Japan Myopia Control Lenses Market: By Product Type (Spectacle Lenses and Contact Lenses); Lens Type (Multifocal Lens, Orthokeratology Lens, Dual Focus Lens, Peripheral Defocus Lenses); Material (Soft Contact Lenses (Silicone Hydrogel, Hydrogel), Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses, Polycarbonate & High-Index Plastic (for Spectacle Lenses); Age Group (Children and Adults); Sales Channel (Eyeglass Clinic, Eyewear Retailers, Online Retail)–Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Mar-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA03251252 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA03251252 | Delivery: Immediate Access
Market Scenario
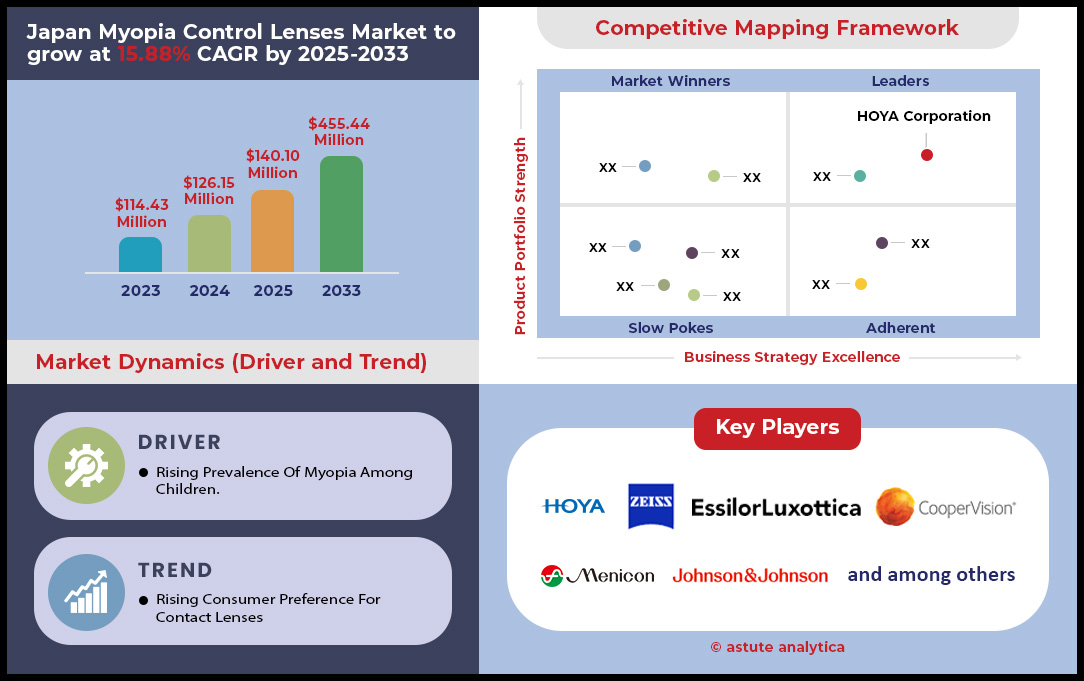
Japan myopia control lenses market was valued at US$ 123.16 million in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 422.09 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 15.21% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
Japan’s myopia control lenses market is underpinned by alarming pediatric vision data. A 2024 Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) survey revealed that 92% of junior high school students in urban prefectures like Tokyo and Osaka have myopia, up from 88% in 2019, driven by prolonged screen use (MHLW, 2024). Among children ages 6–12, myopia progression exceeded 1 diopter annually in 45% of cases, a critical threshold requiring intervention (Japanese Pediatric Ophthalmology Society, 2023). A pandemic-linked spike in indoor activity has worsened this trend: a 2024 Kyoto University study found 60% of parents reported their children’s screen time tripled during lockdowns, accelerating demand for lenses. Today, 18% of optometry practices specialized in pediatric care now prescribe myopia control lenses, a 40% rise in three years.
