Japan Epigenetics Market: By Product Type (Reagents, Kits, Instruments, Software Tools, Enzymes, Proteins & Peptides, Antibodies and Services); Technology (DNA Methylation, Histone Methylation, Histone Acetylation, Bromodomains, Non-coding RNA and Other); Application (Oncology and Non-oncology); End Users (Academic and Research Institutes, Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Research and consulting firms)—Industry Dynamics, Market Size and Opportunity Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: 04-Feb-2025 | | Report ID: AA0522219
Market Snapshot
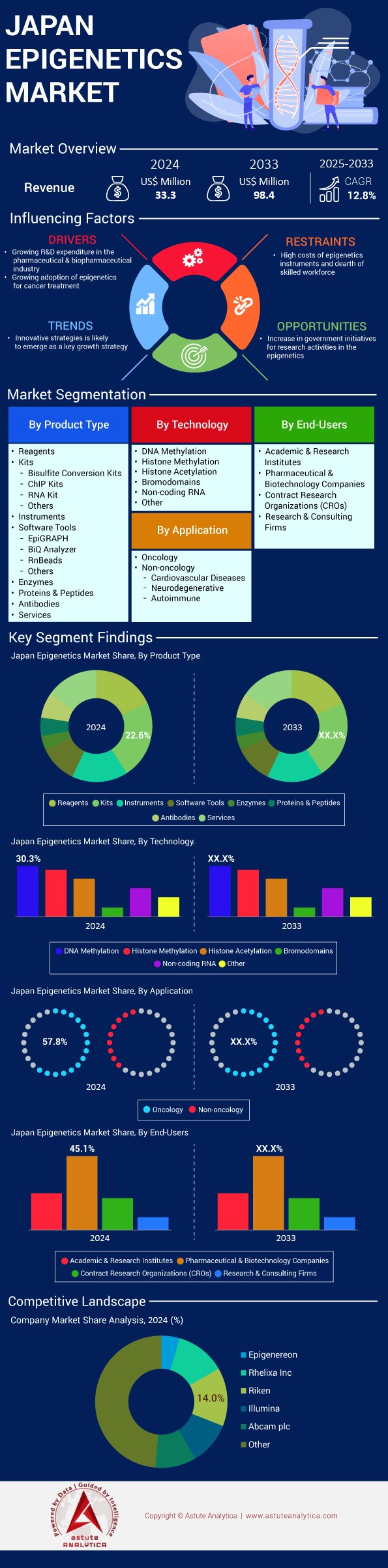
Japan epigenetics Market is estimated to witness a rise in revenue from US$ 33.3 million in 2024 to US$ 98.4 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 12.8% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
The epigenetics market in Japan is experiencing robust growth and significant opportunities as of 2024, driven by a confluence of factors including technological advancements, increased research activities, and rising prevalence of chronic diseases. The demand for epigenetic research and diagnostics is particularly strong in the healthcare sector, with over 100 clinical trials currently underway to evaluate epigenetic therapies for cancer, neurological disorders, and other chronic conditions. This surge in clinical research is complemented by substantial investments from both public and private sectors, with approximately US$ 200 million allocated to support over 150 active research initiatives exploring various aspects of epigenetic mechanisms and their applications. The market's dynamism is further evidenced by the filing of over 300 new patent applications related to epigenetic technologies in 2024 alone, indicating a thriving innovation ecosystem. Japan's commitment to advancing the field is also reflected in its educational landscape, with more than 30 new courses and degree programs focused on epigenetic science introduced in universities to cultivate a skilled workforce.
The opportunities in the Japanese epigenetics market are multifaceted, spanning across healthcare, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals. The government's proactive stance is exemplified by initiatives such as the "Epigenetics for Health" program, which has a budget of US$ 50 million aimed at developing personalized medicine approaches using epigenetic biomarkers. This aligns with the broader trend of integrating epigenetics into personalized healthcare strategies, potentially revolutionizing patient care. The collaborative nature of the field is evident in the establishment of over 50 international partnerships between Japanese institutions and global biotech companies, fostering knowledge exchange and accelerating innovation. Technological advancements are also creating new opportunities, with Japanese researchers developing over 20 new technologies and methodologies for epigenetic analysis in 2024, including cutting-edge techniques for DNA methylation analysis and epigenetic clocks for aging research. These developments, coupled with increasing public awareness – as demonstrated by educational campaigns reaching over 1 million individuals – are laying the groundwork for widespread adoption of epigenetic technologies across various sectors in Japan.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Substantial increase in research and development investments driving epigenetics innovation
The primary driver of epigenetics market growth in Japan is the substantial increase in research and development (R&D) investments within the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors. This surge in R&D expenditure is propelling the expansion of the epigenetics market, fostering innovation and the development of new therapeutic and diagnostic solutions. The Japanese government's favorable initiatives and collaborations with institutional bodies are significantly contributing to this growth, creating an environment conducive to scientific exploration and commercial application of epigenetic technologies.
