Food Safety Testing Market: Microbiological Test (Total Plate Count (TPC), Coliform Testing, Listeria Testing, Salmonella Testing, Campylobacter Testing), Sensory Test (Manual (Smell, Taste, Appearance, Others), Instrumental (Smell, Taste, Appearance , Others), Physical Test, Chemical Test, Allergen Test, Others); Product Type (Processed Food, Fruits &Vegetables, Beverages, Grains & Cereal, Confectionery, Meat& Meat Products, Milk & Milk Products, Others); Technology (Traditional Testing and Rapid Testing); Service Sourcing (Inhouse and Outsource); End User (Food & Beverage, Academic and Research Institutions, Testing Laboratories); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Mar-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA03251218 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA03251218 | Delivery: Immediate Access
Market Scenario
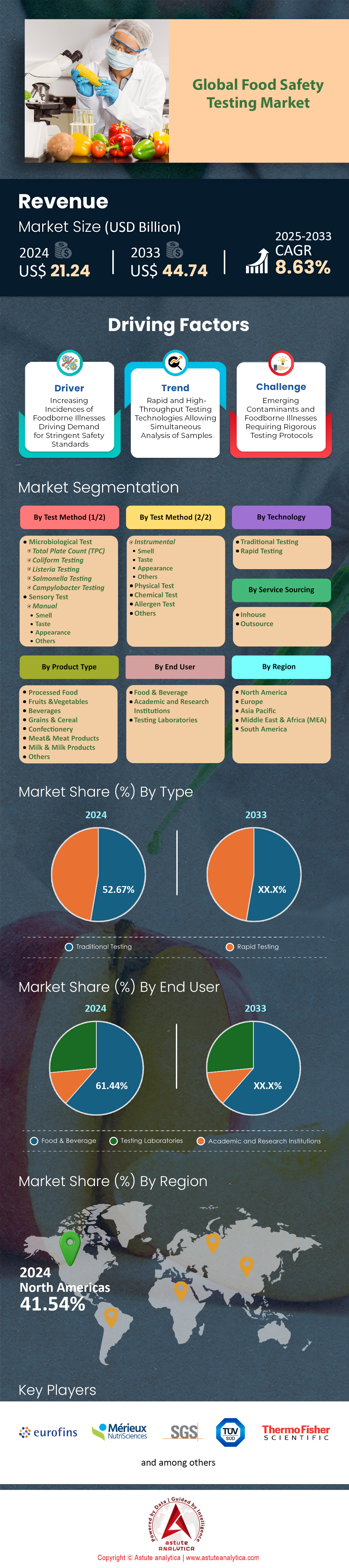
Food safety testing market was valued at US$ 21.24 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 44.74 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 8.63% during the forecast period 2025–2033.
The global food safety testing market is witnessing unprecedented growth, fueled by rising concerns over foodborne illnesses and the need for stricter quality assurance. An estimated 600 million people fall ill annually due to contaminated food, highlighting the urgency for robust testing protocols. In 2024 alone, the United States witnessed approximately 300 food recalls, resulting in 1,400 illnesses, 487 hospitalizations, and 19 deaths. The globalization of food supply chains has further intensified the need for rigorous testing, with regulations like the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) mandating comprehensive checks for contaminants. The economic impact of foodborne illnesses is staggering, costing Americans $75 billion annually in medical expenses, lost productivity, and premature deaths. These factors have spurred significant investments in food safety testing, making it a critical focus for governments and businesses worldwide.

Technological advancements are revolutionizing the food safety testing market, making processes faster, more accurate, and efficient. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning has enhanced the detection of contaminants, enabling quicker responses to potential threats. In 2024, undeclared allergens accounted for 34.1% of food recalls, followed by pathogens like Listeria (22%), Salmonella (13.9%), and E. coli (3.4%). Rapid testing methods, such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), have drastically reduced testing times from days or weeks to hours or even minutes. This efficiency is crucial, given that foodborne illnesses in the U.S. lead to 53,300 hospitalizations and over 900 deaths annually. These advancements are not only improving food safety but also reducing the economic and health burdens associated with contamination.
