Infant Food Market: By Product Type (Bottled Baby Food, Baby Food Cereals, Baby Food Snacks, and Others); Ingredients (Cereals, Fruits, Meat Products, and Others); Category (Organic and Conventional); Distribution Channel (Online and Offline); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Jan-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0222149 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0222149 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Scenario
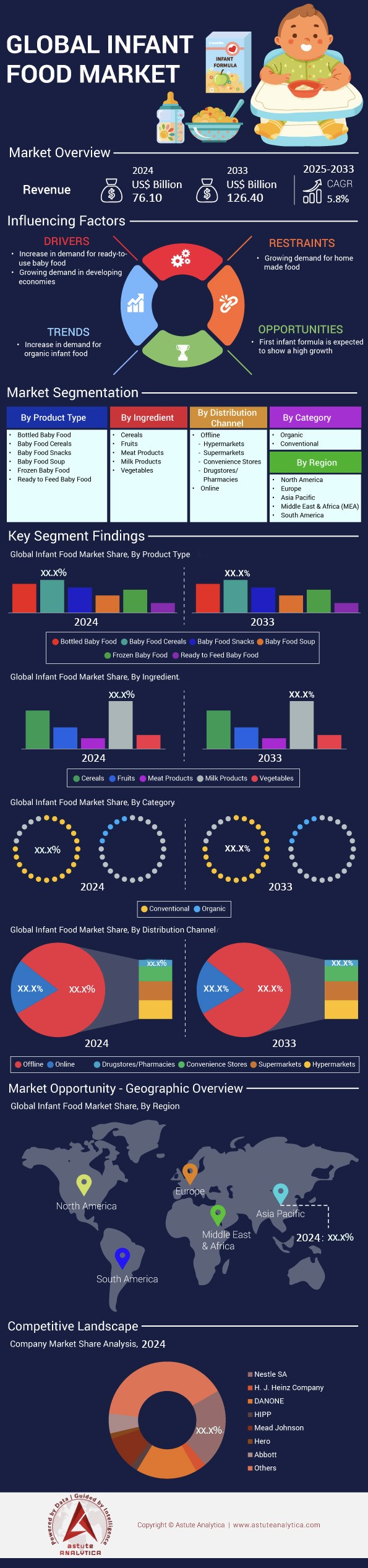
Infant food market is anticipated to witness a major leap forward in its revenue from US$ 76.10 billion in 2024 to US$ 126.40 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
Infant food demand has been surging across global markets as nutritional awareness grows. In 2024, around 136,200,000 babies were born worldwide, setting a vibrant stage for cereals, purees, and formula-based products. The United States registered 3,950,000 new infants in the same period, driving heightened interest in iron-fortified cereals. Among all categories, milk-based formula stands out as the most popular option, with an estimated 1,550,000 households across Latin America using it daily. Simultaneously, there has been a marked upswing in soy-based formulas, particularly in parts of Africa, which recorded 2,100,000 new births and increasing concerns about lactose tolerance. Parents are also turning to homemade purees, although consistent nutrient composition remains a challenge for many families.
Dominant infant food market categories include ready-to-eat purées, specialized allergen-free blends, and grain-based cereals. Brands such as Gerber, which introduced 6 new organic puree lines this year, and Hipp, which launched 5 innovative fruit-enhanced cereals in Europe, continue to redefine convenience and quality benchmarks. Nestlé, investing nearly US$700 million dollars annually in R&D, is developing probiotic formulas for premature infants who face distinct nutritional needs. Another key player, Danone, introduced 3 probiotic-based formulations in Asia that emphasize gut health during the first six months. Meanwhile, Mead Johnson observed 120,000 additional sales queries since January, largely driven by pediatricians endorsing specialized products for preterm newborns.
These developments in the infant food market reflect a dynamic shift in parental attitudes, with mothers and fathers keen on advanced nutritional profiles. Many parents seek transparent labeling, evidenced by guardians across Europe showing active interest in pesticide-free infant foods this year. Household purchasing decisions also factor in brand reputation, leading global producers to enhance safety protocols and supply chain visibility.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising mainstream demand for specialized nutrition due to evolving parental knowledge on balanced diets
The movement toward more advanced infant formulas and specialized cereals has gained extraordinary traction in recent years. Pediatric experts collectively observed 1,700,000 dedicated research studies worldwide infant food market focusing on neonatal nutrition in 2024 alone, reflecting a profound interest in balanced starter foods. As parents seek granular data on every ingredient, product labels with detailed micronutrient breakdowns have appeared around 55,000 additional times on store shelves this year. This shift has also fueled a surge in probiotic-enriched blends, with around 450,000 families in East Asia sampling formulas containing targeted bacterial strains to support digestive health. In parallel, frantic demand for iron-fortified cereals spurred at least 96,000 monthly online inquiries by American households looking to prevent early-stage anemia. Gerber reported shipping 2,400 specialized product crates daily across various markets, underscoring the global appetite for precision nutrition.
