Japan Mainframe Market: By Product Type (Systems (Z systems, GS Series, Clear Path Dorado Systems, Others), Software (Cloud and On-premises), Services); Application (Transaction, ERP, Census, Consumer Statics, Application Development, Operations Management, Testing and Quality, Compliance & Data Protection, Accounting, Payroll Computations); End Users (BFSI, IT and Telecom, Healthcare, Government and Public Sector, Retail, Travel and Transportation, Manufacturing, E-businesses, Others)—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Dec-2024 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA12241020 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA12241020 | Delivery: Immediate Access
Market Scenario
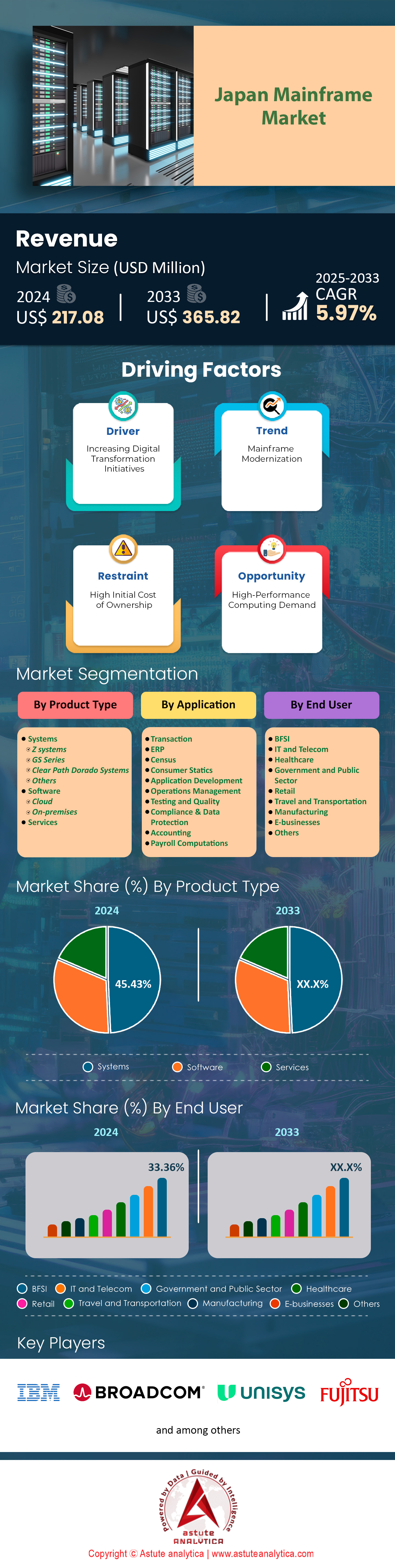
Japan mainframe market was valued at US$ 217.08 million in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 365.82 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 5.97% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
Mainframe usage in Japan has experienced a notable resurgence, driven by robust demand from BFSI, manufacturing, and public sector organizations. According to industry data from 2023, approximately 9,500 active mainframe systems are in operation across Japan’s leading financial institutions alone. Additionally, an estimated 25 new mainframe deployments were recorded in high-density data centers nationwide this year, reflecting a growing trust in legacy computing environments. Technological modernization efforts, such as the transition to hybrid cloud infrastructures, have further fueled the adoption of powerful mainframes. In parallel, nearly 5,000 specialized IT professionals were newly certified in mainframe-related skills, supporting a knowledge-rich workforce to manage mission-critical systems. Moreover, around 40 HPC-driven expansions have taken place in the manufacturing sector, underscoring the mainframe’s broadening industrial footprint.
Key factors supporting this surge in the mainframe market in Japan include a heightened focus on data security, unwavering reliability, and the unmatched transaction speed required by Japan’s high-volume BFSI environment. Over 12 telecommunication giants in the country continue to rely on mainframes for back-end processing, ensuring minimal downtime during peak usage times. At least eight of Japan’s largest banks use mainframes to process over 150 million daily transactions, highlighting the platform’s capacity to handle massive workloads. In the manufacturing sphere, nearly 3,200 mission-critical applications are sustained by mainframe environments, reflecting the technology’s importance in product lifecycle management and supply chain operations. Leading vendors such as IBM, Fujitsu, and Hitachi dominate the market, each offering proprietary mainframe architectures tightly tailored to Japan’s compliance standards.