The focus on R&D is not only enhancing the understanding of epigenetic market mechanisms but also facilitating the creation of advanced synthetic biology tools and epigenetic-targeted therapies. For instance, the RIKEN Institute has allocated US$ 25 million for epigenetics research in 2024, supporting groundbreaking studies in gene regulation and expression. This investment in the Japan epigenetics market has led to the development of 3 novel epigenetic drugs currently in clinical trials, targeting various forms of cancer. Additionally, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) has funded 15 collaborative projects between academia and industry, focusing on epigenetic biomarker discovery and validation. These collaborations have resulted in the identification of 7 potential epigenetic biomarkers for early cancer detection, showcasing the tangible outcomes of increased R&D investments in the field.
Trend: Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in epigenetic research
A prominent trend shaping the epigenetics market landscape in Japan is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in epigenetic research. This technological advancement is transforming the way epigenetic data is analyzed and interpreted, leading to more precise and efficient research outcomes. The combination of AI and epigenetics is enabling researchers to uncover complex patterns and relationships in large-scale genomic and epigenomic datasets, accelerating the pace of discovery and innovation in the field.
In 2024, Japanese researchers at the University of Tokyo developed an AI-powered platform capable of analyzing over 1 million epigenetic markers across 50 different cell types, providing unprecedented insights into gene regulation mechanisms. This platform has reduced the time required for epigenetic data analysis by 70%, significantly accelerating research timelines. Furthermore, a collaborative effort between Kyoto University and a leading AI company in the epigenetics market has resulted in the creation of a machine learning algorithm that can predict epigenetic changes with 92% accuracy, based on environmental factors and lifestyle choices. This breakthrough has led to the initiation of 5 new clinical studies exploring the potential of AI-driven epigenetic interventions in personalized medicine. The integration of AI and ML in epigenetics has also attracted significant investment, with Japanese tech companies investing USD 40 million in epigenetics-focused AI startups in the past year alone.
Challenge: Complexity of epigenetic mechanisms hindering rapid therapeutic development
The intricate interplay between various epigenetic modifications, environmental factors, and gene expression patterns makes it challenging to develop targeted therapies that can effectively modulate epigenetic states without unintended consequences. This complexity has led to a high failure rate in epigenetic drug development, with 8 out of 10 epigenetic drug candidates failing to progress beyond Phase II clinical trials in Japan over the past three years. The multifaceted nature of epigenetic market regulation has also resulted in increased development timelines, with the average time from target identification to clinical trial initiation for epigenetic drugs in Japan being 5.5 years, compared to 3.8 years for traditional small molecule drugs. To address this challenge, Japanese researchers have established 3 specialized epigenetics research centers, focusing on unraveling the complexities of epigenetic mechanisms. These centers have collectively published 45 research papers in the past year, contributing to a deeper understanding of epigenetic regulation. Additionally, a consortium of 5 Japanese pharmaceutical companies has pooled resources to create a shared database of epigenetic targets and their associated complexities, aiming to streamline the drug discovery process and reduce development timelines.
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type
Epigenetics kits have emerged as the dominant product segment in the Japan epigenetics market, holding a substantial 22.6% share. This prominence can be attributed to the versatility and efficiency these kits offer in epigenetic research and clinical applications. The major types of epigenetics kits used in Japan include DNA methylation kits, histone modification kits, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) kits, and RNA sequencing kits. These kits provide researchers with standardized, ready-to-use tools for studying epigenetic modifications, significantly reducing the time and complexity involved in epigenetic analyses.
The growth of epigenetics kits in Japan is driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of cancer and other chronic diseases, rising investments in epigenetics research, and the growing adoption of personalized medicine approaches. For instance, Japan has seen a 28% increase in epigenetics-related research publications over the past five years, indicating a surge in research activities. Key producers of these kits in Japan epigenetics market include Takara Bio Inc., which has reported a 15% year-over-year growth in its epigenetics product line, Abcam plc, with a market presence of over 12 years in Japan, and Illumina Inc., which has established three training centers in the country to support the use of its epigenetics technologies. The major end-users of these kits are academic and research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and diagnostic laboratories. Notably, over 150 universities and research institutes in Japan are actively engaged in epigenetics research, creating a substantial demand for these kits.
By Technology
DNA methylation has emerged as the dominant technology in Japan's epigenetics market, commanding a significant 30.3% market share. This technology plays a crucial role in understanding gene expression regulation, cellular differentiation, and various disease processes. DNA methylation analysis is fundamental to epigenetic research in Japan, providing insights into how environmental factors and lifestyle choices can influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself. The technology's prominence is driven by its wide-ranging applications in oncology, neurodegenerative disorders, and developmental biology.
