Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market: By Drug Type (Branded Prescription Drugs, Generic Prescription Drugs, Over-The Counter Drugs (OTC)); Formulation (Tablets, Capsules, Injectables, Sprays, Suspensions, Powder, Other Formulations); Route of Administration (Oral Medicine, Topical Medicine, Parenteral Medicine, Inhalations, Other Routes of Administration); Therapeutic Application (Cardiovascular Disease, Pain, Disease, Cancer, Respiratory Diseases, Neurological Diseases, Orthopedics, Other Therapeutic Application); Manufacturing Facility (In- House Facility and Outsourced facility); Distribution Channel (Retail Channel, Non-retail, and Online Channel)—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Jan-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0923598 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0923598 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Snapshot
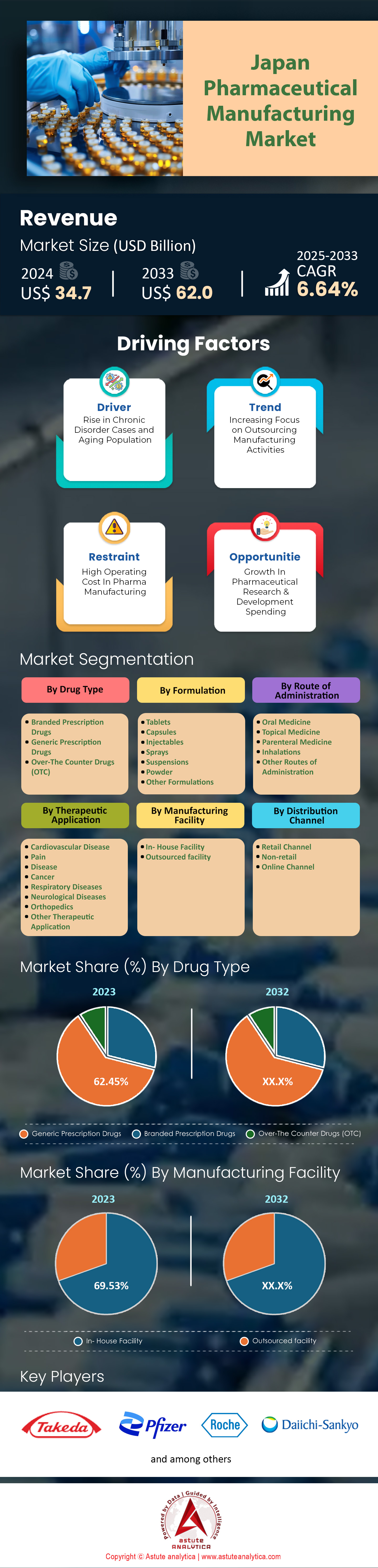
Japan pharmaceutical manufacturing market was valued at US$ 34.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of US$ 62.0 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 6.64% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
Japan’s pharmaceutical manufacturing market is witnessing a notable upswing in domestic and international investments in 2024, drawing on the nation’s robust regulatory framework and proven record of innovation. Shionogi boosted production capacity of influenza antivirals by adding two specialized manufacturing lines this year to meet growing global demand. Eisai secured regulatory approval for three experimental treatments targeting neurological conditions, reflecting the government’s licensing encouragement for breakthrough drugs. Chugai introduced a cutting-edge mRNA-based therapy for rare autoimmune disorders, marking the entry of advanced biological formulations in the pipeline. Fujifilm Toyama Chemical added one gene therapy product for inherited retinal diseases in early 2024, fueling hopes for advanced precision interventions. Driven by a heightened focus on health security, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare greenlighted five new regenerative medicine products aimed at chronic diseases. The sector has thus become a magnet for advanced research, fueling swift growth never seen before.