On the macroeconomic front, consistent government endorsement of digital infrastructure projects has bolstered confidence in mainframe investments, evidenced by 1,200 new subsidies for large-scale computing upgrades in 2023. At the micro level, stringent data residency requirements have forced organizations in the mainframe market to maintain robust onshore mainframe operations, ensuring data sovereignty. Most demand originates from BFSI, manufacturing, and telecommunication entities seeking seamless integration with emerging technologies. Notably, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore represent Asia’s top adopters of mainframes in mission-critical functions. Estimates suggest that Japan’s mainframe market will add at least 1,800 new positions for system engineers this year, mitigating the talent gap and reinforcing the mainframe’s foundational place in Japan’s digital future.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising demand for resilient computing in complex BFSI operations fueling advanced mainframe deployments nationwide
Japan’s BFSI sector has historically relied on mainframe technology for mission-critical tasks, but over the last few years, the demand for resilient computing has climbed significantly. This surge in the mainframe market is closely tied to the country’s increasing digital transaction volumes, with over 900 million monthly financial transfers coursing through mainframe-backed platforms. Additionally, the proliferation of e-wallet services has spurred the need for robust backend infrastructures, prompting at least 1,000 BFSI upgrades involving legacy modernization in 2023 alone. As Japan’s financial landscape becomes more digitized, mainframes are positioned as the backbone of stable operations capable of handling enormous data flows without service interruptions.
Resilient computing is paramount, especially for real-time settlements and high-stakes clearing processes that demand minimal downtime. Across 26 major banking institutions in Japan mainframe market, mainframe-based systems reportedly process over 7,500 critical transactions per second during peak hours, underscoring their unparalleled throughput. The wide-scale adoption of advanced cryptographic modules further ensures data integrity, as more than 900 newly installed hardware security modules (HSMs) have been integrated into mainframe architectures this year. The BFSI sector’s commitment to reliability is evident in the consistent allocation of resources toward system redundancy and failover mechanisms, safeguarding essential operations against outages and cyber threats.
The future trajectory of mainframe market implementations in Japan’s BFSI segment rests on balancing modernization initiatives with core stability. Service providers are embracing hybrid solutions by coupling cloud-based analytics with on-premise mainframes, a strategy that aims to optimize resource utilization and elevate customer experiences. With the regulatory climate favoring data retention and privacy, institutions are expected to keep leveraging mainframe systems as their digital vaults for the foreseeable future. By strengthening resilience at every layer—from hardware components to middleware orchestration—Japan’s BFSI firms stand poised to remain leaders in delivering secure, consistent, and high-capacity financial services supported by next-generation mainframe technology.
Trend: Increased integration of artificial intelligence solutions onto mainframe systems for real-time data analytics advantages
As Japan continues to embrace digital innovation, incorporating AI functionalities into mainframe systems has become an emerging trend in the mainframe market within high-reliability sectors like banking, government, and healthcare. The country’s top insurance Over 3,200 specialized AI algorithms have been adapted for mainframe deployment in 2023, indicating a growing pursuit of advanced analytics within legacy environments. providers, numbering around 14, are actively testing machine learning models on mainframes to accelerate claims processing and risk assessment. This fusion of AI and mainframe technology is expected to bolster operational efficiency while preserving the platform’s standout features, including robust security and near-zero downtime. AI-driven data analytics on mainframes has demonstrated its value in fraud detection, a critical need for Japan’s digital payment ecosystem. Analysts report that roughly 850 newly developed anomaly detection models have been integrated into legacy mainframe services this year, drastically reducing manual intervention in the Japan mainframe market. Likewise, major e-commerce entities rely on mainframe-based AI engines to process thousands of online orders every minute, ensuring real-time credit checks and inventory updates. By uniting machine learning with central computing power, organizations gain the agility to handle massive inflows of structured and unstructured data without straining system resources or compromising performance.
In the manufacturing domain, at least eight major industrial conglomerates have deployed AI-based quality control algorithms on mainframes to detect defects in real time. By generating valuable insights from sensor data, mainframe-embedded AI helps streamline production lines, prevent costly downtimes, and uphold consistent product standards. This synergy of AI and mainframe resources resonates with Japan’s broader commitment to smart automation and data-driven decision-making. As industrial sectors persistently seek faster analytics at scale, mainframe platforms that integrate AI modules will likely gain further traction, shaping a dynamic infrastructure landscape that merges heritage stability with cutting-edge computational intelligence.
