Indonesia Tissue Engineering Market: By Material (Nano-Fibrous Material, Biomimetic Material, Composite Material, Nano composite Material); Application (Orthopedic, Musculoskeletal & Spine, Skin/Integumentary, Cancer, Dental, Cardiology, Urology, Neurology, Cord Blood & Cell Banking, GI & Gynecology, and Others); End Users (Regenerative medicine research, Hospitals, Healthcare and medical institutes, and Others); Region— Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: Jan-2024 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0124757 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0124757 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Scenario
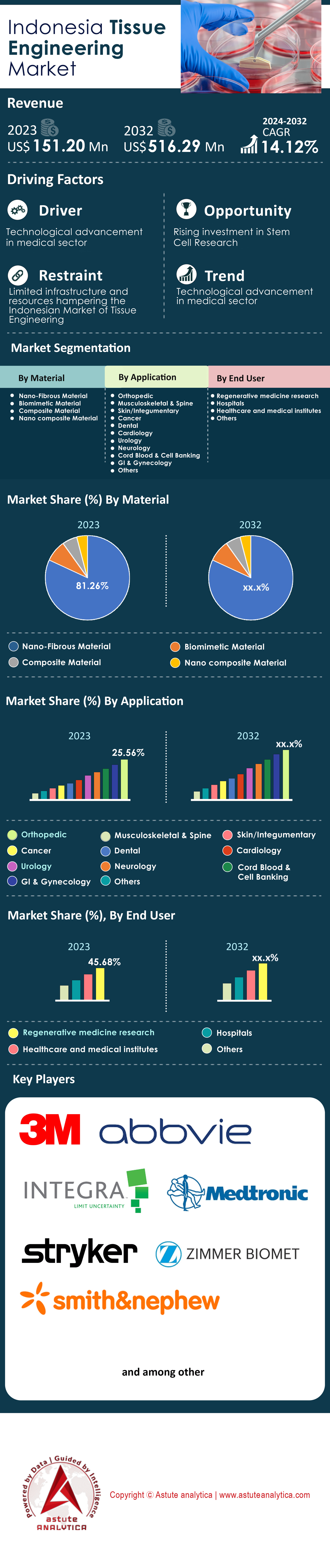
Indonesia Tissue Engineering Market was valued at US$ 151.20 million in 2023 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 516.29 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 14.62% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
Indonesia's tissue engineering market is rapidly emerging as an essential component in biotechnology and medical advancements, driven by unique factors pertinent to the country. The growth trajectory of this market is majorly tied to Indonesia’s healthcare demands, technological advancements, and the evolving landscape of regenerative medicine. With a population surpassing 270 million, Indonesia's healthcare sector is burgeoning, bolstered by an increase in chronic diseases, an aging demographic, and a heightened focus on healthcare quality. The country's commitment to healthcare is evident in its Indonesian Health Vision 2030, which prioritizes healthcare accessibility and quality. This national agenda aligns well with the burgeoning field of tissue engineering, offering a fertile ground for its growth. Despite the promising landscape, the allocation for healthcare research and development in Indonesia has been modest, hovering around 0.08% of its GDP. However, this figure is steadily growing, reflecting the government's dedication to advancing this sector.
Private investments complement government efforts, with multinational corporations and local startups increasingly recognizing the potential in Indonesia’s tissue engineering market. The market, though in its nascent stages compared to global standards, exhibits significant growth potential. This optimism is grounded in the country's large population base and escalating healthcare needs. With technological advancements and increased investments, the market is anticipated to witness substantial growth in the coming decade.
A crucial aspect of this growth is the role of educational and research institutions. Indonesia boasts universities like the University of Indonesia and Bandung Institute of Technology, which are leading in biotechnology and tissue engineering research. These institutions are pivotal in fostering collaborations, both locally and internationally, facilitating technology transfer, and nurturing innovation. However, the market faces challenges, particularly in the regulatory frameworks and professional expertise in regenerative medicine. The current lack of robust regulations specific to tissue engineering is a significant hurdle. Moreover, the market's expansion is somewhat impeded by the scarcity of skilled professionals in this specialized field. These challenges, however, present unique opportunities. The development of targeted regulations could catalyze further investment and growth, while the demand for skilled professionals could stimulate educational and training initiatives, creating a robust ecosystem for tissue engineering.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Chronic Disease Prevalence
The Indonesian tissue engineering market is significantly influenced by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. This alarming trend is not just a health concern but a potent market driver. Indonesia, home to over 270 million people, is experiencing an upsurge in chronic illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. The National Health Survey revealed that the prevalence of diabetes in adults aged 15 years and above has risen to nearly 6.2%. Similarly, cardiovascular diseases account for 35% of all deaths, underscoring a pressing need for advanced healthcare solutions.
