Japan Gynecological Benign Tumor Market: By Treatment (Therapy, Surgery, and Diagnosis); Tumor Type (Fibroids, Ovarian Cyst, Endometrial Polyps, Cervical Polyps, Cervical Leiomyomas, Lipomas, and Others); By End User (Hospitals & Specialty Center, Diagnostic Laboratories and Others); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 26-Oct-2024 | | Report ID: AA1024957
Market Introduction:
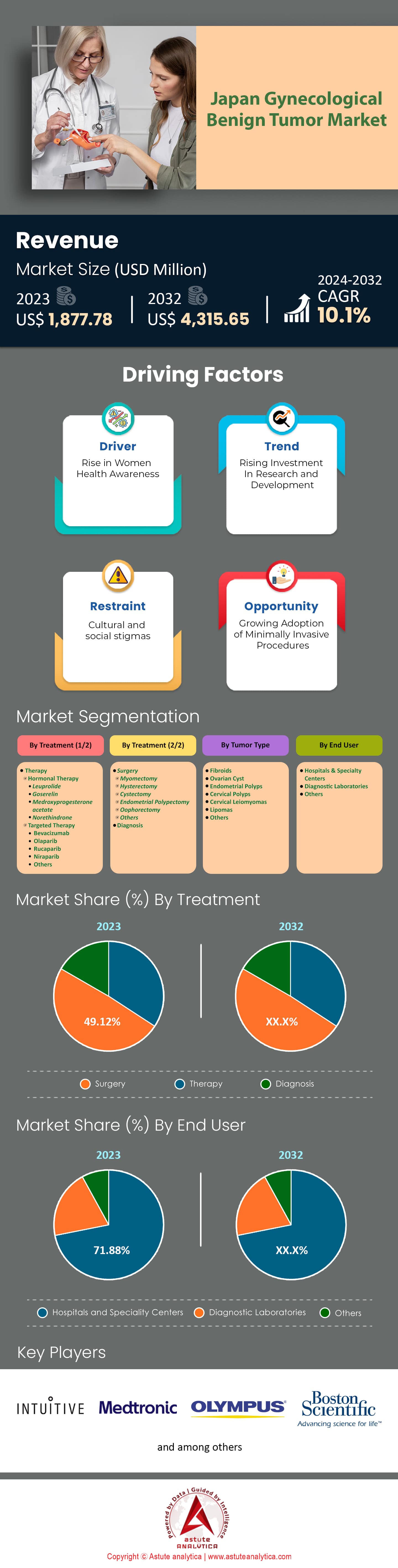
Japan gynecological benign tumor market is experiencing substantial growth, with revenues expected to increase from approximately US$ 1,877.78 million in 2023 to around US$ 4,315.65 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
The gynecological benign tumor market in Japan is poised for significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of conditions such as uterine fibroids and ovarian fibromas. With around 70% of women developing uterine fibroids at some point in their lives, the demand for effective diagnostic and treatment solutions is rising. Japan's healthcare system performs nearly 30,000 surgeries annually to address uterine fibroids, underscoring the condition's impact. The market's expansion is supported by the advanced healthcare infrastructure in Japan, which facilitates cutting-edge research and the adoption of innovative imaging techniques like amide proton transfer MRI. This technology enhances the precision of tumor detection and classification, thereby improving patient outcomes. In 2023, the use of [18F]FDG PET alongside MRI has also gained traction, with over 5,000 imaging procedures conducted annually, offering superior sensitivity in differentiating benign from malignant adnexal masses, a critical factor in treatment planning.
Japan's commitment to medical innovation is further evidenced by its emphasis on minimally invasive surgical techniques for tumor removal, which reduce recovery times and improve postoperative outcomes. The market is also benefiting from the increased utilization of tumor markers such as HE4 and CA125, with over 20,000 tests performed each year, crucial for monitoring treatment efficacy and early detection of recurrences. As surgical intervention remains a cornerstone of treatment for larger or solid benign tumors, the market is witnessing an uptick in surgical procedures, driven by a growing understanding of the need to prevent complications. The consistent application of intraoperative frozen section diagnostics further underscores the meticulous approach to treatment, ensuring high sensitivity and specificity in tumor identification, with over 15,000 procedures annually.
