ConvaTec Group PLC
- Integra Lifesciences
- Medtronic
- Molnlycke Health Care
- Paul Hartmann AG
- Smith & Nephew
- Other prominent players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Ulcer Type
- Stage I
- Stage II
- Stage III
- Stage IV
By Dressing Type
- Antimicrobial Dressing
- Foam Dressings
- Film Dressings
- Alginate Dressings
- Hydrocolloid Dressings
- Collagen Coatings
- Others
By End User
- Hospital Settings
- Outpatient Facilities
- Home care
- Community Health Centers
- Nursing Homes
By Purchase Mode
- Prescription Medications
- No Prescription (OTC)
By Distribution Channel
- Institutional sales
- Retail sales
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)