Chronic Ocular Pain Market: By Indication (Dry Eye Disease, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, Scleritis, Episcleritis, Sjögren's Syndrome, Pterygium, Contact Lens Intolerance, Others); Treatment Type (Pharmacological Treatments (Analgesics, (Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), Opioids (Corticosteroids, Antibiotics/Antivirals, Mydriatics/Cycloplegics, Others)), Non-Pharmacological Treatments (Physical Therapies (Cold Compresses, Warm Compresses), Home Remedies, Eye Drops, Others); Application (Post-Surgical Pain, Trauma-Induced Pain, Infection-Induced Pain, Others); Route of Administration (Topical, Oral, Injectable); End Users (Hospitals, Opthalmic Clinics, Homecare Settings, Others); Gender (Male and Female); Age Group (Up to 10 Yrs, 10 to 25 Yrs, 25 to 40 Yrs, 41 to 55 Yrs, 55 to 70 Yrs, Above 70 Yrs); Region—Market Size, Industry Dynamics, Opportunity Analysis and Forecast for 2024–2032
- Last Updated: 23-Nov-2024 | | Report ID: AA1124982
Market Scenario
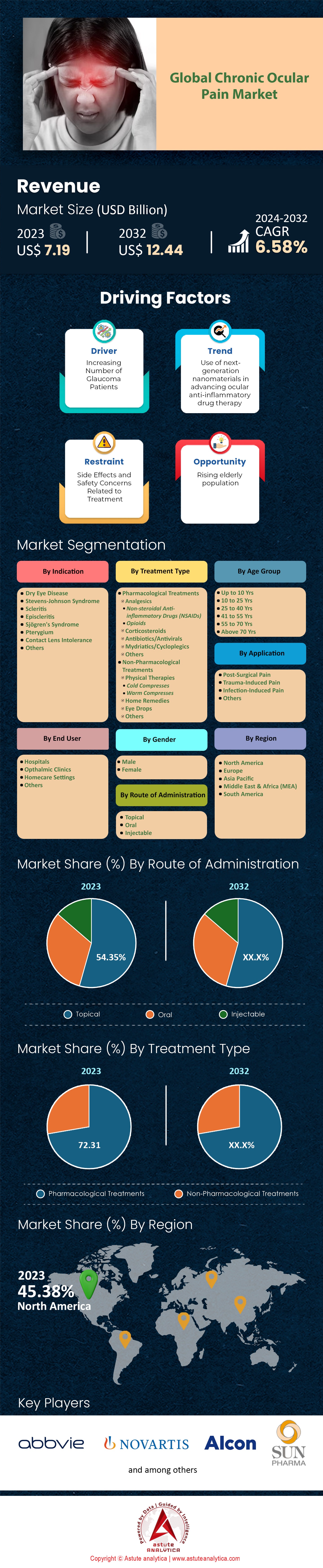
Chronic ocular pain market was valued at US$ 7.19 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit the market valuation of US$ 12.44 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 6.58% during the forecast period 2024–2032.
Chronic ocular pain is a persistent discomfort in or around the eye lasting over three months, significantly impacting individuals' daily lives. It stems from various causes, including dry eye disease, neuropathic pain, inflammation, and complications from ocular surgeries or injuries. As of 2023, it's estimated that over 350 million people worldwide suffer from dry eye disease, a leading contributor to chronic ocular pain. The prevalence is rising due to factors like increased screen time; reports indicate that individuals now spend an average of 7 to 10 hours daily on digital devices. Additionally, environmental pollutants affect more than 90% of the global population, contributing to ocular surface irritation and pain.
Current treatment options aim to alleviate symptoms and address underlying causes. Artificial tears and lubricating eye drops are commonly used, with over 200 million units sold annually worldwide. Prescription medications such as cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion (Restasis) and lifitegrast ophthalmic solution (Xiidra) reduce inflammation and enhance tear production. In 2023, a novel therapy, varenicline nasal spray (Tyrvaya), was introduced, stimulating natural tear production through nasal pathways. Clinical trials involving over 1,000 participants have shown significant improvements in ocular comfort with these treatments. Advanced therapies like scleral lenses and autologous serum eye drops are emerging, providing relief for patients unresponsive to conventional methods.