Central to this surge in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market is a combination of technological collaboration, a strong patent environment, and a rapidly aging demographic. Takeda launched four new oncology trials utilizing next-generation monoclonal antibodies, highlighting the emphasis on novel therapeutics. Kyowa Kirin reported a stable pipeline of five enzyme-based pharmacotherapies designed to address rare metabolic conditions, indicating the country’s focus on specialized medicine. In 2024, Mitsubishi Tanabe took steps to establish two state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities in Osaka and Kobe, catering to the localized production of biosimilars. Otsuka opened a specialized research center featuring six gene-editing laboratories in Tokyo, underscoring the drive toward genomic breakthroughs. The demand for innovative manufacturing processes has led to a wave of joint ventures, creating a surge in smaller bioventures that supply advanced research tools. This synergy between established firms and emerging startups has significantly accelerated production timelines, raising expectations for sustained market growth.
Among drug types, small-molecule formulations show consistent demand, but the real momentum comes from immunotherapies, cell-based products, and advanced biologics. Daiichi Sankyo recently finalized three commercial-scale lines for antibody-drug conjugates in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market, underlining the shift toward more targeted treatments and specialized formulations. In 2024 alone, RIKEN collaborated with three local manufacturers to refine cell expansion technologies for cancer immunotherapies, illustrating the synergy between research institutes and industry. Popular therapeutic applications revolve around oncology, neurology, and cardiovascular diseases, each benefiting from fast-track approvals and dedicated research hubs spread across major cities. The collective effort of pharmaceutical giants and research institutes is pushing boundaries in precision medicine, enabling Japan to stay at the forefront of global healthcare innovation. As the nation’s infrastructure expands, the domestic market’s appetite for modern therapies continues to grow, further establishing Japan as a key player in the world’s pharmaceutical landscape.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Reinforced Clinical Collaborations Propelling Innovative Biologic Drug Pipelines Across Domestic and International Manufacturing Networks
Collaborative approaches to research and development are emerging as a primary driver in Japan’s pharmaceutical manufacturing market landscape. Many firms are placing renewed emphasis on collective expertise and streamlined transition from laboratory discoveries to scalable production. These alliances are encouraged by a policy environment that supports early-stage clinical trials and cross-institutional participation, allowing companies to tap specialized knowledge while spreading the risks inherent in complex biologic projects. The shift toward shared protocols has heightened the drive for innovative treatments aimed at oncology, immunology, and advanced regenerative medicine. In early 2024, Otsuka introduced a newly developed monoclonal antibody research program in coordination with an international clinical consortium, underscoring the importance of global input in formulating next-generation therapies. Elsewhere, a biotech venture based in Kobe secured government backing for an experimental cell-based therapy designed for acute neurological disorders, suggesting that public-private synergy is becoming a significant catalyst for pioneering work.
Joint initiatives also help refine manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market, ensuring that pipeline breakthroughs can be translated into market-ready products in a timely manner. Mutual reliance on standardized data systems and synchronized trial phases reduces duplication and speeds up regulatory submissions, a crucial advantage in the rapidly evolving biologics domain. Many partnerships extend beyond national boundaries, focusing on knowledge exchange related to advanced manufacturing techniques such as continuous processing and real-time analytics. In February 2024, Takeda announced a collaboration with Biological E. Limited (BE) to enhance the production of its dengue vaccine, QDENGA. This partnership aims to increase manufacturing capacity to 50 million doses annually, which will significantly support Takeda's goal of delivering 100 million doses per year by 2030 at the latest. This initiative is part of Takeda's broader strategy to improve access to the vaccine in regions where dengue fever is endemic. Shionogi participated in a shared clinical trial network that evaluates biologic candidates for ultra-rare diseases, further illustrating the broadening scope of international cooperation. Chugai, seeking faster pathway-to-market solutions, enacted a pilot study structure in partnership with a university hospital, hoping to shorten the gap between pilot-scale production and commercial distribution. By reinforcing these multi-faceted collaborations, Japanese pharmaceutical firms are poised to deliver novel solutions in areas of high unmet clinical need, ultimately positioning the country at the forefront of cutting-edge biologic therapies.