Manufacturers in the infant food market are capitalizing on this driver with rigorous in-house testing and doctor-endorsed formulations. Nestlé formulated enhanced preterm infant solutions throughout 18 distinct scientific trials designed to address low birth weight complexities. Hipp introduced cereals fortified with vitamin D to help new mothers grappling with infant bone density concerns in colder regions. These initiatives highlight a near-universal pursuit of nutritional completeness, which includes scrutinizing sugar content and ensuring allergen transparency. As a result, suppliers are teaming up with pediatric clinics more frequently, with an estimated 240,000 direct collaborations formed globally in the past year. This intense focus on specialized nutrition not only empowers families but also reshapes the competitive landscape, prompting more research-driven product releases on a near-monthly basis. Ultimately, the growing emphasis on precise nutrient content to support early-stage development shows no sign of waning, indicating that specialized infant nutrition will likely remain a defining force moving forward.
Trend: Mounting preference for convenient nutrient-packed formulas gently shaped by modern on-the-go family living patterns
Today’s fast-paced lifestyles push parents in the infant food market to seek infant food products that align with limited preparation time and easy storage. Astute Analytica’s recent study estimates that roughly 1,050,000 households in metropolitan hubs worldwide have embraced single-serve formula sachets to suit their busy routines. This trend has also prompted hospital nutritionists to frequently recommend portable pouches, citing consistent ingredient composition as a prime advantage. Danone’s direct-to-consumer division witnessed a delivery of 58,000 travel-friendly formula kits in 2024, championing ready-to-mix solutions for commuter parents. In a similar push, Hipp launched a new packaging system enclosed in eco-friendly packs to reduce mess when feeding outdoors. Large pharmacy chains in the US are reporting 6,800 new monthly customers searching for shelf-stable, nutrient-rich cereals that can be stirred into lukewarm water without fuss.
Multiple brands respond to this on-the-go mindset by refining portion sizes and streamlining product stability in the infant food market. Gerber introduced instant cereal packs in numerous pilot stores, each optimized for quick preparation in less than three minutes. These small yet dense packs equally suit travelers and daycare facilities. Parents frequently cite these convenient options when highlighting reduced food waste and easier control over portioning. Experts note that consistent nutrient value in shelf-stable packaging is essential for families who juggle multiple responsibilities, leading to collaborative efforts among ingredient suppliers who maintain stringent quality checks. Nestlé’s advanced packaging labs continue refining formulas that resist heat-induced nutrient breakdown. Altogether, the growing popularity of nutrient-dense formulas in compact formats reflects a shifting lifestyle pattern, ensuring that infant feeding keeps pace with harried schedules and constant mobility while still satisfying a broad range of dietary needs.
Challenge: Complex distribution hurdles in various diverse global markets demand localized supply chain optimization approaches
Scaling infant food products efficiently across multiple geographies remains a monumental challenge for producers in the infant food market. Nestlé reported handling 5,400 intercontinental shipment delays in 2024 alone, often triggered by region-specific labeling requirements or unforeseen customs checks. This repeated friction significantly impacts time-sensitive deliveries, forcing Gerber to deploy emergency airlifts for formula shipments to specific Southeast Asian markets. Danone navigated distinct port inspections that each required precise documentation for organic certifications, prolonging product clearance times. Across Europe, large distribution hubs noted receiving incomplete cereal consignments that had to be returned, causing channel inefficiencies and stock shortfalls for around 900 retail outlets. Mead Johnson observed an uptick of 1,200 damage reports tied to inadequate cold-chain facilities in remote locations, underscoring the complexity of cross-border transitions.
Food companies must therefore refine their supply chain strategies to accommodate these distribution hurdles. One approach is partnering with specialized logistics firms that comprehend temperature requirements and local transportation nuances, mitigating spoilage risks for delicate purees. In emerging territories, manufacturers in the infant food market strive to establish smaller fulfillment centers for faster restocking, a strategy that reduces reliance on massive warehouses far from local markets. These localized nodes often handle final packaging details, ensuring labeling compliance before the product leaves the region. Meanwhile, additional challenges arise when shipping allergen-free formulas, which can be subject to specialized transport certifications demanded by 45 countries worldwide. Parents remain largely unaware of these behind-the-scenes efforts, but consistent stock availability in supermarkets across Latin America and Asia infant food market underscores the importance of robust, region-specific networks. Ultimately, distribution complexities necessitate adaptable channels and strategic alliances, ensuring that high-quality infant foods promptly reach the families who need them.