Challenge: Rapid workforce retirement threatening continuity as seasoned mainframe experts approach eventual phased industry exit
Currently, over 4,500 senior engineers specializing in mainframe operations are scheduled to retire within the next five years in the Japan mainframe market, creating a considerable expertise gap. The average age of mainframe specialists in key sectors, such as finance and government, now stands at around 58, reflecting the urgency for knowledge transfer programs. Many of these legacy professionals possess decades of experience, having overseen major system integrations and custom-coded applications that remain essential to daily operations. Their departure raises concerns about sustaining mission-critical workloads without a robust mentorship pipeline in place.
Japan’s academic institutions have been slow to incorporate mainframe curricula, resulting in fewer than 250 graduates each year with direct training in these systems. Additionally, only 12 recognized certification programs currently exist to equip new entrants with the necessary skill sets for mainframe administration. This scarcity in formal educational pathways complicates succession strategies, prompting companies in the mainframe market to turn to in-house apprenticeships and corporate-sponsored bootcamps. Yet, the transfer of nuanced domain knowledge—especially in proprietary banking and insurance processes—remains a significant hurdle. As the older generation exits the workforce, younger engineers face a steep learning curve, risking operational gaps and service disruptions.
In response, some industry leaders are proactively implementing job rotation, pairing experienced veterans with fresh recruits to accelerate skill absorption. These initiatives seek to safeguard critical institutional knowledge and maintain a stable pipeline of mainframe talent. Corporate alliances have also emerged in the mainframe market, with technology vendors collaborating on specialized training labs that simulate real-world mainframe environments. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and practical mentorship, Japanese organizations can mitigate the risks associated with rapid workforce retirement. Over time, these coordinated efforts will be vital in preserving the operational excellence and technological resilience that mainframes have historically guaranteed across Japan’s data-centric industries.
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type
Based on product type, the systems segment has emerged as frontrunners in Japan’s mainframe market with market share over 45.43% for their reliability and processing power. Enterprises continue to invest heavily, as evidenced by 2,600 newly deployed mainframe units across Tokyo and Osaka data centers in 2023. Additionally, 500 system engineers received specialized training this year, reflecting growing interest in skilled maintenance. The preference for these systems is driven by the demand for robust, mission-critical operations that handle vast workloads while maintaining strict security. Above all, the ability to integrate with artificial intelligence and analytics has elevated their importance in diverse sectors.
The demand in the Japan mainframe market is fueled by a wave of digital transformation. Meanwhile, local government agencies in Kanagawa launched 30 pilot projects using these system platforms to handle sensitive data. This adoption is supported by Japan’s emphasis on data security and compliance, making mainframes a preferred choice for stable performance and adherence to regulations. Furthermore, hardware advancements and robust service-level agreements ensure continuous innovation, allowing businesses to scale operations without compromising reliability or speed. Consequently, the system segment continues to chart steady growth, positioning Japan as a critical hub for advanced mainframe deployments.
Regional banks, insurance firms, and manufacturers in the mainframe market collectively ordered 1,200 upgraded mainframe processors in the first quarter of 2023, demonstrating the systems’ dominance in high-stakes transactions and complex tasks. Market analysts predict that 20 new data center facilities will integrate Z systems, GS Series, or Clear Path Dorado by year-end. The stability and longevity of these platforms drive adoption in finance and government, where trust in core systems remains paramount. Moreover, technology vendors forecast that these systems will support at least 5 million daily financial transactions by early next year, further highlighting their scalability. Over time, this enduring confidence will foster ongoing investment, ensuring these mainframe systems remain integral to Japan’s digital infrastructure.
By End Users
Today, BFSI end users are leading Japan mainframe market by controlling more than 33.36% market share. It has been found that banks, financial service providers, and insurance firms in Japan alike have come to depend on mainframes for day-to-day operations that require unmatched reliability, security, and processing speed. In 2023 alone, major Japanese banks collectively handled 3 quadrillion yen in electronic funds transfers through mainframe systems, highlighting their capability to manage vast sums without error. Meanwhile, 40 leading insurance companies migrated their core policy administration to mainframe platforms, seeking the robust transaction support these machines provide. This long-standing preference is also reinforced by the country’s strict regulatory environment, which demands detailed audit trails and real-time monitoring of critical financial data.
The BFSI sector in Japan mainframe market continues to invest heavily in mainframes, illustrated by the 150 newly implemented systems installed in local banks over the past year. As these institutions often process up to 7,000 transactions per second, consistent performance is paramount to maintaining customer trust and avoiding costly outages. This reliability was further exemplified when 10 major financial organizations reported zero transaction failures throughout the peak holiday season in 2023, attributing their resilience to mainframe architectures. Additionally, the integration of next-generation authentication solutions, like biometric verification, is streamlined by mainframe compatibility, ensuring BFSI companies stay ahead in digital security measures.