The demand for multifocal and dual-focus lenses dominates the Japan myopia control lenses market, capturing 82% of sales in 2024. Brands like Hoya’s MiYOSMART (36% market share) and Zeiss MyoKids (28%) lead, with Japan-specific designs targeting its high myopia severity. Regional disparities are stark: 70% of metropolitan parents prioritize myopia control, compared to just 35% in rural areas (Japan Optometric Association, 2024). Price remains a hurdle: the monthly cost for advanced lenses (¥12,000–¥20,000/pair) outpaces standard lenses (¥4,500–¥7,000), limiting access for lower-income households. However, 23% of urban households now enroll children in “myopia prevention programs” bundled with lenses, a service pioneered by chains like Vision Next and Sugita Hospital.
Japan’s aging population paradoxically fuels demand: 22% of presbyopic patients over 40 seek multifocal lenses correcting both presbyopia and childhood myopia (2024) in the myopia control lenses market. However, 34% of optometrists cite a shortage of trained fitters, a bottleneck as demand grows. Technology is bridging gaps: 25% of clinics now use AI-driven diagnostics speeding prescription accuracy, while apps like MyEyeTracker (3.2 million users) monitor progression. Projections show market size hitting ¥320 billion ($2.1 billion) by 2027 at a 13% CAGR, driven by government initiatives like the 2025 “Child Vision Initiative” subsidizing rural clinics. Yet, 40% of parents remain unaware of lenses’ efficacy, suggesting room for education campaigns. Key challenges include aligning lens supply chains to rural areas and standardizing national reimbursement codes—currently covered for under-18s in only 6 of 47 prefectures.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Myopia Prevalence Among Children Due to Increased Digital Screen Time
The surge in digital screen time has dramatically impacted myopia rates among Japanese children, creating a significant driver for myopia control lenses market growth. Recent studies in the market indicate that Japanese children aged 6-12 years spend an average of 3.5 hours daily on digital devices, with this figure having increased by 30% during the pandemic period, leading to many children spending over 5 hours daily on screens. This substantial increase in screen time has directly contributed to the alarming rise in myopia prevalence, with studies showing that children spending more than 4 hours daily on screens face a 60% higher risk of developing myopia compared to those with less than 2 hours of screen time.
The severity of this driver is further emphasized by statistical evidence showing that myopia rates among Japanese children have reached unprecedented levels. Between 1999 and 2017, myopia prevalence increased dramatically from 10% to 63% among 6-year-olds and from 60% to 95% among 12-year-olds. A 2023 study revealed that approximately 50% of children aged 10-12 years were diagnosed with myopia, marking a significant increase from 40% in 2018. Additionally, research has established that each additional hour of daily screen time corresponds to a 21% increase in the odds of developing myopia, highlighting the urgent need for myopia control solutions.
Trend: Growing Adoption of Overnight Orthokeratology Lenses for Corneal Reshaping Treatment
The orthokeratology (Ortho-K) lens market in Japan myopia control lenses market is experiencing remarkable growth, particularly in the overnight lens segment. This growth is particularly pronounced in the Kanto region, which represents the largest market for Ortho-K lenses in Japan, followed by the emerging Kansai region, both areas benefiting from robust healthcare infrastructure and academic excellence that support the adoption of these innovative technologies. The trend is supported by compelling patient adoption statistics and demographic factors. Studies indicate a high prevalence of myopia among Japanese students, with 76.5% of elementary school students and 94.9% of junior high school students in Tokyo affected. The overnight Ortho-K segment has emerged as the fastest-growing category due to its convenience and effectiveness in correcting myopia overnight. This trend is further reinforced by advancements in lens materials and designs, which have significantly enhanced comfort and safety, making Ortho-K lenses an increasingly attractive option for both patients and eye care professionals.
Challenge: Heavy Reliance on Imports Making Supply Chain Vulnerable Globally
Japan's significant dependence on imported contact lenses, particularly for myopia control, presents a major challenge for myopia control lenses market stability. As of 2023, Japan stands as the world's leading importer of contact lenses, with imports valued at US$1.37 billion, while exports remain relatively minimal at US$43.8 million. This substantial trade imbalance highlights the market's vulnerability to global supply chain disruptions. The myopia control lenses market, specifically, is projected to grow from US$123.16 million in 2024 to US$422.09 million by 2033, with a CAGR of 15.21%, making supply chain resilience increasingly critical.
