Global Harvesting Robot Market: By Robot Type (Semi-Autonomous Robots and Fully Autonomous Robots); Harvesting Type (Fruit Harvesting, Vegetable Harvesting, Grain Harvesting and Others); Application (Outdoor Agriculture and Greenhouse Agriculture); Vegetable Harvesting Application (Outdoor Agriculture and Greenhouse Agriculture); Region— Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 07-Nov-2024 | | Report ID: AA0222136
Market Scenario
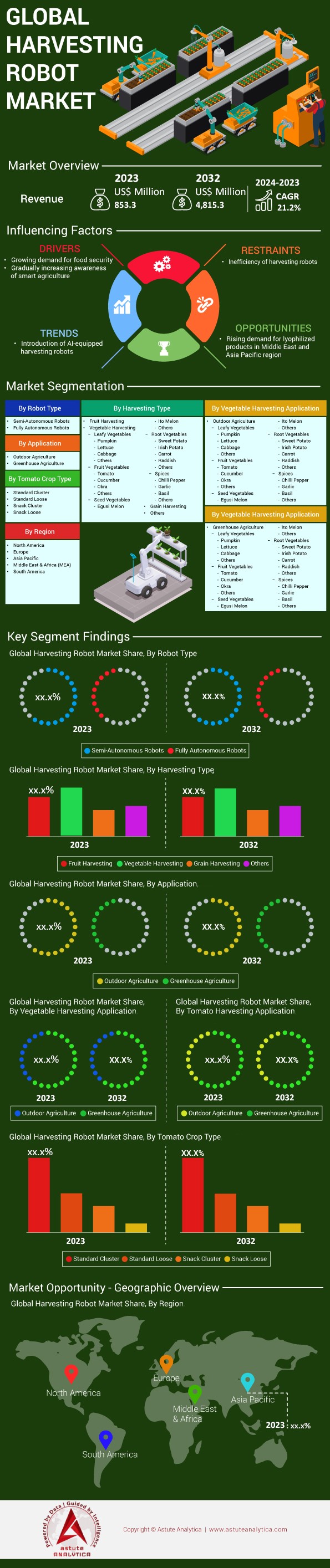
Harvesting robot market was valued at US$ 853.3 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach valuation of US$ 4,815.3 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 21.2% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
In recent years, the significance of the harvesting robot market has been greatly emphasized owing to a dire need to strengthen food security as global population and agricultural problems grow. There are anticipations that the global population would increase by 2.5 billion people by 2050 which will even increase the pressure on the agricultural systems. At the same time, the shortage of labor in agriculture has caused great losses, and every year dearth of labor force renders about 30 million tons of food scraps. Such challenges indicate the need for the use of smart agricultural robots such as harvesting robots so that food production levels are maintained.
The recent advances in harvesting robots demonstrate the progress made in this area. For example, the vegetable picking robot developed by the University of Cambridge is reported to have longer working hours than the average human working non-stop, and has therefore, more endurance and efficiency. Additionally, smart farming concept received more than $100 million from the European Union in 2023 and a sizable amount was meant for the research and implementation of robotic technologies. This trend in the harvesting robot market is spread out, whereas Japan and the United States improve their budget for field automation. As a matter of fact, Japan experienced an increase within 15% in robotic agricultural equipment’s internal sales as the technology is becoming more feasible and successful in practice.
The adoption of smart farming in agriculture changes the scenario tremendously through advertising IoT, sensors, robots and drones. In the year 2023, the total value of the smart agriculture market throughout the world was US$ 20 billion, which showcases its increased usage. The drone use in agriculture has helped in better crop monitoring and more effective resource utilization and even though more than a million units of drones were sold across the globe, pushing the harvesting robot market growth further. In addition, with the advent of precision farming, the use of pesticides and fertilizer has led to cost reduction in farming by over a billion dollars a year. Tracing food items and improving the working procedures lead us to the conclusion that harvesting robots and other related technologies are not a matter of the future but an essential part of the changing agriculture to make it more efficient and more capable to sustain in producing food.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising Labor Shortages and the Need for Automated Agricultural Solutions Worldwide
The global food market is faced with extreme scarcity of workers, making it even more important to integrate automation in harvesting such as robotic harvester systems. The number of hired farm workers in the US harvesting robot market continues to slide as evidenced by the USDA where back in 2016 there were around 1 million hired as farm workers, a drop as compared to earlier years. It has also been the case in Japan where the overall age of the population dealing with farm harvesting robotics is now more than 67 years and the number of those involved in agriculture shrunk to roughly 1.7 million in 2018 from 2.2 million in 2005. Similarly Spain and Italy together have reported loss of tens of thousands of seasonal agricultural workers in the last decade alone.
