Edge AI Software Market: By Component (Solution, Services); Application (Access Control, Autonomous Vehicles, Energy Management, Predictive Maintenance, Remote Monitoring, Telemetry, Video Surveillance, Others); Data Source (Biometric Data, Mobile Data, Sensor Data, Speech Recognition, Video and Image Recognition); End User (Advance Industries, Banking and Insurance, Chemical Agriculture, Consumers, Cross Vertical, Energy and Material and more) By Region, Competition, Opportunities, and Forecast for 2025–2033
- Last Updated: Jan-2025 | Format:
![pdf]()
![powerpoint]()
![excel]() | Report ID: AA1121103 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA1121103 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
Market Scenario
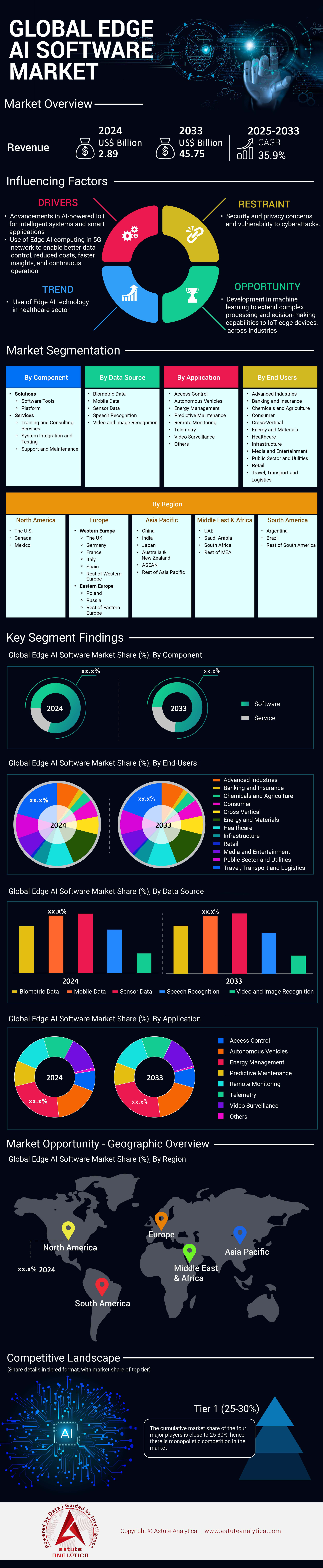
Edge AI software market was valued at US$ 2.89 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach valuation of US$ 45.75 billion in 2033, at a CAGR of 35.9% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
Edge AI software is seeing a surging need from industrial manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and automotive players who require faster, on-device intelligence for seamless autonomy and decision-making. IBM revealed 4,500 enterprise deployments of its Edge Application Manager in 2024, reflecting significant interest in managing distributed AI workloads. Microsoft recorded 12,000 developers building solutions on Azure Percept for automated data processing at the edge, signaling an expanded talent pool. Intel documented 1,300 fresh real-time analytics use cases using the OpenVINO toolkit, attesting to the technology’s pivotal role in critical processes. These sectors prioritize low latency, reliable connectivity, and robust security—key factors that make edge deployments indispensable.
One of the strongest growth drivers in the edge AI software market is the emergence of specialized hardware and software designed for accelerated inference on local devices. NVIDIA announced 650 new robotics startups leveraging its Jetson modules, pointing to widespread usage in supply chain automation. Qualcomm powered 80 million smartphones with on-device AI capabilities in 2024, highlighting the everyday integration of edge inference. Google introduced 700 regional expansions of its Edge TPU in Asia and Europe to support microservices in local data centers. NXP Semiconductors released 25 advanced reference designs specifically tailored for industrial automation, reflecting a growing appetite for scalable platforms. Bosch adopted 4,300 sensor-based systems with embedded AI for automotive e-mobility initiatives, showcasing momentum in specialized solutions.