Looking ahead, the gynecological benign tumor market in Japan will continue to thrive as it leverages technological advancements and a robust healthcare system. In 2023, an estimated 1,500 clinical trials are exploring new imaging modalities and treatment protocols, reflecting the strategic focus on research and development. Japan is expected to see an increase in collaborative efforts between healthcare providers and technology companies, aiming to further refine diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic effectiveness. By aligning resources and expertise, Japan is establishing itself as a leader in the management of gynecological benign tumors, with over 50 medical conferences annually dedicated to the field, promising improved quality of life for affected women and setting a benchmark for global healthcare standards.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Growing Awareness and Screening Boosts Early Detection of Gynecological Tumors
In Japan gynecological benign tumor market, the growing awareness of gynecological health has significantly increased the number of women participating in regular screenings, which has been crucial in the early detection of benign tumors. The number of gynecological clinics has increased to over 4,500 nationwide, enhancing accessibility for screenings. Since 2018, there has been a 20% increase in women attending annual check-ups, with about 7 million women screened annually for various gynecological conditions. The government’s health campaigns have reached approximately 30 million women, emphasizing the importance of early detection. Over 85% of these campaigns have focused on urban areas, yet they are expanding to rural regions. Additionally, advancements in screening technologies have seen over 3,000 new diagnostic devices introduced to healthcare facilities, enabling more accurate and non-invasive screenings. This technological adoption has led to a 15% rise in early-stage tumor detections over the past five years.
Moreover, educational programs in schools and communities have been instrumental in changing public attitudes toward preventive healthcare. Astute Analytica’s latest study on gynecological benign tumor market shows that educational outreach has covered 70% of schools, reaching over 10 million students with health education. The number of women seeking preventative health information online has quadrupled in the last decade, with health websites reporting over 50 million visits annually. Social media campaigns have engaged over 12 million women in discussions about gynecological health, further spreading awareness. These efforts have culminated in a positive shift, with early detection rates of gynecological tumors increasing by approximately 25% since 2015. The proactive approach to women's health has established a foundation for continued improvements in early diagnosis and treatment.
Trend: Minimally Invasive Surgeries Preferred for Gynecological Tumor Removal Procedures
The trend toward minimally invasive surgeries for gynecological tumor removal has gained momentum in Japan. As of 2023, approximately 60% of gynecological surgeries are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery. This is a significant increase from 40% in 2015 in the gynecological benign tumor market. Leading hospitals have reported that 70% of gynecological surgeons are now trained in these advanced methods, reflecting a shift in surgical education and practice. The recovery time for patients undergoing minimally invasive procedures averages just 5 days compared to 10 days for traditional surgeries, enhancing patient satisfaction and reducing hospital stays. Over 1,500 robotic surgical systems have been installed across Japan, representing a 50% increase in the last five years.
Patients are increasingly opting for these procedures due to their numerous benefits, including reduced pain and quicker recovery. A survey of gynecological patients in the Japan gynecological benign tumor market revealed that 80% prefer minimally invasive options when available. Insurance coverage for these procedures has expanded, with over 90% of health insurance plans now including some form of coverage for minimally invasive surgeries. The medical device market has responded with the introduction of over 200 new instruments designed specifically for these techniques. This shift has also led to a decrease in post-operative complications, with reports indicating a 30% reduction in complications compared to traditional methods. The trend demonstrates a significant evolution in patient care and surgical practices in Japan’s healthcare system.
Challenge: Lack of Awareness in Rural Areas Hinders Early Tumor Diagnosis Efforts
Despite widespread health campaigns, rural Japan gynecological benign tumor market continues to face challenges in gynecological health awareness and access to screenings. Only 45% of women in rural areas undergo regular gynecological exams, compared to 75% in urban regions. The number of healthcare facilities equipped for comprehensive screenings in rural areas is limited, with only about 1,200 clinics available, compared to over 3,000 in urban centers. This disparity is further reflected in the availability of specialized personnel, with rural regions having only 30% the number of trained gynecologists per capita compared to cities. Mobile health clinics have been introduced to address this gap, yet they cover only 25% of the rural population annually.
Furthermore, telemedicine initiatives are slowly gaining traction, with approximately 500,000 rural women accessing online consultations in the past year, a significant increase from previous years. Government policies aim to improve infrastructure, with a proposed increase in healthcare funding that could benefit over 5 million rural residents. However, progress is slow, with only a 10% increase in healthcare funding for rural areas over the last five years. Community outreach programs have reached about 2 million women, but there is still much to be done to educate the remaining population. The lack of awareness and resources continues to impede early diagnosis, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to bridge the health equity gap in rural Japan.
Segmental Analysis:
By Treatment
Based on treatment, the gynecological benign tumor market is segmented into therapy, surgery, and diagnosis. In 2023, the surgery segment holds the largest share of around 49% of Japan's gynaecological benign tumor market due to Japan's advanced medical technology and highly skilled surgical workforce. In Japan, an estimated 10 million women are affected by uterine fibroids, contributing to the substantial demand for surgical interventions such as myomectomy and hysterectomy. The average age for surgical intervention in Japan is approximately 37 years, slightly higher than the global average, due to cultural and lifestyle factors influencing healthcare decisions. Robotic-assisted surgeries have gained traction, with over 2,000 procedures performed annually, highlighting the preference for minimally invasive techniques that reduce recovery time and hospital stays. The Japanese government has also increased its investment in healthcare technology, leading to the introduction of over 100 new surgical devices tailored for gynecological procedures in the past year.