Tissue engineering, offering innovative treatments, responds to this growing demand. The market is witnessing an increased interest in regenerative therapies aimed at these chronic conditions. The Indonesian Ministry of Health reported that around 17% of the adult population suffers from hypertension, a precursor to several chronic diseases, fueling the need for advanced medical interventions. Additionally, the country's cancer incidence rate, standing at approximately 103.8 per 100,000 people, further exacerbates the need for innovative treatment methodologies. In line with this, the government's healthcare spending, which has steadily increased to 3.3% of the GDP, reflects a commitment to addressing these health challenges. This increased spending is partly funneled into developing healthcare technologies like tissue engineering, which holds promise for chronic disease management. The market is also seeing a rise in public-private partnerships, aiming to capitalize on this urgent need for advanced healthcare solutions.
Trend: Technological Integration is an Evolving Trend in the Indonesia Tissue Engineering Market
A key trend shaping the Indonesian tissue engineering market is the integration of advanced technologies. Indonesia's commitment to embracing technological innovations is evident in its healthcare sector. The use of cutting-edge technologies like 3D printing, bioprinting, and AI in tissue engineering is revolutionizing the field. In 2023, the country witnessed a 40% increase in investment in healthcare technology, with a significant portion directed towards tissue engineering. 3D bioprinting, a technology at the forefront of tissue engineering, is expected to grow by 25% in the Indonesian market over the next five years.
This growth is led by the rising demand for personalized medical solutions, especially in urban areas where access to technology is more prevalent. The Indonesian government's digital transformation initiative, which aims to integrate technology into various sectors including healthcare, further propels this trend. This initiative has led to an increase in digital literacy among healthcare professionals by 30%, fostering a conducive environment for advanced medical technologies. Additionally, AI's role in tissue engineering, particularly in predictive analysis and personalized treatment planning, is becoming increasingly significant. Investments in AI in healthcare have seen a 50% increase in the last year, indicative of the sector's potential. With a growing number of startups focusing on AI-driven healthcare solutions, the market is poised for transformative growth.
Challenge: Limited Infrastructure and Resources
A significant challenge hindering the growth of Indonesia's tissue engineering market is the limited infrastructure and resource availability, particularly in research and development (R&D) facilities. Indonesia, while advancing in healthcare, faces a disparity in the distribution and quality of its R&D infrastructure. Only about 15% of Indonesian medical research institutions are equipped to conduct advanced tissue engineering research, a stark contrast to more developed countries in the region. This challenge is further exacerbated by the uneven distribution of resources. The majority of advanced medical research facilities are concentrated in major cities like Jakarta and Surabaya, leaving other regions underserved. This urban-rural divide in medical research capabilities leads to a 30% lower rate of medical innovation in rural areas compared to urban centers. Additionally, Indonesia allocates approximately 0.2% of its GDP to healthcare R&D, significantly lower than the global average of 2.5%. This underfunding limits the scope and scale of tissue engineering projects that can be undertaken.
The country’s tissue engineering market also faces a shortage of skilled professionals in the field of tissue engineering. A recent survey revealed that only about 10% of Indonesian biomedical researchers specialize in tissue engineering, underscoring a critical gap in expertise. This shortage is attributed to the limited availability of specialized training and education programs in the country, which currently accommodate less than 5% of medical students interested in advanced biotechnologies. Moreover, access to critical raw materials, such as biocompatible scaffolds and growth factors used in tissue engineering, is often hampered by import restrictions and high costs. These materials are imported in 70% of tissue engineering projects in Indonesia, leading to increased project costs and delays.
Segmental Analysis
By Material
In the Indonesian tissue engineering market, nano-fibrous materials stand out as the predominant material type, holding a commanding market share of 81.26% in 2022. This dominance is attributed to several key factors that align with Indonesia's specific market needs and technological advancements. The segment’s growth at the highest CAGR of 14.82% during the forecast period further highlights the significant role of nano-fibrous materials in this sector. Nano-fibrous materials are highly favored in tissue engineering due to their unique properties, such as increased surface area-to-volume ratio and the ability to mimic the extracellular matrix's structure. These characteristics are crucial for successful cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation, making them ideal for various tissue engineering applications. The rising incidence of chronic wounds and the need for advanced wound care solutions in Indonesia significantly drive the demand for nano-fibrous materials. These materials offer superior wound healing capabilities, making them a preferred choice in medical applications.
