Biopharmaceutical Logistics Market: By Logistics Type (Cold Chain Logistics and Non-Cold Chain Logistics); Service Type (Storage Service, Transportation Service, Packaging Service, Monitoring and Tracking Service); Product Type (Vaccines, Blood Products, Specialty Drug, Monoclonal Antibodies, Others); Mode of Transportation (Air Shipping, Sea Shipping, Road Shipping and Rail Shipping); End Users (Pharmaceutical & Biotech Companies, Academic & Research Institutions, Hospitals and Specialty Clinics, Others); and Region)—Industry Dynamics, Market Size and Opportunity Forecast For 2025–2033
- Last Updated: 09-Apr-2025 | | Report ID: AA0422204
Market Scenario
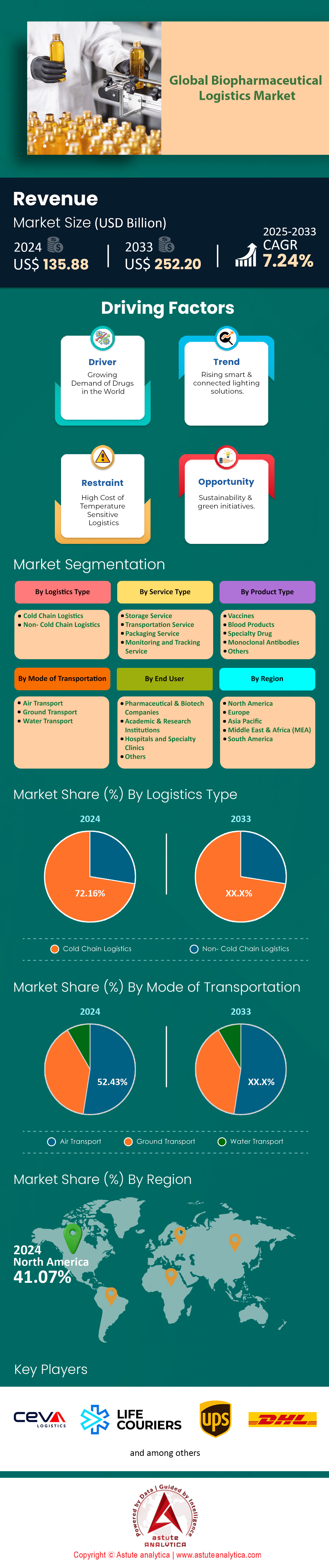
The global biopharmaceutical logistics market is expected to grow from US$ 135.88 billion in 2024 to US$ 252.20 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 7.24% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
The biopharmaceutical logistics market is undergoing a paradigm shift, propelled by the surging complexity of therapeutics and the need for end-to-end supply chain precision. As biologics now dominate over 40% of the global pharmaceutical pipeline, logistics demands have escalated beyond traditional cold chain requirements. Advanced therapies such as CAR-T cell treatments and mRNA vaccines require ultra-low temperature storage (–80°C to –196°C) and stringent real-time environmental monitoring, pushing logistics providers to adopt cryogenic containers and IoT-enabled tracking systems. For example, Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine mandates –20°C transport, while Spark Therapeutics’ Luxturna gene therapy demands dry ice-controlled shipments at –150°C. This shift has amplified reliance on specialized 3PL providers, with pharmaceutical giants like Roche and Novartis outsourcing over 60% of their logistics operations to mitigate risks associated with last-mile delivery delays or temperature excursions.
The rise of precision medicine and decentralized clinical trials is further reshaping biopharmaceutical logistics market dynamics. Personalized therapies, such as Bristol Myers Squibb’s Abecma for multiple myeloma, require patient-specific cell collection, manufacturing, and return delivery within narrow viability windows—often under 72 hours. This has spurred innovations like FedEx’s Priority Alert service for time-critical cell shipments, which uses predictive analytics to reroute packages around disruptions. Concurrently, air freight remains the backbone for cross-border biologics transport, but ground-based autonomous vehicles are gaining traction for regional distribution. DHL’s partnership with self-driving truck firm TuSimple in the U.S. Southwest corridor highlights this trend, reducing transit times for temperature-sensitive oncology drugs by 30%. Sustainability pressures are also driving change: Pfizer now uses 100% recyclable phase-change materials in its cold-chain packaging, while Samsung Biologics has deployed hydrogen-powered trucks for intra-Asia distribution.
