India Smart Meter Market: By Type (Smart Electricity Meter, Smart Water Meter, Smart Gas Meter); Communication Mode (Radio Frequency (Heat-based Meters and Diode Detector-based Meters), Power Line Communication, and Cellular); Phase (GISM (Single Phase), GIST (Three Phase), GISS (Heavy Consumers)); Technology (Automated Meter Reading (AMR) and AMI); End User (Residential, Commercial, and Industrial); Region— Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: Apr-2024 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA0923615 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0923615 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Scenario
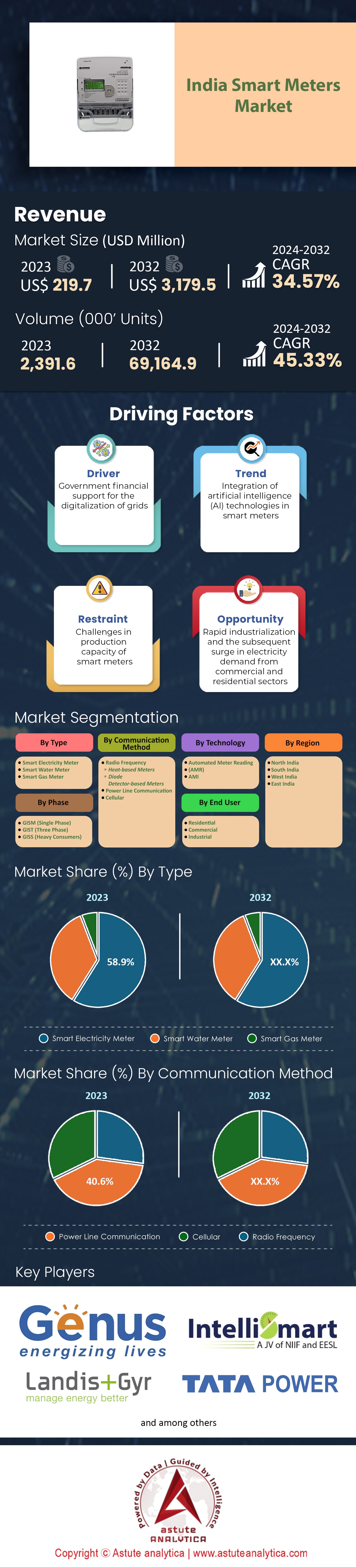
India Smart Meter Market was valued at US$ 219.7 million in 2023 and is projected to attain a market size of US$ 3,179.5 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 34.57% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
India smart meter market is rapidly unfolding, marking an impressive trajectory driven by strategic initiatives and mammoth investment plans. Central to this growth story is the Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) – a conglomerate of public sector undertakings functioning under the aegis of the Ministry of Power. Their recent announcement of successfully installing 3.6 million smart meters across the nation until April 2023 is a testament to the aggressive pace and commitment to revamping India's energy landscape. This extensive rollout, under the banner of the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP), extends across multiple states including Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Bihar, NDMC-Delhi, and Telangana. The primary goal behind SMNP's expansive mandate is to bolster the billing and collection proficiencies of the distribution companies (DISCOMs) that dot the vast Indian terrain.
These smart meters, integral to the future energy grid of India, come equipped with web-based monitoring systems. Such features are anticipated to drastically cut down commercial losses and provide a much-needed boost to the revenue streams of the energy sector in the India smart meters market. The nation's intent isn't just reflected in its installations but also in its financial commitments. Earlier in June, the Ministry of Power unveiled a colossal financial incentive of ₹664 billion (approximately $8 billion) for enhancing power sector reforms across India's states. Crafted to be disbursed through the 2021-2022 union budget, these incentives take the shape of borrowing permissions. They aim to catalyze states into action, urging them to adopt reforms that magnify the efficiency and overall output of the power sector.
Furthermore, the fiscal year 2023-2024 has been marked with even greater ambition. A staggering ₹1.4 trillion (or $17.4 billion) has been set aside as an incentive, reinforcing the country's unwavering commitment to transform its power infrastructure and practices.