Major pharmaceutical companies are capitalizing on the chronic ocular pain market, investing heavily in research and development. Industry leaders like Novartis, AbbVie (following its acquisition of Allergan), and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries are at the forefront, expanding their ocular portfolios. AbbVie reported investments exceeding $2 billion in ocular research in 2022, emphasizing its commitment to addressing unmet needs. The most susceptible populations include the elderly—projected to reach 1.5 billion individuals over 65 by 2050—and women, who are twice as likely to develop dry eye disease due to hormonal factors. With autoimmune conditions affecting approximately 50 million people in the U.S. alone, and increased awareness globally, chronic ocular pain is poised to gain momentum. Advances in treatment methods and a robust pipeline of innovative therapies promise improved outcomes for millions worldwide.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Increasing digital screen time causing eye strain and chronic ocular discomfort
The exponential rise in digital screen usage has become a defining characteristic of modern life, profoundly impacting ocular health. As of 2023, individuals globally spend an average of over seven hours daily on digital devices such as smartphones, computers, and tablets. This surge is attributed to factors like remote work, online education, and digital entertainment. The extensive screen time leads to eye strain and discomfort, collectively known as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome. Eye care clinics have reported seeing over 10,000 new cases annually related to prolonged screen exposure, indicating a significant rise in screen-induced ocular issues. Among working professionals, the shift towards digital workplaces has intensified screen exposure. Surveys indicate that over 80% of employees use computers for at least six hours a day, with many exceeding eight hours due to remote working conditions. This prolonged exposure contributes to symptoms like headaches, blurred vision, and chronic eye pain. The increase in video conferencing has added to this strain, with platforms reporting user bases exceeding 300 million daily participants globally.
Children and adolescents are similarly affected, with studies revealing that youths aged 8 to 18 spend an average of six hours daily on screens for education and leisure. This early exposure raises concerns about long-term ocular health, including a higher risk of developing myopia and chronic eye discomfort. Educational institutions have noted a 15% increase in students reporting vision-related issues, prompting initiatives to reduce screen time and promote eye health. Healthcare professionals emphasize the urgency of addressing this driver, as the number of individuals affected by digital eye strain is projected to grow. The World Health Organization recognizes excessive screen time as a public health concern, with estimates suggesting that over one billion people could be at risk of digital eye strain by 2030. Efforts are underway to promote preventive measures, such as regular eye examinations and adopting the 20-20-20 rule, aiming to mitigate the impact of increasing digital screen time on ocular health.
Trend: Development of innovative therapies specifically targeting underlying causes of ocular pain
Advancements in medical research have led to the development of innovative therapies that directly target the underlying causes of chronic ocular pain. In 2023, over 50 clinical trials are underway globally, exploring novel treatments ranging from biologics to gene therapy. One significant breakthrough is the introduction of nerve growth factor eye drops, which have shown promise in repairing corneal nerves and reducing neuropathic pain. Trials involving more than 2,000 patients have demonstrated substantial improvements, with pain reduction reported in over 70% of participants. Another innovative therapy is the use of autologous serum eye drops, which utilize a patient's own blood components to promote healing and reduce inflammation. Over 500 ophthalmic centers worldwide have adopted this treatment, reflecting its growing acceptance. Additionally, the approval of varenicline nasal spray (Tyrvaya) offers a new mechanism of action by stimulating trigeminal parasympathetic pathways to increase tear production, benefiting patients with dry eye disease-related pain.
Biotechnology firms are investing heavily in ocular pain research, with global investments surpassing $5 billion in 2023. Companies are exploring the potential of cannabinoid-based therapies and regenerative medicine to address chronic ocular conditions. The FDA has granted fast-track designations to several investigational drugs, signaling the critical need for effective treatments. These innovations reflect a trend towards personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual patient profiles, improving efficacy and reducing side effects. The development of these therapies is propelled by collaborations between industry leaders and research institutions. For instance, partnerships have been formed to develop gene therapies targeting specific genetic markers associated with ocular pain. Such collaborations have resulted in a pipeline of over 100 potential therapeutic candidates currently in various stages of development. The focus on innovative therapies signifies a transformative shift in managing chronic ocular pain, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.