Leading providers in the edge AI software market such as Intel, NVIDIA, Qualcomm, Microsoft, and Google continue to refine frameworks like OpenVINO, TensorRT, Azure Percept, and Edge TPU, making them among the most dominant Edge AI software environments worldwide. Amazon Web Services reported 2,200 retail partners integrating AWS IoT Greengrass for on-premise data tasks, underscoring the global climate of adoption. Siemens deployed 1,100 AI-driven implementations at the edge to optimize manufacturing lines, reflecting a targeted approach for localized AI. Overall, the world is shaping up to invest heavily in solutions that streamline data processing and ensure quicker insights, with industries of all types leveraging new and refined edge AI platforms.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Proliferation Of Real-Time Analytics Requirements Continually Fueling Rapid Worldwide Edge AI Software Adoption Surge
The need for instantaneous insights has propelled edge AI software market to the forefront of global innovation. Organizations demand split-second task execution within rugged, on-site environments, driving heightened interest in minimal-latency algorithms and specialized chipsets. In 2024, Arm reported 600 new low-power designs to support advanced on-device processing, illustrating the vitality of real-time analytics at the hardware level. Samsung validated 2,500 production lines globally that now employ edge inference for anomaly detection, underscoring the pace of industry-wide adoption. Fujitsu revealed 3 new chip prototypes capable of running AI workloads locally for predictive maintenance, reinforcing steady progress in micro-level operational intelligence. Hitachi introduced 5 discrete integrated solutions that merge SCADA systems with AI models at the periphery, sharpening decision-making capabilities on factory floors. Zebra Technologies highlighted 2,200 handheld devices with embedded analytics for logistics tracking, showcasing a surge in real-time data capture.
Wider availability of faster connectivity further enhances the importance of real-time analytics in the edge AI software market. Cisco tested 500 pilot projects that rely on sub-millisecond communication for robotic guidance in warehousing, demonstrating the drive for nimble infrastructures. This confluence of connectivity, hardware development, and growing reliance on immediate insights underpins the upward trajectory of edge AI software solutions. As more industries see the value of local data processing—particularly when solution reliability is vital—edge platforms become an indispensable asset. The driver behind this trend will persist as enterprises witness tangible gains in business continuity, reduced bandwidth usage, and near-instant responses. With consistent improvements in sensor technology and distributed computing architectures, real-time analytics will cement its role as a critical catalyst for the next horizon of edge AI software capabilities.
Trend: Rising Deployment Of Secure On-Device Inference Models Shaping Tomorrow’s Critical Edge AI Software Paradigms
Demand for heightened privacy and data sovereignty is fueling an uptick in field-ready AI models that process information entirely on local hardware in the edge AI software market. Palo Alto Networks announced 9 new zero-trust solutions designed to safeguard edge inference, illustrating security’s top place in this emerging landscape. Atos documented 550 facility installations where sensitive medical records are evaluated exclusively at the edge, pointing to a shifting regulatory climate that stresses patient data protection. VMware released 4 hardened virtual appliance templates tailored for on-device analytics in distributed environments, underscoring how privacy concerns drive technical refinements. ABB introduced 7 custom software modules enabling localized deep learning for power generation controls, granting industrial clients more confidence in their operational secrecy. Nokia reported 1,200 private network setups leveraging edge-based authentication to avoid cloud exposure, reflecting broader trust in sealed environments. Red Hat showcased 8 open-source frameworks that encrypt local AI operational layers, ensuring each inference cycle remains confidential.
From consumer electronics to autonomous vehicles, the trend is consistent in the edge AI software market: more organizations prefer to keep data near its source. Continental adopted 600 advanced modules in its next-gen driver-assist systems, ensuring immediate, secure insights without constant cloud communication. Because these models run independently of remote data centers, they mitigate external threats, enhance uptime, and lower bandwidth usage. This approach aligns with a world increasingly conscious of cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Privacy standards within finance, healthcare, and defense accelerate the movement, prompting solution providers to refine and miniaturize inference engines. As the shift to on-device AI continues, businesses achieve a unique competitive advantage: real-time, secure intelligence that doesn’t risk confidentiality. The trajectory of this trend suggests that future edge software will lean even more toward self-contained processing, forever evolving how organizations innovate at the edge.