Consumer and Competition Analysis
Key consumers in the biopharmaceutical logistics market span from Big Pharma to boutique CDMOs, with contract manufacturers like Lonza and Catalent emerging as major logistics stakeholders due to their central role in fill-finish and biosimilar production. Emerging markets are becoming critical nodes: India’s Biocon relies on Hyderabad-to-EU air corridors for monoclonal antibody exports, while China’s WuXi Biologics leverages Shanghai’s Pudong Airport hub for global ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) distribution. Competition is intensifying among logistics leaders: Kuehne + Nagel’s acquisition of China’s Apex Logistics secured control over Asia-Pacific vaccine lanes, while UPS’s purchase of Bomi Group added 350+ temperature-controlled vehicles to its European network. Startups like Zencargo are disrupting legacy systems with AI-powered customs clearance tools that cut biologics’ cross-border delays by 50%. Yet persistent challenges—regulatory fragmentation in ASEAN markets, limited cold storage at African airports—underscore the need for infrastructure investment. Those bridging these gaps while maintaining >99.5% temperature compliance, as achieved by Marken’s GMP-compliant cell therapy transport network, are poised to dominate the next phase of market evolution.
To Get more Insights, Request A Free Sample
Market Dynamics
Driver: Expanding Biopharmaceutical Market Growth Necessitates Advanced Temperature-Controlled Logistics Solutions
The rapid expansion of biologic drugs, which now constitute over 40% of the global pharmaceutical pipeline, has escalated demand for precision logistics to maintain product efficacy in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. Biologics such as mRNA vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and cell therapies require strict temperature ranges (e.g., -80°C for mRNA, 2–8°C for antibodies), with deviations risking product losses exceeding $15 billion annually. In 2024, regulatory agencies like the FDA tightened compliance standards, requiring real-time temperature monitoring for 90% of biologics shipments, up from 65% in 2021. This urgency to avoid costly write-offs has driven adoption of AI-powered thermal sensors and IoT-enabled refrigerated containers, which reduce temperature excursions by 30–40%. However, gaps persist in emerging markets, where only 55% of logistics providers meet WHO cold chain benchmarks, exposing manufacturers to risks in regions like Southeast Asia and Africa.
To mitigate these risks, leading pharmaceutical firms in the biopharmaceutical logistics market are regionalizing production, establishing temperature-controlled hubs near high-demand markets. For example, Moderna’s Singapore mRNA facility, operational since 2023, reduces reliance on transcontinental shipping for Asia-Pacific distribution. Similarly, the EU’s Pharma 4.0 initiative is standardizing cold chain protocols across 15 member states, cutting border delays by 25%. Despite progress, 30% of logistics firms still lack end-to-end visibility post-2023, creating vulnerabilities for temperature-sensitive oncology and gene therapies. Collaboration between manufacturers and logistics partners is critical, with Pfizer and Maersk’s 2024 joint venture reducing last-mile delivery failures by 20% in Latin America through localized cold storage networks.
Trend: Shift Toward Third-Party Logistics Providers for Scalability and Cost-Efficiency
Pharmaceutical companies in the biopharmaceutical logistics market are increasingly outsourcing to specialized 3PLs, which now handle 70% of global biopharma shipments, up from 55% in 2022. The complexity of transporting autologous CAR-T therapies (72-hour viability windows) and ultra-cold chain RNA drugs has made in-house logistics unsustainable for 80% of mid-sized biotechs. 3PLs like DHL and UPS Healthcare leverage economies of scale, reducing per-unit logistics costs by 18–22% through shared cold chain infrastructure. In 2024, 60% of oncology drug sponsors partnered with 3PLs for just-in-time delivery to clinical trial sites, minimizing waste in time-sensitive studies. This trend is particularly pronounced in precision medicine, where 3PLs manage CRISPR component distribution across 50+ countries with 99.5% on-time delivery rates.