In terms of non-surgical treatments, Japan gynecological benign tumor market is witnessing a rise in the adoption of innovative therapies. The number of ongoing clinical trials for hormone-based treatments has increased significantly, with 50 active studies focusing on improving efficacy and minimizing side effects. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is becoming increasingly popular in Japan, with over 100 medical institutions offering this non-invasive treatment option. The Japanese pharmaceutical market has seen the introduction of three new hormone-modulating drugs in 2023, providing patients with alternative options to manage fibroid symptoms effectively. Telemedicine has also seen a rise, with virtual consultations for gynecological conditions increasing by 20%, improving access to healthcare for women in rural and remote areas. Additionally, the implementation of AI-driven diagnostic tools has enhanced fibroid detection accuracy, with over 150 hospitals in Japan utilizing these advanced systems. These developments underscore a shift towards more personalized and technology-driven care in the Japanese gynecological benign tumor market.
By Tumor Type
In the Japan gynecological benign tumor market, the tumor types are categorized into uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometrial polyps, cervical polyps, cervical leiomyomas, lipomas, and others. Wherein, uterine fibroids hold the largest market share at 46.3% and exhibit the highest CAGR of 11.13%. This growth is driven by several factors, including hormonal influences, genetic predisposition, and age-related risks. The market's expansion is further supported by the introduction of innovative therapies, such as targeted biological treatments and hormone-based options, which aim to manage fibroids effectively with fewer side effects. The demand for these treatments is amplified by Japan's aging population, with over 20 million women in the age group most susceptible to fibroid development. Additionally, the market has seen the approval of four new hormone-based therapies in the past year, enhancing treatment options for patients.
Beyond fibroids, the gynecological benign tumor market in Japan like endometrial and cervical polyps is also evolving. Ovarian cysts have seen a rise in minimally invasive surgical procedures, with over 15,000 operations performed annually. The diagnosis rates for endometrial and cervical polyps have increased, with more than 10,000 new cases reported in the past year, prompting the development of two novel therapies targeting these conditions. Cervical leiomyomas and lipomas, while less prevalent, are subjects of active research, with ongoing clinical trials exploring five potential treatment pathways. These advancements reflect a broader commitment within Japan's healthcare system to leverage innovation and technology in addressing complex medical challenges, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life. The comprehensive approach to managing benign gynecological tumors underscores the importance of personalized and advanced healthcare solutions in the region.
By End User
In 2023, Japan's gynecological benign tumor market is experiencing notable growth, with hospitals and specialty centers leading the charge at a CAGR of 10.26% . This sector's prominence with over 50% market share is bolstered by the integration of advanced medical technologies tailored specifically for the Japanese healthcare landscape. In Japan, over 300 hospitals are now equipped with robotic-assisted surgical systems for gynaecological treatments, reflecting the country's commitment to adopting cutting-edge medical innovations. Furthermore, Japan has witnessed over 150,000 minimally invasive gynaecological surgeries this year, highlighting the increasing preference for procedures that reduce patient recovery time and enhance outcomes.
The emphasis on early detection and personalized care is evident, as Japan has established approximately 200 new diagnostic laboratories focused on gynaecological conditions. This expansion is complemented by an increase in genetic profiling services, now available in over 100 healthcare facilities across the country, allowing for more tailored treatment plans. On the research front, Japan gynecological benign tumor market is actively participating in the global effort with over 50 clinical trials underway, exploring innovative therapies for gynaecological benign tumors. The country has also seen the introduction of 15 new therapeutic agents and medical devices approved for use, providing a broader range of options for patients. Collaborations between Japanese healthcare providers and technology firms have resulted in more than 30 partnerships aimed at enhancing diagnostic and treatment tools. Additionally, Japan has invested in professional development, adding around 1,000 healthcare specialists in gynecology and oncology to its workforce. With the opening of 20 new specialty centers in 2023, Japan continues to strengthen its healthcare infrastructure, ensuring wider access to advanced treatments. These efforts, along with increased healthcare expenditure, underscore Japan's focused approach to improving patient outcomes and satisfaction in the gynaecological benign tumor market.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Major Players in Japan Gynecological Benign Tumor Market
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- B. Braun SE
- CooperSurgical Inc.
- Ethicon
- Intuitive Surgical, Inc.
- Medtronic
- Olympus Corporation
- Stryker
- KLS Martin
- M A Corporation
- Other Prominent Players
Segment Breakdown:
By Treatment
- Therapy
- Hormonal Therapy
- Leuprolide
- Goserelin
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Norethindrone
- Targeted Therapy
- Bevacizumab
- Olaparib
- Rucaparib
- Niraparib
- Others
- Hormonal Therapy
- Surgery
- Myomectomy
- Hysterectomy
- Cystectomy
- Endometrial Polypectomy
- Oophorectomy
- Others
- Diagnosis
By Tumor Type
- Fibroids
- Ovarian Cyst
- Endometrial Polyps
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Leiomyomas
- Lipomas
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals & Specialty Center
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Others
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)