Global Influenza Vaccine Market: By Type (Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) (Quadrivalent and Trivalent) and Live-attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)); Process (Egg Based, Cell Culture-Based, and Recombinant); Route of Administration (Injectable and Intra-nasal); Age Group (Pediatric and Adult); Distribution Channel (Hospitals & Pharmacies, Government Suppliers, and Others); Region— Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 11-Jan-2024 | | Report ID: AA0124744
Market Scenario
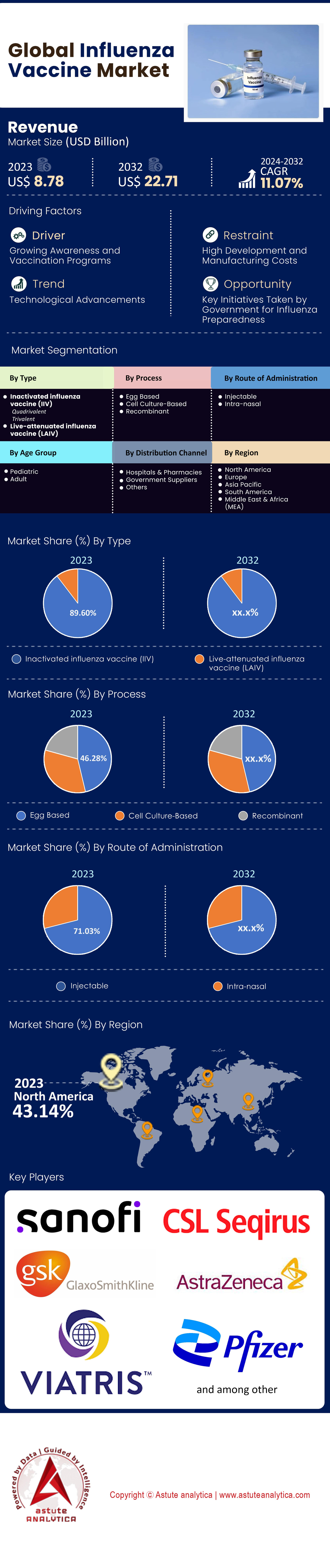
Global Influenza Vaccine Market was valued at US$ 8.78 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 22.71 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 11.07% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
The influenza vaccine market is influenced by a range of factors ranging from epidemiological trends to public health policies. In the 2022-2023 influenza season, the United States witnessed an estimated 9 million flu illnesses, 4 million flu-related medical visits, 100,000 hospitalizations, and 5,000 deaths, according to the CDC. This burden of disease underscores the significant demand for effective influenza vaccines. However, drawing direct comparisons with previous years poses challenges due to methodological differences in estimation and changes in the population's age distribution. The 2023-2024 season observed a notable decrease in flu vaccine doses administered in pharmacies and medical offices compared to the previous year. As of December 2023, there were 7.85 million fewer doses administered in these settings, indicative of a fluctuating vaccination uptake trend. This variation in vaccine administration rates is a critical factor for market stakeholders to monitor, as it directly influences vaccine supply and distribution strategies.
The effectiveness of the influenza vaccine market is a key aspect of market dynamics. Preliminary data suggests that the 2022-2023 flu vaccine was 68% effective against pediatric hospitalization, a statistic that plays a significant role in public perception and acceptance of the vaccine. The CDC's various Vaccine Effectiveness Networks, such as the US Flu VE Network and the VISION Vaccine Effectiveness Network, are instrumental in evaluating and communicating the vaccine's efficacy, thereby impacting public trust and vaccine uptake. Globally, influenza's impact is stark, with 99% of deaths in children under 5 years of age with influenza-related lower respiratory infections occurring in developing countries. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for enhanced vaccine accessibility and coverage in these regions, presenting a significant opportunity for market expansion and targeted public health initiatives.
Symptomatically, influenza presents with fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue, typically lasting about a week. However, in the 2022-2023 season, only 41.9% of U.S. children and adolescents had received their annual influenza vaccination by the end of November, compared to higher rates in previous years. This lower vaccination rate among hospitalized children, combined with the season's high severity, particularly for kids, indicates a potential market gap and an opportunity for increased vaccination campaigns.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Global Influenza Incidence
The influenza vaccine market is significantly driven by the increasing incidence of influenza cases worldwide. This surge is a consequence of factors like global travel, urbanization, and evolving virus strains, making influenza a ubiquitous threat. The World Health Organization estimates that annual influenza epidemics result in about 3 to 5 million cases of severe illness globally. In the United States alone, the 2019-2020 flu season saw an estimated 38 million cases, leading to 400,000 hospitalizations and 22,000 deaths. These staggering numbers highlight the escalating need for influenza vaccination.