Cutting-edge innovations in 2024 are further propelling the food safety testing market. The adoption of blockchain technology is enhancing transparency and traceability in the food supply chain, addressing issues like the 9,000 foodborne illness outbreaks reported in the U.S. between 2011 and 2022. Non-destructive testing methods, such as near/middle infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging, are being widely adopted for real-time monitoring of food quality. Additionally, the expansion of surveillance networks, like FoodNet’s inclusion of all of Colorado in 2023, has improved population representation and disease trend monitoring. The increasing use of culture-independent diagnostic tests (CIDTs) has also led to higher detection rates of foodborne pathogens. These advancements are collectively driving the rapid growth of the food safety testing market, ensuring safer food supplies and better public health outcomes globally.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Increasing Incidences of Foodborne Illnesses Driving Demand for Stringent Safety Standards
The rising incidence of foodborne illnesses has become a global public health concern, driving the demand for more stringent food safety standards. In 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported that foodborne diseases affect an estimated 600 million people annually, leading to 420,000 deaths worldwide. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for robust food safety measures, adding fuel to the growth of the food safety testing market. For instance, in the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) documented over 1,400 illnesses, 487 hospitalizations, and 19 deaths linked to food recalls in 2024. These incidents are often caused by pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli, which have been responsible for significant outbreaks in recent years. One notable example is the 2023 Listeria outbreak linked to contaminated cheese, which resulted in 26 hospitalizations and 2 fatalities. Such outbreaks not only pose serious health risks but also lead to substantial economic losses, with foodborne illnesses costing the U.S. economy an estimated $75 billion annually in medical expenses, lost productivity, and premature deaths.
In response to these challenges, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide food safety testing market are implementing stricter food safety standards. The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in the United States, for example, mandates comprehensive testing of food products for contaminants, emphasizing preventive controls rather than reactive measures. Similarly, the European Union’s General Food Law Regulation has introduced stringent traceability requirements to ensure food safety across the supply chain. These regulatory changes are driving the adoption of advanced testing technologies and protocols. For instance, the FDA’s GenomeTrakr network, which uses whole genome sequencing to track foodborne pathogens, has identified over 50,000 bacterial isolates since its inception, significantly enhancing outbreak detection and response capabilities. The increasing focus on food safety is also evident in the growing number of food recalls, with the FDA reporting 300 recalls in 2024, a 15% increase from the previous year.
Trend: Rapid and High-Throughput Testing Technologies Allowing Simultaneous Analysis of Samples
The food safety testing market is witnessing a significant shift towards rapid and high-throughput testing technologies, which allow for the simultaneous analysis of multiple samples. This trend is driven by the need for faster and more efficient detection of contaminants in the food supply chain. In 2024, the adoption of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) has become increasingly widespread, reducing testing times from days or weeks to hours or even minutes. For example, PCR-based methods have been instrumental in detecting Salmonella in poultry products, with a testing time of just 24 hours compared to the traditional 5-7 days. Similarly, ELISA tests are being used to identify allergens such as peanuts and gluten in food products, with results available within 2-3 hours. These advancements are crucial, given that undeclared allergens accounted for 34.1% of food recalls in 2024, followed by contamination with pathogens such as Listeria (22%) and E. coli (3.4%).
The integration of automation and robotics in food safety testing market has further enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of these technologies. Automated systems, such as the Bio-Rad CFX96 Touch Deep Well Real-Time PCR Detection System, allow for high-throughput screening of up to 96 samples simultaneously, significantly increasing laboratory productivity. This is particularly important in light of the growing complexity of food supply chains, which often involve multiple ingredients and processing steps. For instance, in 2024, the FDA reported that 60% of food recalls involved products with multiple ingredients, making it challenging to identify the source of contamination. Rapid testing technologies are also being combined with digital platforms to enable real-time data sharing and analysis. The use of blockchain technology, for example, has improved traceability and transparency in the food supply chain, allowing for faster identification and removal of contaminated products.
Challenge: Emerging Contaminants and Foodborne Illnesses Requiring Rigorous Testing Protocols
In 2024, the global food supply chain is facing an increasing number of novel pathogens and chemical contaminants, posing significant risks to public health. For instance, the CDC reported a 20% increase in cases of Cyclospora infections in the United States food safety testing market, linked to contaminated fresh produce such as lettuce and basil. Similarly, the emergence of Cronobacter sakazakii in powdered infant formula has raised concerns about the safety of baby food products. Chemical contaminants, such as heavy metals and pesticide residues, are also becoming more prevalent, with the FDA detecting elevated levels of arsenic in rice-based products and cadmium in chocolate. These emerging contaminants are often difficult to detect using traditional testing methods, necessitating the development of more advanced and sensitive technologies.
The complexity of the global food supply chain further exacerbates these challenges in the food safety testing market, as products often cross multiple borders and undergo various processing steps before reaching consumers. In 2024, the FDA reported that 70% of food recalls involved products sourced from multiple countries, making it difficult to trace the origin of contamination. This has led to the adoption of more rigorous testing protocols, including the use of whole genome sequencing (WGS) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) to identify and track foodborne pathogens. For example, the FDA’s GenomeTrakr network has been instrumental in detecting outbreaks of Listeria monocytogenes, with over 50,000 bacterial isolates sequenced to date. Additionally, the use of non-destructive testing methods, such as near/middle infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging, is gaining traction for real-time monitoring of food quality and safety. These technologies allow for the detection of contaminants without damaging the product, making them ideal for high-value items such as fresh produce and seafood. Despite these advancements, the rapid evolution of contaminants and pathogens continues to pose significant challenges, highlighting the need for ongoing innovation and collaboration in the food safety testing industry.