Challenge: Lack Of Distributed Processing Architectures Challenging Broad Implementation Of Scalable Edge AI Software Solutions
Many organizations grappling with vast sensor networks and complex AI models find it arduous to implement truly distributed processing systems in the edge AI software market. IBM noted 700 pilot programs struggling to interlink disparate devices into one seamless edge framework, highlighting this challenge’s prevalence. Huawei revealed 950 resource-constrained deployments lacking uniform infrastructure for dynamic load balancing, underscoring the strategic difficulty of scaling at the edge. Ericsson encountered 375 major client inquiries regarding orchestration complexities across multiple micro data centers, reflecting the need for robust management solutions. Dell Technologies observed 1,100 instances where older network architectures could not fluidly handle AI inference at remote nodes, emphasizing the burden of outdated hardware. Schneider Electric reported 220 industrial setups that faced synchronization hitches between local controllers and higher-level analytics engines, illustrating how system fragmentation can hamper real-time insight. Rockwell Automation recorded 620 edge implementations requiring external intervention to maintain consistency in training cycles.
This fragmentation in the edge AI software market often delays edge AI adoption by complicating interoperability, resource allocation, and centralized oversight. Without a standardized approach, industries face an uphill task in rolling out advanced analytics or deep learning at scale. It becomes challenging to ensure data fidelity, rapid model updates, and consistent performance across thousands of devices. The absence of well-defined distributed processing not only engenders higher operational costs but also curtails expansion into new geographies or extended use cases. With a clear gap in unified frameworks, organizations attempt to incorporate custom-built or hybrid solutions—yet these can introduce new integration dilemmas. Resolving this challenge requires a combination of flexible network topologies, robust orchestration layers, and cohesive hardware-software synergy. As companies move toward a future that demands universal connectivity and on-demand intelligence, they must surmount the complexities of distributed processing architectures to unlock the full potential of edge AI software solutions.
Segmental Analysis
By Component
Software segment holds a commanding lead over service-oriented solutions in the Edge AI software market with over 80% market share thanks to its flexibility, rapid deployment, and continuous innovation cycles. Major players such as Microsoft invest around 5,000 dedicated engineering hours monthly to refine Azure-based edge AI packages capable of running complex inference directly on embedded devices. NVIDIA, with more than 20 specialized software development kits like TensorRT and CUDA-X, enables real-time computer vision in robotics and autonomous systems. Intel’s OpenVINO toolkit sees over 60,000 developer sign-ups each year, indicating a strong community focused on on-device analytics. Arm integrates its libraries with at least 2,000 hardware partners to streamline data processing in wearables, drones, and industrial controllers. Meanwhile, Google’s Edge TPU runtime supports more than 50 model architectures, proving software versatility in optimizing neural networks at the edge.
This focus on software over services stems from the broader ecosystem of frameworks that allow continuous updates without replacing hardware. Amazon’s SageMaker Neo optimizes machine learning models in edge AI software market for more than 10 unique edge hardware architectures, lowering the barrier to entry for smaller enterprises. IBM’s Watson libraries have surpassed 2,500 edge-based enterprise deployments globally, reflecting a growing demand for automated device-based intelligence. Bosch’s software solutions power at least 1,500 AI-driven sensor modules, underscoring a preference for integrated packages rather than external service add-ons. Qualcomm invests around 4 million dollars annually in developer programs to improve on-device inference in mobile and IoT devices, showcasing how software ecosystems fuel advanced use cases. Xilinx’s edge AI compilers, tested across 300 real-world pilots, demonstrate the robust capabilities software brings to manufacturing, retail, and healthcare without incurring massive service overheads.
By Application
Edge AI software has become indispensable in the energy sector as it control over 20.5% market revenue due to its potential to optimize resource utilization and reduce operational costs for utilities. General Electric’s digital platforms, deployed in at least 300 power plants worldwide, leverage on-device analytics to detect inefficiencies in turbines. Siemens uses edge AI at around 250 wind farms to fine-tune turbine pitch control, significantly reducing mechanical stress. Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure software in the edge AI software market coordinates electricity distribution in roughly 350 microgrids, instantly balancing load fluctuations. Enel Green Power runs on-site prediction models that analyze weather data from 8,000 solar panels, preventing energy wastage through intelligent dispatch. Emerson’s plant optimization solutions rely on real-time sensor intelligence in at least 100 offshore rigs, improving safety and cutting downtime.