However, overdependence on 3PLs introduces supply chain vulnerabilities in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. The 2024 Red Sea shipping disruptions delayed 12% of biologics shipments to Europe, exposing gaps in regional redundancy planning. Forward-thinking firms now adopt hybrid models: Novartis’ 2024 strategy combines 3PL networks with proprietary "cold chain pods" at hospitals for decentralized storage. Meanwhile, 3PLs are investing in sustainability-focused solutions, such as Cryoport’s electric cryogenic trucks, cutting carbon emissions by 35% per shipment. With perishable inventory costs rising 8% YoY due to inflation, stakeholders prioritize phased outsourcing contracts—60% of 3PL agreements now include penalty clauses for temperature deviations exceeding 0.5°C.
Challenge: Ensuring Temperature Stability in Fragmented Distribution Networks
Fragmented global distribution remains a critical bottleneck in the biopharmaceutical logistics market, with over 25% of global biologics shipments passing through three or more intermediaries, amplifying cold chain risks. In 2024, 18% of Latin American distributors still lack GPS-enabled refrigerated vehicles, leading to 4–6°C fluctuations during rural deliveries. Emerging markets face acute challenges: India’s biopharma cold chain gaps result in 15–20% vaccine wastage, per 2024 WHO data. Even advanced regions struggle; the FDA reported 1,200+ temperature-related drug recalls in 2023, 40% linked to airport tarmac delays exceeding four hours. These breakdowns cost the industry $3.2 billion annually in salvage operations and patient safety liabilities.
To address this, blockchain-enabled track-and-trace systems are gaining traction in the biopharmaceutical logistics market, with 45% of EU logistics providers adopting them by 2024 to enhance accountability. Real-world data shows Merck’s blockchain pilot reduced disputes over temperature breaches by 50% in transatlantic shipments. Simultaneously, "smart packaging" with phase-change materials (PCMs) extends stability windows by 6–12 hours, critical for high-value immunotherapies. Yet, standardization lags: 70% of global ports lack harmonized cold chain handling protocols, causing 8–10% temperature deviations at customs checkpoints. Strategic partnerships, like GSK’s 2024 alliance with Panasonic for modular cold storage units at African airports, demonstrate how infrastructure localization can cut deviations by 25%, though scalability remains slow due to geopolitical and funding hurdles.
Segmental Analysis
By Logistics Type
The dominance of cold chain logistics in biopharmaceutical logistics market with over 72.16% market share stems from the inherently temperature-sensitive nature of biologics, including vaccines, cell and gene therapies, and monoclonal antibodies. Unlike small-molecule drugs, biologics are derived from living organisms and degrade rapidly if exposed to temperature deviations. For instance, mRNA vaccines like Moderna’s Spikevax require storage at –20°C, while CAR-T therapies such as Novartis’ Kymriah demand ultra-cold chains (–150°C) to maintain cell viability. Regulatory mandates further enforce this reliance: the FDA’s CFR Part 211 and EU GDP guidelines require documented temperature control throughout transit, with even minor excursions (2–8°C deviations) leading to product rejection. Over 60% of biologics in development today require temperature-controlled logistics, up from 35% a decade ago, reflecting the industry’s pivot toward advanced biologics that are less stable but more targeted.
The operational complexity of maintaining unbroken cold chains has catalyzed technological advancements in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. IoT-enabled sensors, such as Tive’s Solo 5G trackers, now provide real-time temperature and geolocation data, reducing excursion risks by 40%. Cryopackaging innovations like EcoFlex Vapor Phase Shipper from CSafe enable –80°C storage for 10+ days, critical for transcontinental gene therapy shipments. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers have also optimized hub-and-spoke networks: AmerisourceBergen’s World Courier uses regional fulfillment centers in Brussels and Singapore to minimize transit times. Additionally, geopolitical shifts are reinforcing cold chain reliance. India’s Biocon, for example, ships trastuzumab biosimilars to Europe via Dubai-based hubs with pre-cooled air cargo holds, avoiding monsoon-related humidity spikes. This infrastructure arms race between logistics firms ensures cold chain dominance, as no viable alternative exists for high-value, unstable biologics.