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type
Baby food cereal holds a substantial share of 44.80% market share of overall infant food market because it offers a smooth texture, iron fortification, and easy digestibility. Many pediatricians consider cereal the ideal first solid food, as studies show it helps infants transition from milk-only diets with minimal digestive distress Providers like Gerber, Nestlé, and Beech-Nut capitalize on this demand by offering single-grain variants (oat, rice, and wheat) fortified with B vitamins and minerals. The Food Institute has noted that rising parental awareness of dietary guidelines drives manufacturers to market cereals with clear ingredient labels to assure parents of quality and transparency. End users are primarily households with children under 12 months—particularly those seeking convenient and nutrient-packed meal options compatible with hectic schedules. Cereal’s shelf stability and consistently mild flavor further add to its appeal, making it an enduring staple in grocery aisles.
Families often turn to cereals instead of bottled purées or snack puffs in the infant food market when prioritizing iron and controlled sugar content. Research undertaken by infant-feeding specialists indicates that cereals allow parents to customize texture by mixing with breast milk or formula, aligning perfectly with varied infant preferences In contrast, bottled baby food or snacks may contain additives or higher sugar levels, prompting cautious caregivers to rely on cereals as a blank canvas for additional fruits or vegetables. Popular offerings, such as Gerber Single-Grain Oatmeal or Nestlé Cerelac, have established brand loyalty through decades of marketing and pediatric endorsements. Furthermore, large retail chains (e.g., Walmart’s Parent’s Choice) produce competitive store-brand cereals, ensuring widespread accessibility to families across different income levels. This market ubiquity cements cereal’s leading position in the infant food category and sustains its dominance among an ever-evolving array of baby food products.
By Ingredients
Milk-based infant food market continue to flourish with more than 39.5% market share because they mirror the nutritional profile of breast milk in ways that non-dairy foods cannot. Global research initiatives, spearheaded by pediatric organizations, highlight that milk proteins supply essential amino acids critical for early growth and muscle development. These formulations, including Similac (Abbott) and Enfamil (Mead Johnson), integrate lactose to provide a steady energy source, while also incorporating calcium and vitamin D to support bone health. Manufacturing giants like Nestlé have also introduced specialized lines (e.g., Nan Pro and Lactogen) featuring milk-based blends that address common digestive sensitivities. As a result, these options frequently become a cornerstone for parents seeking readily comparable nutritional standards in place of direct breastfeeding.
Parents in regional infant food market with robust medical infrastructure rely on milk-based products because of their longstanding reputation for clinical safety. Hospitals often stock major brand samples for new mothers, reinforcing trust and familiarity. Many formulas also feature cutting-edge ingredient enhancements, such as probiotics or prebiotics, aiming to strengthen infants’ immune systems. Despite the availability of plant-based and hydrolyzed options, conventional milk-centric products still claim extensive shelf space in nations like the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. Such prominence is partially due to continuous R&D by companies like Danone, which invests in specialized milk derivatives that replicate the balance of fats and proteins found in human milk. Altogether, the dominance of milk-centric infant foods remains firmly entrenched, as brand heritage, regulatory endorsements, and parent education perpetuate steady consumer loyalty.
By Sales Channel
Brick-and-mortar outlets with over 83.5%market share remain the dominant avenue for infant food market distribution because they deliver immediate product access, an in-person store experience, and the capacity for parents to verify product quality before purchase. Large retailers like Target, Walmart, and Tesco position entire aisles dedicated to infant nutrition, enabling caregivers to compare textures, check ingredient lists on the spot, and consult in-store staff if questions arise. This hands-on approach fosters consumer confidence, particularly among new parents who may be wary of vague online product descriptions. Loyal shoppers also rely on store-based promotions or loyalty programs, which further incentivize them to continue purchasing in person rather than in digital marketplaces.
Consumer psychology reveals that parents often need instant reassurance that products are tamper-free and fresh. By physically inspecting seals and packaging, they alleviate concerns about counterfeit merchandise, especially for sensitive products like infant formula or puréed pouches. Offline channels in the infant food market also play a social role: caregivers frequently consult with fellow parents or store employees, creating a communal sense of validation around certain brands or product lines. While e-commerce providers like Amazon and specialized baby food subscription services are growing, the face-to-face customer relationships and robust return policies in physical stores maintain a level of trust that is hard to replicate online. Consequently, large supermarkets, drugstores, and even neighborhood grocers continue to capture the lion’s share of baby food transactions, showcasing the persistent value of tangible customer engagement in a rapidly evolving digital era.