For end users, the appeal lies in cutting-edge insights without latency. IBM’s energy division reported that factories integrating on-site AI avoided 600 hours of unscheduled maintenance across a fleet of installed sensors. Honeywell’s Forge-based edge software transforms consumption data from around 280 commercial buildings, identifying anomalies in HVAC usage. Hitachi’s advanced analytics optimize hydroelectric facilities—over 40 of them—by anticipating power demand surges in local grids in the edge AI software market. Mitsubishi Electric integrates on-board AI controllers in more than 60 industrial furnaces to stabilize heat profiles, leading to consistent product quality. The growth is fueled by global mandates for cleaner, smarter energy systems, and by the fact that local computing significantly trims data transmission fees. Ultimately, edge AI’s realtime decision-making and cost-effective scaling make it an essential tool for large and small energy providers alike.
By End Use Industry
The travel, transport, and logistics industry with over 20.6% market share embraces edge AI software market to streamline complex operations, reduce delays, and enhance safety across multimodal networks. FedEx deploys advanced route optimization tools in at least 2,000 distribution facilities, helping cut average delivery times. UPS has integrated on-device vision systems into 3,500 sorting machines to identify damaged parcels without manual checks, accelerating throughput. Boeing leverages AI-driven sensor data in over 500 commercial aircraft for predictive maintenance, effectively reducing turnaround downtime. Bombardier’s rail systems unit uses machine learning at over 40 train depots for scheduling repairs based on real-time telematics. DHL’s robotics program in 14 major warehouses applies edge-based picking algorithms to minimize travel time between storage racks.
Key factors such as cargo security and fuel savings drive widespread adoption in the edge AI software market. Maersk uses onboard analytics in 150 container ships to track refrigeration units without relying on satellite bandwidth. Airbus employs AI at more than 20 manufacturing sites to monitor assembly lines and supply chain movement. Caterpillar’s autonomous haulage trucks, presently in 12 active mine locations worldwide, demonstrate how immediate edge inference can prevent collisions and downtime. Volvo’s truck division, equipping 80 test vehicles with collision-avoidance sensors, exemplifies how localized computing ensures safer road transport. Amazon’s widespread use of Kiva robots—over 250,000 in operation—highlights the logistics sector’s reliance on decentralized AI for high-volume order fulfillment. By handling data directly on vehicles, robots, and equipment, transport and logistics providers see immediate improvements in schedule accuracy, cargo integrity, and customer satisfaction.
By Data Source
Sensor data dominates the edge AI software market by controlling over 25.1% market share because it offers immediate, real-time visibility into physical processes. LiDAR feeds in self-driving cars process tens of thousands of data points per second—leading to high demand for algorithms that can handle dense, constantly changing streams. In industrial automation, Schneider Electric has outfitted at least 400 factories with temperature and vibration sensors to predict equipment failures before they happen, driving robust adoption of event-based AI platforms. Flir Systems produces more than 1,200 thermal imaging sensors annually for edge analytics in security and firefighting. Texas Instruments integrates machine learning accelerators into over 50 microcontrollers that interpret signals from motion and pressure sensors. SICK AG’s sensor solutions rank among the top five in warehouse logistics, enabling advanced edge inference for inventory tracking.