The challenge is further complicated by the market's size and growth trajectory. Japan's contact lens market, valued at US$2.6 billion in 2023, ranks as the second-largest globally, trailing only behind the United States. The COVID-19 pandemic has already exposed the fragility of these global supply chains, causing delays and shortages in optical products. This vulnerability is particularly concerning given Japan's high dependence on imported myopia control solutions and the growing demand driven by increasing myopia prevalence.
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type
Spectacle lenses maintain a formidable 56.25% share of Japan’s myopia control lenses market by leveraging longstanding consumer trust, proven clinical efficacy, and broad accessibility. Many Japanese parents prefer spectacles as the first line of defense against childhood myopia, especially since they combine vision correction with specific defocus designs to suppress axial eye growth. Renowned local manufacturers, such as HOYA with its MiyoSmart lenses, have integrated cutting-edge technology into spectacle form, offering peripheral defocus management without sacrificing comfort or clarity. Because many schools in Japan actively encourage annual eye exams, parents become aware of deteriorating vision early—prompting them to seek simple, “low-effort” interventions. Spectacles fit that demand perfectly, requiring minimal skill to use and no complex hygiene regimen. In addition, insurance support often covers a portion of the cost for children’s eye care, reducing out-of-pocket expenses. This affordability, coupled with widespread acceptance, sustains spectacles as the market’s largest segment.
A critical factor driving spectacle lens dominance in the myopia control lenses market is the relatively high compliance rate among pediatric patients. Young children, especially those in elementary school, may struggle with inserting or removing contact lenses, making spectacles a more practical choice. Moreover, lens manufacturers have adapted their product offerings to suit Japan’s stringent quality guidelines, ensuring that specialized coatings—like anti-reflective and anti-scratch—perform well under daily use. In a technologically advanced market, spectacle lenses now incorporate features such as near-add power adjustments and enhanced optical zones to manage myopia progression effectively. Retail clinics and optical stores in high-traffic areas also play a pivotal role, as most offer on-site refraction services, sameday dispensing, and a wide range of frames tailored to younger wearers. By pairing convenience with credible myopia-control outcomes, spectacle lenses continue to secure the highest market share in Japan, outpacing more niche yet growing categories like orthokeratology and specialized contact lenses.
By Lens Type
Multifocal lenses capture a considerable 44.81% stake in Japan’s myopia control lenses market by delivering targeted peripheral defocus capabilities along with the convenience of multi-distance vision correction. Unlike single-vision lenses, multifocals segment light distribution to address near, intermediate, and distance zones simultaneously, which is especially advantageous in a society as digitally oriented as Japan’s. Eye care practitioners increasingly report that such designs help reduce excessive accommodative stress—one of the key contributors to progressing myopia in younger populations. Japanese manufacturers and global brands alike have introduced multifocal formats in both daily disposable and monthly replacement schedules, catering not only to teenagers who juggle school and extracurricular activities, but also to adults experiencing early presbyopia concurrent with longstanding myopia. These lenses have gained further traction through robust technological advancements in lens fitting software, allowing optometrists to fine-tune the power gradient according to each patient’s lifestyle needs.
High patient satisfaction with multifocal designs drives repeat purchases and fosters stronger word-of-mouth recommendations, contributing to this category’s rapid growth in the Japan myopia control lenses market. Barnabas-like pilot programs in select Tokyo eye clinics, for instance, have demonstrated improved compliance and consistent axial elongation slowdowns among children fitted with multifocal contacts. Many Japanese policymakers also view multifocal lens adoption as a practical step toward managing the nation’s steadily rising myopia prevalence, particularly in metropolitan areas where digital screen use soars. Additionally, manufacturers highlight the all-in-one appeal of multifocal designs by integrating advanced oxygen-permeable materials and wetting agents that reduce dryness, a pressing concern for lens wearers in Japan’s varying climates. As more local clinics adopt sophisticated topography measurements and real-time ocular data assessments, personalized fitting of multifocal lenses becomes easier, yielding sharper vision and sustained myopia control.