The digital revolution within the energy sector promises a goldmine of opportunities for the smart meters market. A study from the Ministry of Power showcased that by leveraging data analytics, Discoms could potentially save INR 10,000 crores annually by mitigating power theft and improving billing efficiency. As Big Data seeps into the energy matrix of India, businesses stand at the cusp of redefining customer service, ensuring efficient power management, and pioneering groundbreaking business models.
However, like any sunrise sector, the smart meters market in India isn’t without challenges. The regulatory framework, although supportive, can sometimes pose hurdles for new entrants. With stringent standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) and the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), businesses need to ensure compliance, interoperability, and data security. Knowledge of these regulations isn't just a compliance measure; it's a competitive edge.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Supportive Government Initiatives and Policy Push
The Ministry of Power, in collaboration with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) and the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), has recognized the potential of smart meters in improving billing efficiency, reducing transmission losses, and bridging the demand-supply gap. In the National Tariff Policy 2016, the government articulated its commitment by recommending the replacement of conventional meters with smart prepaid meters within a three-year timeframe. This policy push opened up opportunities for rapid expansion in the India smart meters market, with projections indicating that approximately 250 million conventional meters are set to be replaced by 2027.
Furthermore, under the Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana (UDAY) scheme, state governments and their respective DISCOMs committed to deploying smart meters for consumers with monthly consumption levels exceeding 200 units. By 2024, over 5 million smart meters were earmarked for installation, marking a whopping 250% increase from the numbers in 2022. Such a steadfast government stance has undeniably created a conducive environment for stakeholders to invest, innovate, and implement smart metering solutions.
Trend: Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The energy landscape of smart meters market is undergoing a monumental shift. As the nation grapples with the dual challenge of meeting its energy demands and reducing its carbon footprint, the integration of smart meters with renewable energy sources has emerged as a trend that's reshaping the India smart meters market dynamics.
As of march 2023, India's renewable energy capacity touched the 172 GW mark. The government, setting ambitious targets, aims to achieve 450 GW of renewable energy by 2030. This explosive growth in renewable energy is interlinked with the proliferation of smart meters. How? Renewable sources, particularly solar and wind, are intermittent. Their integration into the grid requires dynamic monitoring, load forecasting, and real-time adjustments – capabilities inherent to smart meters. A study by the India Smart Grid Forum indicated that by 2025, nearly 40% of smart meter installations will be directly integrated with decentralized renewable energy systems in India smart meters market. These integrated setups not only allow for efficient energy consumption tracking but also enable grid-balancing. With real-time data, DISCOMs can manage energy influx from renewable sources and maintain grid stability.
The financial ramifications of this trend are equally substantial. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) estimated that with smart meter integration, renewable energy systems could witness a 20% increase in efficiency, translating to potential savings of INR 8,000 crores annually by 2030.
Challenge: Infrastructure and Connectivity Issues
India's vast geographical expanse, combined with its diverse topography, poses a unique challenge to the nationwide rollout of smart meters: infrastructure and connectivity hurdles. As the country endeavours to transition from conventional metering to smart metering systems, the gaps in infrastructure and reliable communication networks are becoming starkly evident in the smart meters market. According to a 2021 report by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), while urban areas like Delhi and Mumbai boast a smart meter penetration of nearly 70%, many remote and rural areas lag behind with a 10% penetration. The disparity is primarily attributed to infrastructural shortcomings. In a country where approximately 66% of the population resides in rural areas, this presents a substantial challenge.
Connectivity is another major roadblock. The efficacy of a smart meter lies in its ability to relay real-time data for efficient energy management. However, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) highlighted that as of 2021, nearly 50,000 villages in India still lack a stable mobile network. This lack of communication infrastructure means that even if smart meters are installed, they can't function optimally due to intermittent or non-existent network connections. Bridging this infrastructure and connectivity gap requires substantial investment. Preliminary estimates by the India Smart Grid Forum suggest an investment requirement of around INR 20,000 crores over the next five years, solely for infrastructural upgrades to support smart metering in remote regions.