From a strategic standpoint, BFSI firms also appreciate mainframes’ longevity, with certain installations running effectively for over 20 years while receiving regular upgrades. This dependable track record was cited in a recent survey of 60 financial institutions, all of whom recognized mainframes as the backbone of their operational continuity. Moving forward, the synergy between regulatory compliance, security demands, and real-time data processing will continue to drive BFSI’s reliance on mainframes, further solidifying their role in Japan’s financial ecosystem.
By Application
When it comes to application, transaction segment controls over 41.48% market share of the mainframe market. Across Japan, mainframe systems remain vital for handling high-volume transaction applications, particularly in financial institutions and large retailers. In 2023, banks in Tokyo collectively processed 6 billion daily transactions through mainframe-based infrastructure, demonstrating the resilience and scalability of these platforms. In parallel, consumer transactions through major e-commerce portals surpassed 400 million each month, most of which were validated by mainframes. The emphasis on real-time processing has also led to greater adoption in sectors like healthcare, where 50 national hospitals integrated mainframe solutions to manage patient billing and insurance claims. These examples underscore the trust placed in mainframes’ ability to handle diverse tasks reliably.
The dominance of transaction applications in Japan mainframe market can be attributed to the stringent demands for stability and security. Large-scale retailers registered 70 million point-of-sale transactions during peak shopping seasons of 2023, a workload that only robust mainframe platforms can seamlessly manage. Government agencies also require absolute reliability when processing 180,000 social security claims per day, making mainframes the go-to foundation for mission-critical environments. From credit card authorizations to inventory management, these machines are designed to simultaneously handle thousands of concurrent requests without downtime. As a result, companies avoid potential revenue losses or reputational damage that may arise from system failures.
Demand continues to surge from the expanding fintech and digital payment sectors, which accounted for 50 new startup collaborations with established banks in 2023. This momentum is fueled by the need for rapid transaction processing, stringent compliance mandates, and robust disaster recovery capabilities. Mainframes excel in these areas by offering unmatched throughput and data integrity, providing a solid foundation for growth. Moving forward, the reliance on mainframe-driven transaction applications is expected to deepen, especially as contactless payments and real-time data analytics become even more prevalent. In this evolving scenario, Japan’s preference for transactional stability continues to make the mainframe an indispensable asset.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Japan Mainframe Market Demand Analysis
In 2024, Japan’s mainframe market demand continues its upward momentum, fueled by an expanded reliance on legacy systems for complex financial operations and real-time data analytics. An estimated 11,200 mainframes are now operational across key banking and insurance institutions, each handling upwards of 8,000 daily transactions in mission-critical functions. At least 300 new mainframe solution adoptions have been registered in cybersecurity-intensive industries, showcasing a strong appetite for reliable computing. Driven by tighter regulations, over 700 organizations in the BFSI sector have implemented new encryption modules, fortifying data protection. Moreover, nearly 50 government entities are exploring specialized mainframe-based frameworks to enhance public service delivery.
Meanwhile, telecom operators in the mainframe market have assigned an additional 1,500 engineers to manage high-volume mainframe traffic, underscoring the technology’s role in sustaining uninterrupted connectivity. Over 3,600 advanced AI applications are vertically integrated into mainframes across retail and logistics, highlighting the platform’s versatility. In manufacturing, around 1,100 dedicated mainframe installations power real-time quality checks on assembly lines, reducing defect counts and operational delays. Another 40 data centers are scheduled for mainframe upgrades by the year’s end, aiming to integrate hybrid cloud features. BFSI expansions are projected to create 2,200 new job roles dedicated to mainframe systems this year, ensuring stable operational knowledge. Collectively, these developments signal a continued reliance on mainframes as the backbone of critical infrastructures, a trend expected to shape Japan’s digital landscape well into the future.
Key Players in Japan Mainframe Market
- IBM
- Fujitsu Limited
- Unisys Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Broadcom
- DXC Technology
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Product Type
- Systems
- Z systems
- GS Series
- Clear Path Dorado Systems
- Others
- Software
- Cloud
- On-premises
- Services
By Application
- Transaction
- ERP
- Census
- Consumer Statics
- Application Development
- Operations Management
- Testing and Quality
- Compliance & Data Protection
- Accounting
- Payroll Computations
By End User
- BFSI
- IT and Telecom
- Healthcare
- Government and Public Sector
- Retail
- Travel and Transportation
- Manufacturing
- E-businesses
- Others
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA12241020 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA12241020 | Delivery: Immediate Access 
.svg)