The situation is dire in developing countries as well. The National Bureau of Statistics of China reported that between 2015 and 2020, China's rural labor force was reduced by roughly 23 million as a result of mass relocation to urban areas. The National Farmers’ Federation estimates the number of agricultural workers was 26 000 less than needed to fill job vacancies in agriculture in Australia particularly during high seasons. This shortage of labor was made worse by the COVID-19 pandemic. In Canada for example, there was a shortfall of more than 8,000 agriculture workers in 2020 and huge amounts of crops were lost. According to the International Labour Organization, there was loss of agricultural employment opportunities comprising around 16 million jobs per year on average in the period from 2019 to 2020. Moreover, in Great Britain along the harvesting robot market, the Union of Farmers revealed in a survey that around 50% of the farms had a labor shortage problem in 2019.
According to the report by UC Davis, in the state of California, labor shortages in the harvesting robot market caused crop that was not harvested leading to a loss of revenue of around $3.1 billion every year. The European Union supported Horizon 2020 to advance agricultural robotics with over € 80 million. In 2019, John Deere and other companies poured around $300 million or more in acquisitions in robotics. According to the Ministry of Agriculture statistics, the market of Japan harvesting robots recorded an increase of agricultural robots in sales to 2500 in 2019. In addition, Israel is reported to have more than 600 agri-tech startups by 2020, most of which concentrated on automation to solve the problem of labor.
Trend: Integration of IoT Devices for Real-Time Data Collection in Harvesting Operations
There has been a rise in the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices for harvesting, which will add to the value of the agricultural sector by improving efficiency and productivity. It was estimated that the global agriculture IoT market stood at $11.2 billion in 2023. By the end of 2023, over 85 million devices such as IoT sensors, drones, and smart irrigation systems were believed to be in use in agriculture worldwide. It was reported by USDA that in the US, more than 1000 farms in 2019 used IoT soil sensors for moisture management. Furthermore, the number of farms utilizing IoT technology reach 49,000 in Australia by 2020 as stated by Australian Bureau of Statistics.
Also, the major players in the harvesting robot market are embedding IoT in their equipment. For example, John Deere IoT devices are connected in more than 200,000 machines across the globe for enhanced performance, IoT is one of the technologies being used. Also, in Netherlands about 1,500 greenhouses used mechanized IoT systems by the year 2020 in order to sustain climate conditions which translated to about €2 billion per year. Also, according to the China’s ministry of agriculture, In 2019 over 10,000 farms implemented IoT approaches. Also, by 2020, the prominent agricultural drone company DroneDeploy had used IoT drones for mapping over 40 million acres of farmland.
Harvesting robots are also being transformed in the use of harvesting technology thanks to IoT’s ability to collect data in real-time. Tech-deploying robots have been developed by companies such as Harvest CROO Robotics to assist in determining the rightness of fruits enabling the picking of up to 8 acre harvesting robots per day. In 2020, Small Robot Company in the UK deployed 50 IoT-enabled robots for weed control, covering 2,500 hectares. The practice of precision agriculture which has been made possible by IoT interfacing has been shown to in reduce input costs on average by $15 per acre as per the study PrecisionAg Institute.
Challenge: High Initial Investment Costs Hindering Widespread Adoption of Robotic Technologies
Even though the potential of robotic applications is prominent, the harvesting robot market faces a serious challenge of high price. For instance, the average amount of a single harvesting robotic equipment exceeds US$ 250,000 making a hefty fall on cost for a huge number of farmers. For small-scale to medium-scale farms, which correlate with the USDA, 89% of farms in the country, become quite hard. In the year 2019, a paper presented by the National Farmers Union gave a picture of the situation where, because of costs among others, less than ‘10% of farmers would be using or planning to use the robotic technology access.’
The situation in Europe harvesting robot market is more or less the same, agricultural organizations estimate that the number of European practitioners – about 10 million farms, but only a small percentage has introduced robotization and this is primarily due to the shortage of funds. Meanwhile, in Australia, depending on the size of farm owned, about AUD 500,000 will have to be spent to establish a robotic milking system, this amount appears huge given that the average farm income was about AUD 190,800 in the year of 2020 according to Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource button. Not to mention that already USD 20000 additionally has to be paid every year for operational and maintenance which has been all enough discouraging for the integration of such technologies among farmers.