By Material Type
Soft contact lenses, including both silicone hydrogel and hydrogel variants, have established a 47.45% material share in Japan’s myopia control lenses market by aligning comfort, breathability, and proven slowing of myopia progression. Silicone hydrogel lenses, which exhibit superior oxygen permeability, are especially prized in a health-conscious market like Japan, where end users (and parents) scrutinize corneal health and dryness meticulously. Hydrogels excel in soft, pliable wear, reducing issues such as lens awareness and improving daylong tolerance—a critical advantage for students and office workers burdened with extensive screen time. Domestic and international lens manufacturers have refined production processes that embed peripheral defocus zones directly into soft lens architecture, tackling the root causes of progressive myopia. Such technology is widely promoted across Japanese e-commerce platforms and specialized optical stores, highlighting not just the convenience factor but also the sight-preservation benefits of daily or monthly soft contact lens regimens.
A parallel driver is Japan’s robust lens distribution infrastructure, spanning brick-and-mortar clinics to powerful online outlets where consumers can rapidly access newly launched products. This convenience in the myopia control lenses market propels the soft lens category forward, especially among teenagers who value hassle-free purchasing experiences. Innovation in polymer chemistry further cements their success: advanced coatings ensure high wettability and reduced lipid deposition, outcomes that resonate with the lifestyle of active students and busy professionals. Additionally, frequent replacement schedules (daily, bi-weekly, or monthly) dovetail with public health recommendations aiming to minimize microbial contamination and lens overwear. Some lens makers even collaborate with public health initiatives, marketing soft lenses as safe, hygiene-friendly, and potent at slowing axial elongation through peripheral defocus strategies. As the overall myopia control lenses market grows, soft lenses remain a pivotal choice in Japan, melding user comfort with clinically validated efficacy against progressive myopia.
By Age Group
Children represent a commanding 78.63% share of Japan’s myopia control lenses market, underscoring the country’s resolute focus on early intervention in pediatric eye health. Frequent school-based screenings, some conducted annually, facilitate the prompt identification of vision issues among young students. Once a child is flagged for myopia, eye care providers often recommend specialized lenses—ranging from advanced spectacle designs to bespoke contact lenses—that incorporate peripheral defocus elements validated to slow axial elongation. This proactive approach stems from growing awareness of the health and economic consequences linked to untreated high myopia, such as retinal detachment and increasing reliance on complex corrective procedures later in life. Simultaneously, the Japanese Ministry of Education has been vocal about the detrimental impact of excessive screen time, prompting parental vigilance and accelerating adoption of medically approved solutions. This confluence of institutional support and familial concern establishes children as the largest consumer group.
Moreover, local lens manufacturers and international corporations in the Japan myopia control lenses market have introduced pediatric-specific product lines, integrating child-friendly features such as minimal insertion discomfort, robust antifog coatings, and easy-lens-handling instructions. These innovations align well with Japan’s safety-oriented marketplace, where parents scrutinize product certifications and clinical endorsements before purchase. Clinics specializing in pediatric optometry often partner with schools and community centers to hold vision workshops, further educating parents on the significance of precise myopia management during childhood. As a result, many families opt for technologically advanced options, including multifocal or orthokeratology strategies, if standard single-vision approaches prove insufficient. This holistic framework—encompassing early detection, tailored product design, and direct engagement with parents—reinforces the remarkable 78.63% market dominance of the children’s segment. Considering the continual rise in pediatric myopia cases across Asia, fueled by intensive academic demands and digital device usage, this demographic is poised to remain the primary driver of Japanese market.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Players in the Japan Myopia control lenses market
- Essilor International
- Johnson & Johnson Vision
- CooperVision
- Hoya Corporation
- Zeiss Group
- Bausch + Lomb
- Menicon Co., Ltd.
- SEED Co., Ltd.
- Alcon (Novartis)
- Tokai Optical Co., Ltd.
- Alpha Corporation Inc.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview
By Product Type
- Spectacle Lenses
- Contact Lenses
By Lens Type
- Multifocal Lens
- Orthokeratology Lens
- Dual Focus Lens
- Peripheral Defocus Lenses
By Material
- Soft Contact Lenses (Silicone Hydrogel, Hydrogel)
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses
- Polycarbonate & High-Index Plastic (for Spectacle Lenses)
By Age Group
- Children
- Adults
By Sales Channel
- Eyeglass Clinic
- Eyewear Retailers
- Online Retail

View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA03251252 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA03251252 | Delivery: Immediate Access 
.svg)