The primary reason sensor data’s dominance in the edge AI software market is its direct impact on operational efficiency and safety. Honeywell reports that adopting on-site sensor intelligence reduces equipment downtime by more than 4,000 operating hours across heavy industries each year. Bosch, shipping roughly 3 million microelectromechanical sensors per quarter, highlights the sheer scale of data production fueling on-device analytics. Siemens deploys MindSphere edge connectors in over 200 discrete manufacturing plants, emphasizing the necessity of real-time sensor feedback loops. Caterpillar’s rugged sensors, numbering at least 2,000 in active use on mining trucks, demonstrate how continuous data ingestion helps prevent large-scale system failures on the spot. These solutions thrive in sectors where immediate, localized decisions are critical—cementing sensor data as the core driver for edge AI software development and implementation globally.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific is currently leading edge AI software market. However, North America with second largest market share is poised to grow at robust CAGR of 36.3%. One of the key reasons is the high concentration of top-tier tech giants and research institutions headquartered in the US—Google, Microsoft, Intel, and NVIDIA collectively fund more than 25 active AI research labs that specialize in edge computing. In addition, the US Department of Defense supports at least 15 ongoing edge AI pilot programs for real-time data processing in unmanned vehicles, creating fertile ground for innovation. Another driving force is the vibrant startup ecosystem; at least 300 new AI-focused ventures launch in Silicon Valley each year, many targeting edge deployments for applications such as industrial IoT, healthcare diagnostics, and autonomous retail. The region also boasts a robust network of GPU and ASIC manufacturers—Xilinx, AMD, and Qualcomm collectively ship over 2 million integrated circuits annually to power emerging on-device intelligence.
American enterprises in the edge AI software market heavily invest in a wide range of verticals. Amazon, with more than 600,000 small business sellers using its platform, has developed edge-based supply chain optimization software to aid partners in inventory forecasting. John Deere, operating 23 test farms, implements computer vision on agricultural machinery to spot weeds in real time. Pfizer supports at least 10 pilot projects for on-site drug quality checks using edge analytics in manufacturing lines. Walmart leverages AI cameras in upwards of 3,000 stores to manage shelf stock and detect unusual activity. IBM, delivering advanced AI libraries to more than 2,500 global enterprises, underscores the country’s role in shaping commercial-scale adoption of localized analysis.
Looking ahead, federal initiatives in the North America edge AI software market such as the proposed expansion of the National AI Institute promise to finance additional applied research in synergy with private sector programs. Telecommunications giants—including AT&T—are rolling out 5G coverage in at least 2,500 urban zones, paving the way for more sophisticated, low-latency edge applications. As data privacy mandates tighten, large-scale US-based providers plan to embed hardware-level encryption in new chipsets. This approach not only fosters trust among end users but also solidifies the region’s ability to produce secure, high-performance edge AI software. Consequently, North America is primed for sustained leadership, buoyed by policy support, industrial demand, and permanent innovation hubs.
Top Companies in the Edge AI Software Market:
- Alef Edge, Inc.
- Anagog Ltd.
- AWS
- Azion Technologies
- Bragi.Com
- Chaos Prime, Inc.
- Clearblade, Inc.
- Foghorn Systems, Inc.
- Gorilla Technology Group, Inc.
- IBM
- Imagimob
- Microsoft
- Nutanix
- Octonion
- Sixsq Sarl
- Synaptics
- TACT.AI
- TIBCO Software
- Veea Inc.
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Component
- Solution
- Software Tools
- Platform
- Services
- Training and Consulting Services
- System Integration Testing
- Support and Maintenance
By Data Source
- Biometric Data
- Mobile Data
- Sensor Data
- Speech Recognition
- Video and Image Recognition
By Application
- Access Control
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Energy Management
- Predictive Maintenance
- Remote Monitoring
- Telemetry
- Video Surveillance
- Others
By End Users
- Advance Industries
- Banking and Insurance
- Chemical Agriculture
- Consumers
- Cross Vertical
- Energy And Material
- Health Care Infrastructure
- Media and Entertainment
- Public Sector Utilities
- Retail
- Travel, Transport, and Logistics
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
View Full Infographic
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 2.89 Bn |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 45.75 Bn |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Bn) |
| CAGR | 35.9% |
| Segments covered | By Component, By Data Source, By Application, By End Users, By Region |
| Key Companies | Alef Edge, Inc., Anagog Ltd., AWS, Azion Technologies, Bragi.Com, Chaos Prime, Inc., Clearblade, Inc., Foghorn Systems, Inc., Google, Gorilla Technology Group, Inc., IBM, Imagimob, Microsoft, Nutanix, Octonion, Sixsq Sarl, Synaptics, TACT.AI, TIBCO Software, Veea Inc., Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST

 | Report ID: AA1121103 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours
| Report ID: AA1121103 | Delivery: 2 to 4 Hours 
.svg)