Investment in the agricultural robotics space is a big risk according to banks, so they are reluctant to provide loans. As per Rabobank’s data, in the year 2023, the percentage of agricultural loans globally aimed at advancement through technologies such as robotics was only 2%. Some places in the harvesting robot market do have government funding and grants, but these are usually not enough to cater to anyone. In 2023, the Common Agricultural Policy allocated a budget of €40 million towards precision farming which has helped less than 1% of European farmers. In developing countries, such as India for example, farming has a typical farm size of 1.08 hectares, however, acquiring robotic equipment requires large amounts of funds which makes it a challenge.
Segmental Analysis
By Robot Type
The harvesting robot market in 2023 has grown considerably, with semi-autonomous robots taking the lead than with a greater 59.8% share. The reason why these robots have become the most popular type is because they can be automated while still having human supervision for some tasks. However, Unlike completely autonomous robots, that are usually expensive and only seem to work well when dealing with structured environments, semi-autonomous robots offer a more practical alternative by employing human facets to make decisions whilst the robot does the work. Because of this combination, they can handle a wide range of crops and varying conditions on the farm, thus making a variety of agricultural needs possible. Some of the important factors responsible for their growth are improvement in sensor technology, new machine learning algorithms and IoT assistance which automatically make them more precise and reliable while performing tasks like fruit picking, pruning and even weeding. Moreover, the increased emphasis on eco-friendly farming practices means that there is now a greater demand for effective and efficient labor saving technologies, thereby increasing their market reach.
When it comes to the harvesting robot market, the usage of semi-autonomous robots in agriculture is increasing. The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a significant adopter, a clear indication of the region’s accelerating technological growth and its vast requirements for intensive agriculture. Europe and North America come next respectively, which emphasizes their efforts in transforming agriculture for the better. It is important to note that the market for these robots has advanced to a great extent with companies such as Agrobot, Harvest CROO Robotics and FFRobotics leading the industry in creative and new ideas. Agrobot’s Bug Vacuum and FFRobotics robotic hand are excellent examples of technologies that can pick delicate crops and have higher accuracy thus minimizing wastage. On the other hand, these robots decreased the need for workers in agriculture by 20,000, which shows how they help solve labor problems in the industry. As technology keeps changing, the application range of semi-autonomous robots will also widen which will help them have a stronger position in the harvesting robot sector.
By Application
When it comes to applications, the outdoor segment with more than 57.2% revenue share is dominating the global harvesting robot market. The use of harvesting robots is widespread in outdoor farming practice compared to greenhouse farming due to the enormous size of outdoor farming practices that calls for cultivation automation to effectively manage and cover larger acreage. Approximately 20 million acres of land worldwide were cultivated with the help of robots in 2023 indicating a growing need for autonomous systems within the outdoor environment. In addition, outdoor farms grow more diverse range of crops which require different robotic systems to grow different varieties of crops and different conditions. Furthermore, outdoor environments have their own difficulties such as uneven terrains or weather conditions, which accelerate the development of strong and flexible robotic systems.
The outdoor segment, in contrast to the sheltered environments of greenhouses, and their relatively smaller coverage area face picking robot marketing constraints. Due to their small size, greenhouses are estimated to compose approximately 500,000 acres worldwide, meaning vast areas do not require any sort of automation. However, the growing need for precise and controlled environments does create a need for robots but not as much as there is outdoors.
As per Astute Analytica's report on harvesting robot market, investments in outdoor harvesting robots and equipment came to a total of US$ 3 billion in 2023, compared to $500 million invested in greenhouse technologies. In addition, regulatory policies and support systems in major farming regions such as North America and Europe have emphasized outdoor robotic advancements. This is reflected with 1,200 government-backed initiatives promoting outdoor robotic farming in these regions. In 2023, 1.5 million farmers around the globe claimed to use agricultural robots, which means 70% of these domestic applications were outdoors, which further highlights the fact that there is a higher demand and necessity for growth for automation of large-scale farms.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific remains dominant both in the manufacturing and consumption of harvesting robot market. The robotics technology market in the Asia Pacific region reached nearly US$ 43.7 billion in 2023, which is an indicator that there has been quite a good investment in automation technologies, especially in Agriculture sector. In that year, the region recorded the introduction of about 403,727 industrial robots so that it reached about 73% of the total robots of 553,052 units installed in the world. This massive adoption further emphasizes the region's objective to deploy cutting edge technologies in a bid to raise agricultural efficiency and production. China, India, and Japan are developing countries with a large agricultural economy which, together with promoting the harvesting robots, are expected to help boost food security and increase farming efficiency. It is farther anticipated that by 2032, the global harvesting robot market will have grown to be worth US$4,218 million because of the rapid technological advancements and the widespread use of precision agriculture in the Asia Pacific.