Trend: Escalating Use of Smart Robotics and Automated Facilities Further Enhancing Drug Quality and Consistency
A pronounced shift toward robotics and automated platforms is transforming the operational core of Japan’s pharmaceutical manufacturing market. Companies are rapidly upgrading their facilities to support unmanned processes and continuous production, allocating significant resources to digital technologies that promise greater consistency and faster throughput. This move reflects a market-wide push to minimize human intervention in areas such as sterile filling, mixing, and compound handling, ensuring heightened precision for advanced therapeutics like biologics and cell-based treatments. Many firms also adopt robotics to assist in repetitive tasks that require strict adherence to contamination-free conditions. In early 2024, a state-of-the-art facility in Nagoya integrated robotic handling systems for high-potency active ingredients, highlighting the rising importance of fully enclosed production cycles. Fujifilm Toyama Chemical implemented an AI-driven control system that monitors molecular stability in real time, underscoring the role of predictive analytics in modern manufacturing.
Automation strategies do not merely optimize routine tasks; they also serve as a bridge to advanced quality assurance. Implementing real-time data capture at each stage of production allows instant adjustments to temperature, pressure, or mixing parameters, which can be critical when managing sensitive biologics. AI systems in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market help predict defects before they occur, generating valuable feedback loops for research and development teams. In 2024, another automated line in Shizuoka began employing machine vision to detect minute variations in tablet coatings, a step reflecting the intricate demands of precision dosing. Chugai tested robotic batch-sampling equipment for gene-based formulations, seeking to streamline sampling protocols that once relied heavily on manual processes. A pilot program with a domestic tech startup introduced an automated sanitization unit designed for cell culture spaces, pushing contamination control standards to new heights. As robotics and automation become more sophisticated, Japan’s pharmaceutical sector gains an agile edge in delivering safe, consistent therapies, illustrating how modern technology can fundamentally elevate drug manufacturing quality across the board.
Challenge: Rapid and Complex Shift in R&D Priorities Creating Imbalances in Streamlined Clinical-to-Commercial Manufacturing Pipelines
Despite significant progress in Japan’s pharmaceutical manufacturing market, ongoing realignments in research priorities present a tangible challenge for companies trying to maintain efficient production. Firms often pivot their pipelines to address novel discoveries, such as gene-editing breakthroughs or newly uncovered biologic pathways, which leaves existing infrastructure out of sync with updated clinical goals. This discord can lead to idle equipment, staff retraining, and prolonged timelines as manufacturing centers scramble to adapt. Shifting focus also complicates supply chain management; reagents and specialized materials slated for specific drug families may become redundant when strategic interests change suddenly. One Osaka-based biotech group recently halted work on a late-stage antibiotic formulation to concentrate on advanced immunotherapies, revealing how abrupt realignments can disrupt established workflows. As of early 2024, a Tokyo research wing under a major pharmaceutical firm repurposed a single high-end production suite intended for a suspended neurology project, demonstrating the ripple effects of sudden pipeline redirections.
Such imbalances are magnified in areas requiring precision engineering, where cross-functional compatibility is critical for seamless transition from pilot to commercial scale. Rapid shifts in therapeutic focus demand swift revalidation of processes, protocols, and automation controls in the Japan pharmaceutical manufacturing market. This burden extends to compliance teams who must secure new regulatory approvals or modify existing applications for updated uses. In mid-2024, Takeda revised a previously approved biologic manufacturing process to accommodate changes in formulation techniques, causing an unplanned three-month delay before the company could reinitiate production. Another challenge arises when staff with niche skill sets have to pivot to drastically different applications. A specialized immunology team in Yokohama was realigned to an emerging RNA-based project, forcing the company to invest in retraining. A collaborative trial site in Kyoto was also briefly put on hold due to an unexpected pipeline overhaul in neurology. These overlapping adjustments highlight the intricacies of managing cutting-edge pipelines, underscoring the necessity for forward-looking strategies that balance scientific discovery with stable and consistent manufacturing capacity.