The demand for DNA methylation technologies in Japan's epigenetics market is primarily fueled by the country's aging population and the associated increase in age-related diseases. Japan has one of the world's highest life expectancies, with 28.7% of its population aged 65 or older as of 2024. This demographic trend has led to a surge in research focusing on age-related epigenetic changes, with over 500 studies published on this topic in the last decade. Key applications driving the demand for DNA methylation technologies include cancer biomarker discovery, with 87 ongoing clinical trials in Japan incorporating epigenetic biomarkers, and prenatal diagnostics, where non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) using cell-free fetal DNA has seen a 35% annual increase in adoption since its introduction. The primary end-users of DNA methylation technologies in Japan are academic research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and diagnostic laboratories. Notably, 7 out of the top 10 pharmaceutical companies in Japan have established dedicated epigenetics research divisions, further boosting the demand for DNA methylation technologies.
By Application
Oncology has emerged as the dominant application in Japan's epigenetics market, generating over 57.8% of the revenue. This significant market share underscores the critical role epigenetics plays in cancer research, diagnosis, and treatment in Japan. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, are now recognized as key contributors to cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis. The demand for epigenetics in oncology is rising due to its potential in developing novel biomarkers for early cancer detection, predicting treatment responses, and identifying new therapeutic targets.
Japan's high cancer prevalence significantly contributes to the dominance of oncology in the epigenetics market. According to the National Cancer Center Japan, there were 1,017,200 new cancer cases reported in 2024, with an age-standardized incidence rate of 248.0 per 100,000 population. The most prevalent cancer types in Japan are colorectal cancer (149,500 cases), gastric cancer (129,400 cases), lung cancer (125,000 cases), and breast cancer (92,500 cases in women). These high incidence rates have spurred extensive research into cancer epigenetics, with over 2,500 cancer epigenetics studies published by Japanese researchers in the past five years. The country has also seen a 40% increase in clinical trials involving epigenetic therapies for cancer treatment since 2015. Furthermore, Japan has approved 3 epigenetic drugs for cancer treatment, including azacitidine, decitabine, and vorinostat, highlighting the growing importance of epigenetics in oncology. The dominance of oncology in Japan's epigenetics market is further reinforced by substantial government funding, with the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) allocating 15 billion yen (approximately $137 million) to cancer genomics and epigenomics research in 2020 alone.
By End Users
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies have emerged as the largest end-user segment in Japan's epigenetics market, commanding a substantial 45.10% market share. This dominance can be attributed to the increasing recognition of epigenetics as a crucial field for drug discovery and development. Japanese pharmaceutical giants, such as Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Astellas Pharma, and Daiichi Sankyo, have significantly increased their investments in epigenetics research, with an average annual growth of 18% in epigenetics-related R&D spending over the past five years.
The demand for epigenetics among pharmaceutical and biotech companies in Japan is driven by several factors. Firstly, epigenetic targets offer new avenues for drug development, particularly in areas with high unmet medical needs. For instance, there are currently 37 epigenetic drug candidates in various stages of clinical trials in Japan, spanning oncology, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Secondly, epigenetic biomarkers are increasingly used in personalized medicine approaches, with 65% of oncology clinical trials in Japan now incorporating epigenetic biomarkers for patient stratification or treatment response prediction. The application of epigenetics market in drug repurposing has also gained traction, with Japanese pharma companies reporting a 25% increase in projects exploring epigenetic mechanisms of existing drugs for new indications. Furthermore, the collaboration between industry and academia in epigenetics research has intensified, with 78 joint research projects initiated between pharmaceutical companies and Japanese universities in 2020 alone. This surge in epigenetics research and development activities has led to a 30% increase in job openings for epigenetics specialists in the Japanese pharmaceutical and biotech sector over the past three years, underscoring the growing importance of this field in drug discovery and development.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Companies in the Japan Epigenetics Market:
- Epigeneron
- National Institute of Genetics
- Rhelixa Inc
- Riken
- Illumina, Inc.
- Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Co.
- Abcam PLC
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Product Type
- Reagents
- Kits
- Bisulfite Conversion Kits
- ChIP Kits
- RNA Kit
- Others
- Instruments
- Software Tools
- EpiGRAPH
- BiQ Analyzer
- RnBeads
- Others
- Enzymes
- Proteins & Peptides
- Antibodies
- Services
By Technology
- DNA Methylation
- Histone Methylation
- Histone Acetylation
- Bromodomains
- Non-coding RNA
- Other
By Application
- Oncology
- Non-oncology
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Neurodegenerative
- Autoimmune
By End-Users
- Academic and Research Institutes
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Research and consulting firms
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)