Europe harvesting robot market is shifting towards becoming an important market with growth expected at a notable pace in the upcoming years. The region was also able to record impressive performances in terms of automation in perspective with the fact that during the year 2023; Europe registered 15% of total industrial robot sales having 82,957 units. It has also been found out that the European agricultural robots’ market is said to grow at a staggering valuation of US$ 5,994.27 million by the end of 2024. Countries such as Germany, the Netherlands, and France are also leading in employing harvesting robots as they possess the necessary technological resources and have a strong agricultural industry. The global industrial robot market is also expected to grow which is projected to reach US$ 35.68 billion by the year 2029 with Europe contributing immensely to this growth. Europe’s endorsement for more organic and sustainable farming is likely to fuel the demand for harvesting robots as they can be a solution for such environmentally sustainable farming practices.
The European harvesting robot market is characterized by the healthy presence of key players who promote the development and growth of the industry. Companies are engaged in developing advanced robotic solutions tailored towards the peculiarities of agriculture in Europe. Government initiatives are equally important in this regard, with policies and programs aimed at improving productivity and cutting down on manpower by use of automation. For example, the European Commission has funded efforts directed towards encouraging the application of digital farming technologies including robotics in a bid to make the agricultural ecosystem more modernized.
Top Players in Harvesting Robot Market
- Agrobot
- Dogtooth Technologies Limited
- FFRobotics
- Green Robot Machinery Pvt. Ltd.
- Harvest Automation
- HARVEST CROO
- Other Prominent Players
Tomato Harvester Companies
- CERESCON B.V.
- Panasonic
- Energid Technologies Corporation
- Four Growers
- Metomotion
- Root Al, Inc.
- Tortuga Agriculture Technologies, Inc.
- Appharvest
- Inaho Inc.
- Denso Design
- Xihelm
- Certhon Harvest Robot
- Squse
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Robot Type
- Semi-Autonomous Robots
- Fully Autonomous Robots
By Harvesting Type
- Fruit Harvesting
- Vegetable Harvesting
- Leafy Vegetables
- Pumpkin
- Lettuce
- Cabbage
- Others
- Leafy Vegetables
- Fruit Vegetables
- Tomato
- Cucumber
- Okra
- Others
- Seed Vegetables
- Egusi Melon
- Ito Melon
- Others
- Root Vegetables
- Sweet Potato
- Irish Potato
- Carrot
- Raddish
- Others
- Spices
- Chilli Pepper
- Garlic
- Basil
- Others
- Grain Harvesting
- Others
By Application
- Outdoor Agriculture
- Greenhouse Agriculture
By Vegetable Harvesting Application
- Outdoor Agriculture
- Leafy Vegetables
- Pumpkin
- Lettuce
- Cabbage
- Others
- Leafy Vegetables
- Fruit Vegetables
- Tomato
- Cucumber
- Okra
- Others
- Seed Vegetables
- Egusi Melo
- Ito Melon
- Others
- Root Vegetables
- Sweet Potato
- Irish Potato
- Carrot
- Raddish
- Others
- Spices
- Chilli Pepper
- Garlic
- Basil
- Others
- Greenhouse Agriculture
- Leafy Vegetables
- Pumpkin
- Lettuce
- Cabbage
- Others
- Fruit Vegetables
- Tomato
- Cucumber
- Okra
- Others
- Seed Vegetables
- Egusi Melon
- Ito Melon
- Others
- Root Vegetables
- Sweet Potato
- Irish Potato
- Carrot
- Raddish
- Others
- Spices
- Chilli Pepper
- Garlic
- Basil
- Others
By Region:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2023 | US$ 853.3 Mn |
| Expected Revenue in 2032 | US$ 4,815.3 Mn |
| Historic Data | 2019-2022 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Unit | Value (USD Mn) |
| CAGR | 21.2% |
| Segments covered | By Robot Type, Harvesting Type, Application, Vegetable Harvesting Application, and Region |
| Key Companies | Agrobot, Dogtooth Technologies Limited, FFRobotics, Green Robot Machinery Pvt. Ltd., Harvest Automation, HARVEST CROO, Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)