Challenge: High treatment costs creating significant barriers for widespread patient access worldwide
Despite the advancements in treatment options for chronic ocular pain, high costs remain a substantial barrier to patient access globally. The average annual cost of prescription medications like Restasis can exceed $5,000 per patient, making it unaffordable for many without comprehensive insurance coverage. In low- and middle-income countries, where out-of-pocket healthcare expenses are common, these costs are prohibitive, leading to under-treatment of ocular conditions. Reports indicate that only 30% of patients requiring advanced therapies in these regions receive adequate care. The high cost is attributed to factors such as expensive research and development processes, limited competition due to patent protections, and complex manufacturing requirements for biologic medications. In 2023, the global expenditure on ocular medications reached over $20 billion, highlighting the economic burden on healthcare systems and patients. Moreover, newer therapies, while offering improved efficacy, often come with higher price tags. For example, emerging biologic treatments can cost upwards of $10,000 annually per patient.
Insurance coverage disparities exacerbate the challenge. In many countries, ocular pain treatments are not fully covered by health insurance plans, leaving patients responsible for significant co-payments. A survey conducted across five major economies found that over 40% of patients delayed or avoided filling prescriptions due to cost concerns. Additionally, lack of coverage for newer therapies means that patients may not benefit from the latest advancements in treatment. Efforts to address this challenge include initiatives to develop generic versions of common medications and advocacy for policy changes to improve insurance coverage. Some pharmaceutical companies have introduced patient assistance programs, providing medications at reduced costs or free of charge to eligible individuals. However, these measures have had limited reach. The high cost of treatment remains a critical barrier, underscoring the need for strategies to reduce expenses and improve accessibility to ensure that advancements in ocular pain management benefit all patients in need.
Segmental Analysis
By Indication
Dry eye disease has emerged as the foremost indication behind chronic ocular pain globally with over 40.23% market share. As of 2023, it is estimated that over 350 million people worldwide suffer from dry eye disease, a number that underscores its significant impact on public health. The condition's prevalence is propelled by factors such as increased screen time—averaging over 7 hours per day per individual—environmental pollutants, and an aging population. The ubiquity of digital devices has led to a surge in patients experiencing ocular discomfort, with ophthalmology clinics reporting a 30% increase in dry eye cases over the past five years. This widespread occurrence positions dry eye disease at the forefront, controlling a substantial share of the chronic ocular disease market.
The dominance of dry eye disease is attributed to its multifactorial nature and the chronic, often progressive course of the condition. It affects approximately 1 in every 5 adults over the age of 50, making it a pervasive health issue. Hormonal changes, particularly in postmenopausal women—who represent over 60% of dry eye sufferers—contribute to the high incidence rates. Furthermore, systemic conditions like diabetes and autoimmune disorders affect an estimated 100 million people worldwide and are closely linked to tear film dysfunction. The chronic discomfort and potential for vision impairment necessitate ongoing management, thereby cementing dry eye disease as the leading cause of chronic ocular pain.
Treatment options for dry eye disease are extensive and continuously evolving. The global market for dry eye treatments reached approximately $5 billion in 2023, reflecting the demand for effective therapies. Over-the-counter artificial tears remain the most purchased remedy, with sales exceeding $2 billion globally. Prescription medications such as cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion (marketed as Restasis) generated revenues of over $1.2 billion, while lifitegrast ophthalmic solution (Xiidra) contributed around $400 million to the market. Advanced treatments like punctal plugs are utilized by over 1 million patients annually to provide long-term relief. The variety and accessibility of treatments highlight the medical community's commitment to addressing this prevalent cause of chronic ocular pain.