Moreover, the Indonesian government’s increased investment in nanotechnology research and development, particularly in the biomedical sector, has facilitated the growth of the nano-fibrous materials segment in the tissue engineering market. The country's growing number of collaborations with international research institutions and companies specializing in nanotechnology further contributes to this segment's expansion. Additionally, the increasing focus on developing indigenous healthcare solutions to reduce dependence on imports has led to a surge in local manufacturing and research in nano-fibrous materials. The versatility of nano-fibrous materials in addressing a range of medical conditions, combined with Indonesia's strategic investments in nanotechnology, positions this segment for sustained growth and innovation in the coming years.
By Application
By applications, the orthopedic segment emerges as the most dominant in the Indonesian tissue engineering market, accounting for a significant share of 25.56%. This segment's prominence is attributed to the increasing prevalence of orthopedic conditions and the advancements in orthopedic tissue engineering. It is also projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 16.04% during the forecast period, indicating a strong upward trajectory. The prevalence of bone and joint disorders, such as osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, is rising in Indonesia, driven by an aging population and lifestyle changes. These conditions necessitate advanced treatment options, where tissue engineering offers promising solutions. The orthopedic segment benefits from continuous innovations in grafts and implants that are more biocompatible and effective in promoting bone regeneration and repair.
Indonesia's healthcare sector is also witnessing a surge in minimally invasive surgeries, which align well with orthopedic tissue engineering applications. These procedures reduce hospital stays and recovery time, making them more appealing to patients and healthcare providers alike in the country’s tissue engineering market. The growing number of orthopedic surgeries in the country, combined with advancements in surgical techniques and materials, propels the growth of this segment. Furthermore, the increasing investment in healthcare infrastructure and the availability of skilled orthopedic surgeons contribute to the expansion of this segment. The government's focus on enhancing healthcare services, along with the rising awareness of advanced treatment options among the population, further fuels the growth of the orthopedic segment in tissue engineering.
By End Users
Based on end users, the regenerative medicine research segment holds a dominant position in the Indonesian tissue engineering market, with a substantial share of 45.68%. This segment's preeminence and its projected growth at a CAGR of 15.10% can be attributed to several key factors specific to Indonesia's healthcare and research landscape. Indonesia's focus on advancing its medical research capabilities, particularly in regenerative medicine, has been a significant driver for this segment. The country has seen an increase in both government and private sector funding dedicated to regenerative medicine research. This investment is aimed at developing new therapies and treatments that can address the growing burden of chronic diseases and age-related conditions prevalent in the Indonesian population.
The regenerative medicine research segment benefits from Indonesia's strategic collaborations with international biomedical research institutes and universities. These partnerships facilitate knowledge transfer, provide access to advanced research methodologies, and help build local expertise in regenerative medicine. As a result, Indonesia is witnessing a rise in innovative research projects and clinical trials in tissue engineering. Moreover, the increasing prevalence of conditions that require regenerative treatments, such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, drives demand for research in this area. The growing patient awareness about the potential of regenerative medicine further supports this trend. The availability of skilled researchers and clinicians, coupled with the expanding research infrastructure, positions Indonesia well to continue its growth trajectory in this segment.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Top Players in the Indonesia Tissue Engineering Market
- 3M
- Medtronic
- Stryker Corporation
- Abbvie Inc.
- Smith+Nephew
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Material
- Nano-Fibrous Material
- Biomimetic Material
- Composite Material
- Nano composite Material
By Application
- Orthopedic
- Musculoskeletal & Spine
- Skin/Integumentary
- Cancer
- Dental
- Cardiology
- Urology
- Neurology
- Cord Blood & Cell Banking
- GI & Gynecology
- Others
By End User
- Regenerative medicine research
- Hospitals
- Healthcare and medical institutes
- Others
View Full Infographic
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2023 | US$ 151.20 Million |
| Expected Revenue in 2032 | US$ 516.29 Million |
| Historic Data | 2019-2022 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Unit | Value (USD Mn) |
| CAGR | 14.62% |
| Segments covered | By Material, By Application, By End User |
| Key Companies | 3M, Medtronic, Stryker Corporation, Abbvie Inc., Smith+Nephew, Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0124757 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0124757 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