Segmental Analysis
By Testing Method
Microbial testing commands over 36% of the food safety testing market due to its critical role in detecting harmful pathogens that cause foodborne illnesses. Pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria, E. coli, and Campylobacter are responsible for more than 600 million cases of foodborne diseases globally each year, necessitating stringent testing protocols. Microbial tests are highly sensitive, with PCR-based methods capable of detecting as few as 10 colony-forming units per gram of food, ensuring accurate results. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EFSA mandate microbial testing, with over 1.2 million tests conducted annually in the U.S. alone. The global microbiology testing market, valued at $5.80 billion in 2024, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.12%, driven by increasing regulatory scrutiny and consumer demand for safer food. Additionally, the rise in global food trade, which exceeds $1.5 trillion annually, has further amplified the need for microbial testing to prevent cross-border contamination.
The demand for microbial testing surpasses other methods in the food safety testing market due to its ability to address a wide range of food matrices, from raw agricultural products to processed foods. For instance, meat and poultry products account for over 25% of microbial tests due to their high susceptibility to contamination. The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, with over 700,000 deaths attributed to antimicrobial resistance annually, has also heightened the importance of microbial testing. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as next-generation sequencing, have enabled the detection of novel and emerging pathogens, further driving market growth. The global food safety testing market continues to see microbial testing dominate due to its unparalleled ability to ensure food safety and public health. With over 80% of food manufacturers relying on microbial testing for quality assurance, its dominance is expected to persist in the coming years.
By Product Type
Processed food testing accounts for more than 20% of the food safety testing market, driven by the increasing consumption of ready-to-eat meals, canned foods, and frozen products. The global processed food market, valued at $4.1 trillion in 2024, necessitates rigorous testing to ensure compliance with safety standards. Processed foods are particularly prone to contamination during production, storage, and transportation, with over 15% of foodborne outbreaks linked to dairy products alone. This has led to over 500,000 tests being conducted annually on processed foods, particularly in the meat, poultry, and seafood sectors. The rise in demand for processed food testing is further fueled by consumer awareness, with 68% of consumers prioritizing food safety labels when making purchasing decisions. Additionally, the introduction of advanced technologies like next-generation sequencing has enabled the detection of novel pathogens in processed foods, driving the market further.
Top processed foods in the global food safety testing market requiring extensive testing include dairy products, meat, poultry, and seafood, which account for over 60% of the processed food testing market. The global trade of processed foods, which exceeds $800 billion annually, has also heightened the need for testing to ensure compliance with international safety standards. For instance, the European Union conducts over 200,000 tests annually on imported processed foods to ensure they meet safety regulations. The increasing prevalence of food fraud, which costs the global economy over $40 billion annually, has further driven the demand for processed food testing. With the global food safety testing market projected to reach $44.1 billion by 2033, processed food testing is expected to remain a dominant segment due to its critical role in ensuring the safety of the global food supply chain.
By Technology
Traditional testing methods dominate the food safety testing market with a 52.67% share, primarily due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and widespread acceptance. Methods like culture-based testing, which can detect up to 99.9% of pathogens, remain prevalent despite the emergence of rapid testing. Traditional tests are often preferred for their ability to provide comprehensive results, with over 80% of food manufacturers relying on them for routine quality checks. The global food safety testing market continues to see traditional methods dominate due to their established protocols and regulatory approval. While rapid testing offers faster results, traditional methods are more cost-effective, with an average cost of $50 per test compared to $150 for rapid tests. Additionally, traditional methods are more adaptable to a wide range of food matrices, making them indispensable in the industry.
The dominance of traditional testing methods in the food safety testing market is also driven by their ability to meet regulatory requirements in over 150 countries. For instance, the FDA mandates the use of traditional methods for certain pathogens, with over 1 million tests conducted annually in the U.S. alone. The global trade of food products, which exceeds $1.5 trillion annually, also relies heavily on traditional testing to ensure compliance with international safety standards. Furthermore, traditional methods are often more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises, which account for over 60% of the food industry.
By Service Sourcing
In-house services leads the food safety testing market with a 52.56% share, as organizations prefer greater control over testing processes and faster turnaround times. Over 70% of food manufacturers have invested in in-house labs, with an average setup cost of $1.5 million, to ensure compliance with stringent regulations. In-house testing allows companies to conduct over 1 million tests annually, reducing dependency on third-party labs. The ability to customize testing protocols and ensure data confidentiality further drives the preference for in-house testing. Additionally, in-house labs can achieve a turnaround time of 24-48 hours, compared to 72-96 hours for outsourced testing, enhancing operational efficiency. The global food safety testing market, projected to reach $44.1 billion by 2033, continues to see in-house testing dominate due to its strategic advantages in ensuring food safety and regulatory compliance.