The demographic spread of influenza also plays a crucial role in driving vaccine demand. Vulnerable populations, particularly children under 5, older adults, and those with chronic health conditions, are at higher risk. For instance, during the 2018-2019 flu season, about 34% of U.S. adults aged 50-64 and 68% of those aged 65 and above received the flu vaccine. Additionally, influenza-related hospitalization rates among children under 5 were 49.4 per 100,000 population in the U.S. during the 2017-2018 season. Compounding this is the increasing awareness and government initiatives promoting flu vaccinations. In many countries, health authorities have intensified their influenza vaccination campaigns, especially after the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, which saw over 60 million cases in the U.S. alone. Furthermore, the integration of influenza vaccines into routine immunization programs in several countries has bolstered the market.
The rising global incidence of influenza, coupled with heightened awareness and government action, thus forms a pivotal driver of the influenza vaccine market, underscoring the urgent and growing demand for effective influenza vaccination strategies worldwide.
Trend: Technological Advancements in Vaccine Development
The global influenza vaccine market is witnessing a significant trend: the rapid technological advancements in vaccine development. This shift is revolutionizing how vaccines are produced, with a move away from traditional egg-based production to cell culture and recombinant DNA technologies. Such advancements not only promise faster production times but also potentially greater vaccine effectiveness. One of the key statistics underscoring this trend is the investment in cell-based vaccine manufacturing. For instance, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services invested over $1 billion in 2019 for the development of cell-based influenza vaccine technology. This shift is crucial, considering the traditional egg-based vaccines take approximately six months to produce, a timeline not conducive to responding quickly to fast-mutating influenza viruses.
Recombinant technology, another frontier in influenza vaccine development, is also gaining traction. During the 2017-2018 flu season, the U.S. saw a 47% vaccine effectiveness rate with traditional vaccines, while the recombinant flu vaccine (Flublok) reported an effectiveness of about 53%. This higher effectiveness rate is a compelling argument for the increasing adoption of recombinant vaccines. Additionally, mRNA technology, which gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic, is being explored for influenza vaccines. The success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, with Pfizer-BioNTech's vaccine showing about 95% effectiveness, has opened new avenues for similar technology in flu vaccines.
The market is witnessing a paradigm shift with these technological advancements, offering potential for more effective, rapidly produced vaccines, thus setting a prominent trend in the global influenza vaccine market.
Restrain: Vaccine Hesitancy is A Major Restraint in the Influenza Vaccine Market
Vaccine hesitancy remains a significant restraint in the global influenza vaccine market. Despite the clear benefits of influenza vaccination, misconceptions and skepticism about vaccine safety and efficacy persist, hindering widespread adoption. This hesitation is not only a public health concern but also a market challenge, impacting vaccine uptake rates. Our study reveals the impact of vaccine hesitancy vividly. In the United States, during the 2019-2020 flu season, only about half of the population received the influenza vaccine. A survey by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases found that 22% of U.S. adults who did not plan to get vaccinated cited doubt about the flu vaccine's effectiveness as a reason. This skepticism is despite CDC estimates that flu vaccination prevented an estimated 7.5 million influenza illnesses, 3.7 million influenza-associated medical visits, and 6,300 influenza-associated deaths in the 2019-2020 season.
In Europe, the situation mirrors these challenges. A Eurobarometer survey reported that in 2019, only 44% of Europeans intended to get the flu vaccine, with varying rates across countries, indicating widespread vaccine hesitancy. Moreover, misinformation about vaccines further exacerbates this issue. In a global survey by the Wellcome Trust in 2018, about 79% of people worldwide agreed that vaccines are safe, leaving a significant proportion susceptible to vaccine-related
Segmental Analysis
By Type
The global influenza vaccine market is primarily dominated by the Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (IIV) segment, holding an impressive 89.60% market share. This dominance is attributable to the long-standing trust in the safety and efficacy of IIVs, their wide availability, and the extensive body of research supporting their use. IIVs have been a cornerstone in flu prevention, offering protection against multiple influenza strains by using killed viruses that cannot cause illness. The projected growth of IIV at a CAGR of 11.15% can be attributed to ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing vaccine efficacy, including advancements in adjuvant technology and efforts to create more strain-specific vaccines. Additionally, the growing awareness of flu vaccination benefits and the increasing government initiatives promoting flu vaccination, especially in developing countries, are driving this segment's growth. The push for annual flu vaccination campaigns in the wake of recent influenza outbreaks has also significantly contributed to this trend.
Moreover, the scalability of IIV production aligns well with the global demand, especially during peak flu seasons, making it a reliable choice for mass vaccination programs. This reliability, coupled with the global healthcare community's familiarity with IIVs, reinforces their dominant position in the market.
By Process
In the global influenza vaccine market, the egg-based segment holds the largest share of 46.28%. This traditional method of vaccine production, involving the cultivation of viruses in chicken eggs, has been the industry standard for decades due to its proven track record in vaccine efficacy and safety. The familiarity and established infrastructure for egg-based vaccine production contribute to its dominance.