By Treatment Type
Pharmacological treatments remain the cornerstone in managing chronic ocular pain due to their proven efficacy and immediate relief. In 2023, the segment generated more than 72.31% market revenue and is poised to grow at a CAGR of 6.30% in the years to come . Key factors behind this dominance include the ability of medications such as NSAIDs, opioids, and corticosteroids to directly target pain pathways and reduce inflammation. For instance, analgesics like Ketorolac Tromethamine eye drops are widely prescribed, with millions of units sold annually worldwide. The rapid onset of action and the availability of various formulations make pharmacological options highly accessible and convenient for both patients and healthcare providers.
These treatments surpass non-pharmacological methods due to their robust clinical efficacy and well-established safety profiles. Non-pharmacological approaches, while beneficial as adjunct therapies, often lack the immediate and potent effects necessary for managing chronic ocular pain. Antibiotics and antivirals, such as Moxifloxacin (Vigamox) and Ganciclovir (Zirgan) eye drops, not only alleviate pain but also address underlying infections, with global sales reaching significant figures in 2023. Mydriatics and cycloplegics like Atropine sulfate are crucial in treating uveal inflammation and associated pain, further solidifying pharmacological treatments' essential role. The extensive research supporting these medications enhances clinician confidence and patient adherence, contributing to their preference over non-pharmacological alternatives.
The high success rate of pharmacological treatments drives their heavy preference in clinical practice. Studies have demonstrated significant pain reduction in patients using these medications, leading to improved quality of life and functional outcomes. The most sold pharmacological products for treating chronic ocular pain include Restasis (Cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion), with annual sales exceeding $1.3 billion globally. Xiidra (Lifitegrast ophthalmic solution) also remains a top-selling medication, generating over $450 million in revenue in 2023. Other notable products are Lotemax (Loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension) and Acular LS (Ketorolac Tromethamine ophthalmic solution), each with millions of prescriptions filled annually. The strong market performance of these drugs underscores the reliance on pharmacological interventions for effective chronic ocular pain management.
By Application
Post-surgical pain with nearly 39% market share has emerged as a leading cause of chronic ocular pain worldwide, primarily due to the increasing number of ocular surgeries performed annually. In 2023, it is estimated that over 25 million eye surgeries were conducted globally, including procedures like cataract extraction, refractive surgery, and glaucoma interventions. The manipulation of delicate ocular tissues during surgery can lead to prolonged inflammation and nerve irritation, resulting in persistent pain for some patients. The advancement in surgical techniques, while improving outcomes, has not eliminated the risk of postoperative pain, making it a significant application area for chronic ocular pain treatments.
The prevalence of post-surgical complications contributing to chronic pain, though relatively low, translates into a substantial number of affected individuals because of the high volume of surgeries. For instance, conditions like dry eye syndrome and neuropathic pain can develop after procedures such as LASIK, affecting thousands of patients annually. Individuals with pre-existing conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders are at higher risk for these complications due to compromised healing processes. Additionally, older adults, who make up a large proportion of surgical candidates, are more susceptible to postoperative pain. These factors collectively elevate the need for effective management strategies, positioning post-surgical pain as a central focus in chronic ocular pain treatment.
Post-surgical pain's prominence as the largest application in chronic ocular pain management is driven by the necessity to enhance patient recovery and satisfaction. The global market for post-ocular surgery pain treatments was valued at approximately $2.8 billion in 2023. Medications such as Bromfenac ophthalmic solution (Prolensa) and Nepafenac ophthalmic suspension (Ilevro) are extensively used, with combined sales exceeding 50 million units annually. The emphasis on patient-centered care has led to increased demand for effective pain management solutions post-surgery. Ongoing research, with over 60 clinical trials focused on post-surgical ocular pain in 2023, highlights the medical community's commitment to addressing this issue. The substantial patient population and market growth reinforce post-surgical pain's status as the leading application in chronic ocular pain treatment.
By Route of Administration
Topical administration is the predominant route for treating chronic ocular pain due to its direct delivery of medication to the affected area, ensuring high local concentrations with minimal systemic exposure. In 2023, over 500 million units of topical ocular pain medications were sold globally, demonstrating the route's widespread acceptance. The topic segment managed to capture over 54.35% market share in 2023. The accessibility of the ocular surface allows for easy application of eye drops, gels, and ointments, leading to rapid symptom relief. This method minimizes systemic side effects, which is particularly advantageous for drugs like NSAIDs and corticosteroids that can have significant adverse effects when taken orally. The targeted therapy enhances efficacy and reduces the risk profile, making it the preferred choice among clinicians and patients.