Segmental Analysis
By Drug Type: Generic Prescription Drugs Takes the Charge with over 28.19% market Share
Generic prescription drugs have gained remarkable traction in Japan pharmaceutical manufacturing market due to a convergence of policy support, stringent quality controls, and the prioritization of affordable healthcare options. Government incentives, especially those sustained by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, encourage physicians to prescribe bioequivalent alternatives. Heightened consumer awareness also contributes to this preference, as patients who regularly manage chronic conditions recognize that generics contain the same active ingredients as branded counterparts. Sawai Pharmaceutical, for instance, reported formulating over 2,700 types of generic medications in 2023—ranging from cardiovascular treatments to anti-inflammatory remedies—underscoring the breadth of offerings. Nationwide, an estimated 5.6 million generic prescriptions are filled each day, according to research compiled in March 2023 by the Japan Generic Medicines Association. The growing cost gap within antibiotic regimens is another factor, where a standard course of brand-name Augmentin can cost roughly 2,300 yen compared to 800 yen for a generic equivalent.
Parallel to affordability, large-scale production capacities have fueled the widespread adoption of generics in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market. Towa Pharmaceutical manufactured more than 800 million units of anti-hypertensive generics in the first half of 2023 alone, demonstrating the industrial clout behind generic expansion. Nichi-Iko has reinforced its position by allocating 14 billion yen in R&D funds this year, much of which is directed toward developing quality-assured bioequivalent drugs. The Ministry’s 2023 guidelines further establish generics as the default in at least 22 critical therapeutic areas, reflecting a regulatory environment that champions cost-efficient solutions without compromising safety. These measures collectively reduce financial strain on Japan’s aging population, where prescriptions often require long-term refills. In essence, by aligning patient needs, government policies, and robust manufacturing infrastructures, generic drugs have secured a pivotal place in Japan’s pharmaceutical landscape, exemplifying how cost and quality considerations can harmoniously drive market dominance.
By Formulation: Tablet Commands Over 32% of the Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market
Tablets command a substantial share in Japan’s pharmaceutical formulations primarily because of dosing convenience, stability, and straightforward mass production. Patients frequently cite the ease of swallowing and the ability to split or crush tablets as significant advantages, especially in geriatric care. Among prominent examples, Eisai introduced an orodispersible tablet for Alzheimer’s patients in 2023 that dissolves instantly, prompting hospitals to stockpile it for dementia wards. This focus on patient-friendly design underscores why many research teams aim to refine tablet coatings for tasteless administration. According to a 2023 publication by the Japan Pharmaceutical Technology Association, approximately 1,200 specialized lines in domestic factories are dedicated to tablet compression and film coating. KYORIN Pharmaceutical invested roughly 6 billion yen in state-of-the-art tablet presses over the past year to ramp up production efficiency.
The preference over capsules, injectables, and other forms also stems from shelf-life advantages and distribution flexibility in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market. Many generics, from anti-ulcer agents to antihistamines, are formulated in tablet form for quick release or extended release, depending on dosage requirements. Tablets are especially amenable to packaging innovations, as exemplified by Takeda Pharmaceutical’s introduction of child-resistant blister packs for household safety in 2023. Hospitals and pharmacies likewise appreciate how tablets simplify inventory management, with wholesaler Suzuken confirming deliveries of at least 350,000 tablet packs per day across major urban centers this year. In addition, manufacturing synergy plays a role: a single production line can often shift between different types of tablet-based treatments with minimal downtime. Such adaptability lowers operational costs and ensures continuous supply, thus reinforcing tablets’ primacy within Japan’s pharmaceutical industry.
By Therapeutic Applications: Over 33% of Manufactured Drugs are Consumed For Pain Management
Japan’s focus on pain medication manufacturing stems from evolving patient demographics and clinical practice patterns. Over 23 million individuals, as reported by the Japanese Association for the Study of Pain in 2023, suffer from chronic pain related to musculoskeletal disorders, neuropathies, or aging. Ibuprofen-based tablets, alongside acetaminophen and naproxen, rank among the most widely produced analgesics in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market, with Daiichi Sankyo reporting output of nearly 450 million ibuprofen tablets during the first quarter of 2023. The aging population’s elevated prevalence of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis has further driven demand for advanced nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The Japan Primary Care Association mentions that acute pain from injuries and medical procedures affects roughly 5 million patients annually, explaining the heightened reliance on both opioid and non-opioid classes of analgesics.