However, the cell culture process is gaining momentum and is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 11.48%. This growth is driven by the method's ability to respond more rapidly to pandemic threats and its suitability for people with egg allergies. Cell culture-based vaccines also offer a higher level of consistency in the production process and can be scaled up quickly, making them increasingly attractive for meeting global vaccine demands. The shift toward cell culture technology is further fueled by its potential to address the limitations of egg-based production, such as susceptibility to mutations in the virus during the growth in eggs, which can lead to reduced vaccine effectiveness. Investment in cell culture technology, including government funding and private sector R&D, is significantly contributing to the anticipated growth in this segment.
By Route of Administration
The injectable route of administration currently dominates the global influenza vaccine market, holding a major share of 71.03%. This dominance is largely due to the widespread availability and established efficacy of injectable flu vaccines. The preference for injectable vaccines is reinforced by their long history of use, ease of administration by healthcare professionals, and extensive data supporting their safety and effectiveness in various population groups.
Contrastingly, the intranasal segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 11.51%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for needle-free vaccination options, especially among pediatric and certain adult populations who may have a fear of needles. The convenience and ease of administration of intranasal vaccines make them a favorable option. Additionally, as intranasal vaccines mimic the natural route of infection, they may offer better mucosal immunity, which is a crucial aspect of influenza protection. The anticipated growth in the intranasal vaccine market is also supported by ongoing research aimed at improving their efficacy and broadening their suitability across different age groups. This form of vaccine is particularly appealing for mass vaccination scenarios, such as schools and community programs, where ease of administration is a significant advantage.
By Age Group
The adult segment in the global influenza vaccine market holds the highest share, accounting for 78.25%. This dominance is primarily due to the higher risk of complications from influenza in adults, especially among the elderly and those with chronic health conditions. Consequently, there is a strong emphasis on flu vaccination as a preventive measure in adult healthcare. The projected growth of this segment at a CAGR of 11.24% can be attributed to increasing awareness about the importance of flu vaccination and more robust vaccination programs targeting adults. Moreover, the expanding global aging population contributes significantly to this trend, as older adults are particularly encouraged to receive annual flu vaccines due to their susceptibility to severe influenza complications.
Efforts to increase workplace vaccination and initiatives by healthcare organizations to promote flu vaccination among adults are also factors driving the growth of this market segment. Additionally, the development of vaccines specifically designed for older adults, such as high-dose and adjuvanted flu vaccines, is playing a crucial role in catering to the unique needs of this age group, thus fueling market growth.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America, particularly the United States, leads the global influenza vaccine market with a commanding market share of over 43%. This dominance is attributed to several factors, including well-established healthcare infrastructure, high public awareness about influenza vaccination, and strong government support in terms of vaccination programs and funding. In the U.S., the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that during the 2019-2020 flu season, approximately 48.4% of the adult population received a flu vaccine, reflecting a significant public health achievement. The region's focus on research and development, evidenced by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services' investment of over $1 billion in cell-based influenza vaccine technology, further solidifies its market position.
Europe follows North America in the influenza vaccine market. The European region's strong performance is driven by robust healthcare systems, high vaccination coverage, and aggressive public health campaigns. Countries like the United Kingdom and Germany have shown considerable government initiatives to increase flu vaccination rates, especially among high-risk groups like the elderly and healthcare workers. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) actively promotes influenza vaccination, contributing to the region's market strength. For instance, in the 2021-20 fl22 flu season, countries like the Netherlands achieved a vaccination rate of about 49.9% among the elderly, demonstrating Europe's commitment to influenza prevention.
Asia-Pacific is another key region in the influenza vaccine market, showing promising growth potential. This region's market dynamics are influenced by its large population base, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness about the benefits of flu vaccination. Countries like Japan, China, and India are rapidly advancing in healthcare infrastructure, which is expected to boost the influenza vaccine market. For example, Japan, with its aging population, has a comprehensive vaccination program, offering subsidized flu vaccines to the elderly. Additionally, China's increasing investment in healthcare, along with its efforts to improve vaccine accessibility and affordability, is expected to drive market growth in Asia-Pacific.
Top Players in the Global Influenza Vaccine Market
- Abbott Laboratories
- AstraZeneca
- Emergent BioSolutions Inc
- Emergex Vaccines Holding Limited
- GSK plc
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- OSIVAX
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi SA
- CSL Limited
- Sinovac Biotech Ltd.
- SK bioscience Co., Ltd.
- Viatris Inc.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Type
- Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV)
- Quadrivalent
- Trivalent
- Live-attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV)
By Process
- Egg Based
- Cell Culture-Based
- Recombinant
By Route of Administration
- Injectable
- Intra-nasal
By Age Group
- Pediatric
- Adult
By Distribution Channel
- Hospitals & Pharmacies
- Government Suppliers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)