Segmental Analysis
By Type
Analysis of India smart meters market based on type prominently reveals the dominance of electricity smart meters, occupying a significant 58% of market share. India's escalating urbanization and industrialization drive has skyrocketed electricity demand. As the country's thirst for power grows, there's a parallel emphasis on monitoring, management, and optimization. Enter electricity smart meters, which not only ensure accurate billing but also enable users to gauge and manage their consumption patterns. In addition, public sector undertakings, such as the Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), have been instrumental in propelling the deployment of electricity smart meters. The ambitious plans of EESL to install an additional 3.33 million smart meters in states like Uttar Pradesh and Haryana further bolster this segment's growth.
By Communication Method
Based on communication method, powerline communication emerges as the undeniable leader, capturing an impressive 40.6% of the India smart meters market share. Given the existing power infrastructure in India, powerline communication presents a cost-effective solution. Since it utilizes existing electrical wiring for data transmission, there’s no need for new infrastructure, making it a viable choice for a country as expansive as India. Moreover, powerline communication offers a more stable connection, especially in densely populated areas. This reliability is crucial for accurate data transmission from smart meters.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge the encroaching wave of IoT-enabled smart meters. Giants like Energy Efficiency Services Limited and Tata Power are spearheading this revolution, especially in Uttar Pradesh and Haryana. The marriage of IoT with smart meters amplifies the latter's capabilities, paving the way for real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with other smart devices. Recent collaborations highlight this trend. Airtel’s partnership with Secure Meters in April 2023 to deploy 1.3 million NB-IoT powered smart meters in Bihar is a testament to the growing appetite for IoT in the energy sector. Furthermore, the 2022 collaboration between VI and EESL to roll out advanced metering infrastructure for DISCOMS in Uttar Pradesh and Haryana reaffirms the industry's trajectory.
By Phase
The segmentation of the India smart meters market offers a profound understanding of the country's focus on optimizing its energy sector. Analyzing the market based on phase provides a compelling narrative. Dominating the scene is the GISM (Single Phase) segment, capturing a significant 45% of the market share. This prominence is attributable to their suitability for residential applications, considering the vast urban and rural residential demographics of India. The ease of installation and maintenance of these meters only amplifies their appeal.
From a financial perspective, single-phase meters present a more economical option for individual households and smaller establishments in smart meters market. India's existing residential infrastructure, especially in non-urban areas, is majorly geared for single-phase supply, making GISM meters a fitting choice. Yet, trailing behind are the three-phase meters. Although not as prevalent as their single-phase counterparts, their role in commercial and industrial settings is pivotal, serving sectors with higher energy demands and intricate circuitry.
By Technology
On the technology front, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) stands tall by commanding over 71.9% revenue share of the India smart meters market thanks to its capability to relay real-time data, enabling utilities to make instantaneous, informed decisions. This real-time transmission doesn't just aid in efficient energy distribution but paves the way for heightened consumer engagement. AMI's two-way communication system heralds a transformative phase in the energy sector, allowing consumers and utilities to be more interconnected. This two-pronged communication ensures real-time billing, consumption tracking, and a new level of consumer satisfaction. From the utilities' standpoint, the adoption of AMI spells operational efficiency. The automated readings that AMI facilitates dramatically reduce the necessity for manual checks, ensuring accuracy and cutting down on operational costs. Given India's vast geographic and demographic expanse, such efficiencies could result in substantial cost savings. As the nation steers towards an integrated, technologically advanced energy landscape, AMI's compatibility with upcoming technologies ensures its continued relevance.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North India's dominance in the smart meters market is a testament to its rapid infrastructural and technological advancements. Capturing more than 50% of the India smart meters market, the region is a hotbed for innovation and large-scale deployment of these energy-monitoring devices. Wherein, the dense population of North India, particularly in states like Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Haryana, and Punjab, propels the demand for efficient energy consumption. Uttar Pradesh alone, with its sprawling urban and rural expanse, accounts for a significant fraction of this market. The sheer volume of households, coupled with industrial and commercial units, necessitates the need for millions of smart meters for effective energy management.