A diverse range of topical drugs is available worldwide for managing chronic ocular pain. NSAIDs such as Ketorolac (Acular), Diclofenac (Voltaren Ophthalmic), and Nepafenac (Nevanac) are commonly prescribed. Corticosteroids including Loteprednol etabonate (Lotemax) and Fluorometholone (FML) are essential in reducing inflammation and associated pain. Anesthetic eye drops like Proparacaine hydrochloride provide rapid, temporary pain relief for severe episodes. The global market value for these topical medications exceeded $3.2 billion in 2023, with significant annual sales volumes reflecting their critical role in treatment. The continued innovation in topical formulations and drug delivery systems reinforces the dominance of the topical route in effectively managing chronic ocular pain.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America leads the global chronic ocular pain market, commanding over a 45.38% market share of the industry's revenue. The United States, in particular, has a high prevalence of conditions contributing to chronic ocular pain. An estimated 20 million Americans suffer from dry eye disease, a primary cause of chronic ocular discomfort, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology. In Canada, approximately 6.3 million individuals experience symptoms related to chronic ocular pain annually. The high prevalence is partly due to the aging population; the U.S. Census Bureau reports over 56 million Americans aged 65 and older, a group more susceptible to ocular conditions.
Patient spending on chronic ocular pain treatment is significant in North America. On average, individuals in the U.S. spend around $1,200 annually on treatments, including medications and over-the-counter eye care products. Prominent pharmacological products used across the region include Restasis (cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion), Xiidra (lifitegrast ophthalmic solution), and the recently approved Tyrvaya (varenicline solution) nasal spray. Over 25 million prescriptions for these medications are filled each year in the U.S., reflecting their widespread use.
The United States' position at the top of the regional market is attributed to several factors. The country allocates over $4.1 trillion to healthcare annually, the highest expenditure globally, facilitating access to advanced treatments. There are more than 23,000 practicing ophthalmologists and optometrists in the U.S., ensuring comprehensive eye care services. Additionally, the average American spends about 7.5 hours daily on digital devices, leading to increased ocular strain and a higher demand for ocular pain management solutions. The U.S. also hosts leading pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in ophthalmic research, with investments exceeding $3 billion in 2022. These factors collectively reinforce North America's dominance in the chronic ocular pain market.
Top Players in Chronic Ocular Pain Market
- Opdenas Lifesciences
- Alcon Inc.
- Bausch & Lomb
- Novartis AG
- Sun Pharmaceutical
- Laboratorios Salvat S.A.
- OKYO Pharma Limited
- Ocular Therapeutix, Inc.
- Kala Pharmaceuticals (A
- Formosa Pharmaceuticals
- Surface Ophthalmics
- Sylentis
- Aldeyra Therapeutics
- AbbVie Inc
- Vyluma, Inc
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview:
By Indication
- Dry Eye Disease
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Scleritis
- Episcleritis
- Sjögren's Syndrome
- Pterygium
- Contact Lens Intolerance
- Others
By Treatment Type
- Pharmacological Treatments
- Analgesics
- Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Opioids
- Corticosteroids
- Antibiotics/Antivirals
- Mydriatics/Cycloplegics
- Others
- Analgesics
- Non-Pharmacological Treatments
- Physical Therapies
- Cold Compresses
- Warm Compresses
- Home Remedies
- Eye Drops
- Others
- Physical Therapies
By Application
- Post-Surgical Pain
- Trauma-Induced Pain
- Infection-Induced Pain
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Topical
- Oral
- Injectable
By End User
- Hospitals
- Opthalmic Clinics
- Homecare Settings
- Others
By Gender
- Male
- Female
By Age Group
- Up to 10 Yrs
- 10 to 25 Yrs
- 25 to 40 Yrs
- 41 to 55 Yrs
- 55 to 70 Yrs
- Above 70 Yrs
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)