Pharmaceutical companies have also diversified into combination and novel formulations aimed at pain management. Takeda’s extended-release tramadol, introduced this year, caters to chronic lower back pain and is dispensed at a rate of about 1.2 million prescriptions monthly. Meanwhile, Teijin Pharma, one of the key players in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market, has pioneered transdermal patches containing buprenorphine for patients who experience difficulty swallowing pills, fostering more targeted and sustained pain control. Innovative studies published in 2023 by the National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology have highlighted the importance of multi-modal treatments that integrate physical therapy, but medication remains a cornerstone. With investment from organizations like the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, local firms channel resources into refining analgesic efficacy while curtailing side effects. These combined efforts reflect a healthcare climate that recognizes pain as a multi-faceted issue, thus propelling Japan’s robust output of pain medications.
By Manufacturing Facility: In-House Facilities are Shining Brighter in Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market, Control Over 69.5% Market Share
Japan’s preference for in-house pharmaceutical production is deeply rooted in strict quality standards, intellectual property considerations, and corporate pride in local manufacturing. Major domestic players such as Astellas Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Otsuka Holdings maintain extensive in-house facilities, underscoring a strategy that prioritizes direct oversight of the supply chain. According to a 2023 industry report from the Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association, around 1,500 high-containment plants operate under Good Manufacturing Practice compliant controls to ensure biosafety and top-tier efficacy. By consolidating research, formulation, and packaging under one roof, these companies can rapidly adapt to regulatory shifts and market needs without the complexities often associated with global outsourcing. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma allocated 22 billion yen in facility enhancements this year, equipped with advanced automation for sterile manufacturing.
In-house production also arises from a cultural emphasis on trust and traceability in the pharmaceutical manufacturing market. The Japan Health Sciences Foundation noted in a 2023 briefing that patient confidence escalates when products bear a well-known domestic label, particularly for sensitive areas like oncology or biologics. Scandals involving substandard imports in past decades reinforced the national commitment to tighter domestic control. Shionogi & Co.’s integrated R&D and manufacturing campus in Osaka exemplifies this model, handling drug discovery, pilot production, and commercial scaling under one organizational structure. As local capacity expands, technology adoption grows as well: robotics for tablet inspection, smart sensors for continuous manufacturing, and data-driven analytics for process optimization. By keeping these processes in-house, Japanese pharmaceutical titans ensure consistent quality while safeguarding proprietary research, making domestic production a strategic mainstay in Japan’s pharmaceutical sector.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Players in the Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market
- Abbott Laboratories
- AbbVie Inc.
- ACADIA Pharma
- Aenova Group
- Amgen
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- AstraZeneca
- Bayer AG
- Biogen
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd
- Daiichi Sankyo
- Eli Lilly and Company
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Novo Nordisk
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Sanofi SA
- Takeda
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Drug Type
- Branded Prescription Drugs
- Generic Prescription Drugs
- Over-The Counter Drugs (OTC)
By Formulation
- Tablets
- Capsules
- Injectables
- Sprays
- Suspensions
- Powder
- Other Formulations
By Route of Administration
- Oral Medicine
- Topical Medicine
- Parenteral Medicine
- Inhalations
- Other Routes of Administration
By Therapeutic Application
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Pain
- Disease
- Cancer
- Respiratory Diseases
- Neurological Diseases
- Orthopedics
- Other Therapeutic Application
By Manufacturing Facility
- In- House Facility
- Outsourced facility
By Distribution Channel
- Retail Channel
- Non-retail
- Online Channel
View Full Infographic
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 34.7 Billion |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 62.0 Billion |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Bn) |
| CAGR | 6.64% |
| Segments covered | By Drug Type, By Formulation, By Route of Administration, By Therapeutic Application, By Manufacturing Facility, By Distribution Channel |
| Key Companies | Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie Inc., ACADIA Pharma, Aenova Group, Amgen, Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, Biogen, Boehringer, Ingelheim International GmbH, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly and Company, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Johnson & Johnson, Merck & Co., Inc., Novartis AG, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Inc., Sanofi SA, Takeda, Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0923598 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0923598 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