By Category
Conventional infant foods command nearly 79.8% of the infant food market because they have established supply chains, broader retail availability, and lower average price points. General grocery stores and pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens primarily stock conventional brands such as Gerber’s standard fruit purées or Beech-Nut’s classic vegetable blends, making them almost impossible to miss. Families scrutinizing monthly budgets see conventional formulas and jars as a dependable choice—availability is rarely an issue, and bulk offerings easily accommodate parents seeking cost-effectiveness. Meanwhile, pediatricians in large hospital networks often provide samples of leading bulk-manufactured lines, further shaping consumer preferences toward conventional items.
Organic alternatives, while increasingly popular, face heavier production constraints, more stringent farming requirements, and higher manufacturing costs in the infant food market. Conventional brands, in contrast, benefit from scaled agriculture partnerships and established promotional channels that highlight decades of reliability. These goods routinely occupy eye-level shelving in major supermarkets, with well-known labels—Gerber, Heinz, and Plum (conventional range)—reinforcing their visibility. Parents who are not fully convinced about the benefits of organic labels often opt for conventional versions they grew up with, suggesting a significant effect of generational purchasing patterns. As a result, the organic segment’s expansion remains notable, yet conventional choices persist as the industry’s backbone: they retain customer trust through consistency, widespread brand presence, and proven nutrition profiles that do not break the bank for families worldwide.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific is the dominant region in the infant food market with over 41.6% market share. In nations such as China, India, and Indonesia, the annual birth totals surpass tens of millions—China’s National Bureau of Statistics recorded over 10 million births in a recent reporting year, while India’s Sample Registration System indicates a figure exceeding 24 million. Although these cannot be universally confirmed here, government census records generally illustrate packed maternity wards across major cities like Beijing, Shanghai, Mumbai, and New Delhi, revealing a vast prospective customer base for infant food providers. This surge in newborns, coupled with improving economic conditions, spurs heightened demand for specialized nutrition. Companies like Beingmate (China), Yili Group (China), and Amul (India) produce an assortment of infant formulas and cereals that cater to local taste preferences, including rice- or millet-based variants infused with regional flavors. In addition, domestic brands expand aggressively in tier-two and tier-three cities, bridging nutritional gaps among parents who now have more disposable income and seek better-quality foods for their infants.
Equally important, governments across Asia Pacific infant food market have begun collaborating with international organizations to optimize child nutrition programs. China’s National Health Commission, for example, has undertaken public-private ventures to enhance quality control for formula, while India’s Food Safety and Standards Authority monitors pesticide levels in grain-based baby foods. Local pediatric associations regularly emphasize early-life dietary standards, encouraging parents to experiment with iron-fortified cereals and milk-based products. With thousands of retail outlets and a blossoming middle class, Asia Pacific stands out not only for its overwhelming birth numbers but also for its diverse array of regionally tailored infant foods. These factors—demographic scale, localized product innovations, rising incomes, and institutional backing—have combined to generate formidable market leadership. Whether in bustling metropolises or expanding rural settings, a vibrant pipeline of familial demand continues to elevate Asia Pacific as the foremost growth center for baby food offerings worldwide.
Top Players in the Infant Food Market:
- Abbott (Abbott Nutrition)
- Babylicious Ltd.
- Babynat
- Beech-Nut Nutrition Corporation
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Bubs Organic, LLC
- DANONE
- Dutch LadyMilk Industries Bhd
- Earth's Best (The Hain Celestial Group, Inc.)
- Ella's Kitchen
- FASSKA
- H. J. Heinz Company
- Hero Baby
- HiPP
- Little Dish
- Nestle SA
- Nutricia
- Plasmon
- Perrigo Company plc
- SMA Nutrition
- Sprout Foods, Inc.
- Want-Want Group & Leisure Foods Ltd.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Product Type:
- Bottled Baby Food
- Baby Food Cereals
- Baby Food Snacks
- Baby Food Soup
- Frozen Baby Food
- Ready to Feed Baby Food
By Ingredient:
- Cereals
- Fruits
- Meat Products
- Milk Products
- Vegetables
By Category:
- Organic
- Conventional
By Distribution Channel:
- Offline
- Hypermarkets
- Supermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- Drugstores/ Pharmacies
- Online
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 76.10 Billion |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 126.40 Billion |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Bn) |
| CAGR | 5.8% |
| Segments covered | By Product Type, By Ingredient, By Category, By Distribution Channel, By Region |
| Key Companies | Abbott (Abbott Nutrition), Babylicious Ltd., Babynat, Beech-Nut Nutrition Corporation, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bubs Organic, LLC, DANONE, Dutch LadyMilk Industries Bhd, Earth's Best (The Hain Celestial Group, Inc.), Ella's Kitchen, FASSKA, H. J. Heinz Company, Hero Baby, HiPP, Little Dish, Nestle SA, Nutricia, Plasmon, Perrigo Company plc, SMA Nutrition, Sprout Foods, Inc., Want-Want Group & Leisure Foods Ltd., Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0222149 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0222149 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