The rise in in-house testing is also driven by the increasing complexity of food supply chains, which now involve over 200 countries. In-house labs allow companies to conduct real-time testing, reducing the risk of contamination and recalls, which cost the global food industry over $7 billion annually. Additionally, in-house testing provides greater flexibility in testing schedules in the food safety testing market, with over 60% of companies reporting improved efficiency. The global trade of food products, which exceeds $1.5 trillion annually, also necessitates in-house testing to ensure compliance with international safety standards. Furthermore, in-house labs can conduct over 500 different types of tests, making them more versatile than third-party labs. With over 80% of large food manufacturers now relying on in-house testing, its dominance is expected to persist in the coming years.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America: The Largest Market for Food Safety Testing
North America dominates the food safety testing market, driven by stringent regulatory frameworks and high consumer awareness. The United States leads the region, with the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) mandating rigorous testing protocols to prevent contamination. In 2024, the U.S. witnessed 300 food recalls, resulting in 1,400 illnesses, 487 hospitalizations, and 19 deaths, underscoring the need for robust testing. The economic burden of foodborne illnesses in the U.S. is estimated at $75 billion annually, further fueling investments in advanced testing technologies. The region is also a hub for technological innovation, with the adoption of AI-powered testing platforms and blockchain for traceability. Major players like SGS Group and Eurofins are expanding their testing capabilities, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. The focus on rapid testing methods, such as PCR and ELISA, has significantly reduced testing times, enhancing efficiency in detecting contaminants like Listeria and Salmonella.
Europe: A Mature Market with Strong Regulatory Oversight
Europe is the second-largest food safety testing market, characterized by stringent regulations and a high emphasis on food quality. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) plays a pivotal role in setting standards, ensuring that food products meet safety requirements. In 2024, Listeria outbreaks in Europe led to 2,500 cases and 250 deaths, highlighting the need for advanced testing solutions. The region is also witnessing a surge in blockchain adoption to enhance supply chain transparency, particularly in tracking contaminated products. Non-destructive testing methods, such as hyperspectral imaging, are gaining traction for real-time monitoring of food quality. Additionally, the European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy aims to reduce pesticide use by 50% by 2030, further driving demand for testing services. Major companies like Bureau Veritas and Intertek are expanding their presence in the region, offering comprehensive testing solutions to meet regulatory and consumer demands.
Asia Pacific: The Fastest-Growing Market with Expanding Opportunities
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing food safety testing market, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing consumer awareness, and expanding food exports. Countries like China and India are witnessing a surge in demand for testing services due to rising concerns over food adulteration and contamination. In 2024, China reported over 1,000 food safety incidents, prompting the government to implement stricter regulations. The region is also adopting advanced technologies, such as AI and IoT, to enhance testing efficiency and accuracy. Blockchain technology is being increasingly used to ensure traceability in the export of seafood and agricultural products. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has introduced new guidelines to improve testing standards, particularly for street food and processed products. Additionally, the region is investing in rapid testing kits to detect contaminants like pesticides and heavy metals, ensuring safer food supplies for its growing population. The focus on sustainability and green supply chains is further driving the adoption of innovative testing solutions in the region.
Top Players in Food Safety Testing Market
- ALS
- Biomerieux
- Eurofins Scientific
- Intertek Group plc
- Merck KGaA
- Mérieux NutriSciences
- NSF
- SGS Société Générale de Surveillance SA
- Symbio Labs
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- TUV SUD
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview
By Test Method
- Microbiological Test
- Total Plate Count (TPC)
- Coliform Testing
- Listeria Testing
- Salmonella Testing
- Campylobacter Testing
- Sensory Test
- Manual
- Smell
- Taste
- Appearance
- Others
- Instrumental
- Smell
- Taste
- Appearance
- Others
- Manual
- Physical Test
- Chemical Test
- Allergen Test
- Others
By Product Type
- Processed Food
- Fruits &Vegetables
- Beverages
- Grains & Cereal
- Confectionery
- Meat & Meat Products
- Milk & Milk Products
- Others
By Technology
- Traditional Testing
- Rapid Testing
By Service Sourcing
- Inhouse
- Outsource
By End User
- Food & Beverage
- Academic and Research Institutions
- Testing Laboratories
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Malaysia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Philippines
- Vietnam
- Rest of ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA03251218 | Delivery: Immediate Access
| Report ID: AA03251218 | Delivery: Immediate Access 
.svg)