Financial allocations towards these initiatives have been massive. Governments, both at the state and central levels, have channeled billions of rupees towards the acquisition and installation of smart meters. Collaborative ventures, such as those between state governments and entities like Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), have led to the procurement and deployment of millions of meters in the region. For instance, recent data suggests that the GMR Smart Electricity Distribution Company secured a Rs 7,593 crore smart meter order for 22 districts in Uttar Pradesh, targeting the installation of several million units over the next few years. Additionally, the region's infrastructural growth rate and urbanization trends provide a fertile ground for expanding the smart meters market. New residential complexes, commercial establishments, and industries in cities like Delhi, Chandigarh, and Lucknow are increasingly being equipped with smart meters from the get-go. The adoption rate in these urban areas has seen an annual growth of approximately 10-15%, a figure that is projected to rise with increasing awareness and governmental push.
Furthermore, policies and initiatives from state governments have also played a pivotal role. Incentive schemes, rebates, and awareness campaigns targeting consumers have significantly boosted the adoption rates. Punjab, for example, recently rolled out an initiative to install smart meters in over 100,000 households as a pilot project, with a proposed budget allocation of over ₹300 crores. Apart from this, Punjab State Power Corporation Limited (PSPCL) has secured a loan amounting to approximately $122 million for the rollout of smart meters. The financial plan for the smart metering initiative stands at around $73 million, with a notable contribution of $11 million coming from the Central Government. On successful and timely completion of the project, an added bonus of roughly $1.08 million will be awarded in the smart meters market. Investments focused on bolstering infrastructure to reduce energy loss are estimated at $48.6 million, of which a significant $40.5 million is being funded as a grant.
However, the India smart meters market landscape isn't without challenges. While urban areas in North India show impressive adoption rates, rural areas, despite their massive population, lag. The reasons range from infrastructural challenges to the lack of awareness. Yet, with a focused approach and continued investments, the region is poised to address these gaps.
Top Players in India Smart meter market
- Meter Manufacturers
- Avon Meters
- Badger Meter, Inc.
- BENTEC India Ltd.
- EDMI Limited
- Eppeltone Engineers Pvt. ltd.
- Gram Power
- Holley Technology Ltd
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Itron Inc.
- Kamstrup
- L&T Electrical & Automation
- Landis+Gyr
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Neptune Technology Group Inc.
- Networked Energy Services
- Schneider Electric
- Sensus
- Siemens
- Wasion International
- AMI Smart Meters Manufacturers
- Adani Transmission Ltd
- Allied Engineering Works Pvt. Ltd. (AEW)
- Apraava Energy Private Limited
- BCITS
- Dongfang Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Elmeasure
- Fluentgrid Limited
- Genus Power Infrastructures Limited
- HPL Electric & Power Ltd.
- IntelliSmart Infrastructure Pvt. Ltd.
- JnJ Powercom Systems Ltd.
- L&T Electrical & Automation
- Lakshmi Electrical Control Systems Ltd
- Montecarlo Limited
- Synergy
- Tata Power
- Techno Electric
- ZenMeter
- ZTE Corporation
- Other Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Type
- Smart Electricity Meter
- Smart Water Meter
- Smart Gas Meter
By Communication Method
- Radio Frequency
- Heat-based Meters
- Diode Detector-based Meters
- Power Line Communication
- Cellular
By Phase
- GISM (Single Phase)
- GIST (Three Phase)
- GISS (Heavy Consumers)
By Technology
- Automated Meter Reading (AMR)
- AMI
By End User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By State
- North India
- Uttar Pradesh
- Delhi
- Haryana
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Himachal
- J&K
- South India
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Andhra Pradesh
- Telangana
- West India
- Gujarat
- Goa
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Chhattisgarh
- East India
- West Bengal
- Bihar
- Assam
- Jharkhand
- Odisha
- Rest of East India
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA0923615 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA0923615 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