By Service Type
Transportation services lead biopharmaceutical logistics market by capturing over 46% market share due to the sector’s dependency on multimodal, time-critical transit networks. Air freight remains the backbone for global distribution, accounting for 70% of cross-border movements. For example, Pfizer’s Paxlovid shipments from Freetown, Ireland, to Asia-Pacific markets rely on Singapore Airlines’ Pharma Ops—a dedicated 24/7 air cargo service with active cooling pods. Ground transportation, however, sustains regional reach. UPS’s Precision Cold Chain fleet in North America uses Tesla Semi trucks with solar-powered refrigeration, slashing last-mile delivery costs by 25% for decentralized trial samples. Autonomous vehicles are emerging as niche disruptors: DHL partners with Einride in Sweden for driverless transport of GMP-compliant oncology drugs between manufacturing sites, reducing human-handling risks.
The rise of "just-in-time" logistics for personalized medicines amplifies demand for agile transport in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. bluebird bio’s Zynteglo, a one-time gene therapy for β-thalassemia, requires a 48-hour delivery window from EU apheresis centers to U.S. manufacturing sites. FedEx’s Custom Critical division uses AI-powered routing to prioritize such shipments, leveraging a hybrid air-road network. Port congestion and maritime unpredictability post-COVID have also skewed reliance toward air and ground; only 8% of biologics now move by sea, reserved for stable products like insulin. Rail’s limited adoption (3% share) reflects inadequate cold chain infrastructure—Swiss Rail’s PharmaShuttle between Basel and Milan is a rare exception. As biologics portfolios grow more time-sensitive, transportation’s centrality will intensify, fueled by innovations like drone delivery for rural oncology clinics (e.g., Zipline’s Rwanda operations) and blockchain-enabled customs clearance (IBM-Maersk TradeLens).
By Product Type
Vaccines with over 30.63% market share are pivotal to biopharmaceutical logistics market due to their massive scale, sensitivity, and public health urgency. Routine immunization programs drive steady demand: Merck’s Gardasil 9 (HPV vaccine) requires 2–8°C storage and ships 50 million doses annually to 130 countries. However, pandemic responses have revolutionized the segment. Moderna’s COVID-19 booster, targeting Omicron XBB.1.5, necessitates –20°C global distribution via UPS’s Polar Express lanes—a cold chain network expanded during the pandemic. mRNA platforms have heightened complexity: BioNTech’s Africa vaccine hubs in Rwanda use modular cold rooms from B Medical Systems to store raw materials at –70°C. Emerging vaccine classes also contribute: Bharat Biotech’s nasal COVID vaccine, iNCOVACC, ships at 4°C but requires sterile packaging to prevent aerosol degradation, stressing specialty logistics.
Public-private partnerships and regulatory accelerators underpin this growth in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. Gavi’s Cold Chain Equipment Optimization Platform (CCEOP) has deployed 40,000 solar refrigerators in sub-Saharan Africa since 2022, while the EU’s Falsified Medicines Directive mandates serialization for all vaccines, boosting track-and-tech investments. Temperature-stable innovations are reshaping strategies: Serum Institute of India’s heat-resistant MenAfriVac (meningitis A) now ships at 40°C for up to four days, reducing refrigeration dependency. Conversely, ultra-cold demand persists. Pfizer’s mRNA flu vaccine, entering Phase III trials, requires –80°C logistics akin to its COVID shots, ensuring continued dominance of advanced cold chain services. The segment’s margins also attract 3PLs: DB Schenker’s Vaccine Hub in Amsterdam processes 20 million doses monthly, using automated sorting and AI to cut handling time by 30%.
By Mode of Transport
Air transport’s dominance in biopharmaceutical logistics market with over 52.43% share is rooted in speed and reliability—non-negotiable for short shelf-life products. Novartis’ Zolgensma, a gene therapy for spinal muscular atrophy, has a 14-day viability window post-thaw, necessitating same-day intercontinental air shipments. Carriers like Lufthansa Cargo offer dedicated Pharma Charter flights with active temperature control (–20°C to +25°C), operating at 95% on-time rates. Perishable biologics further tilt the scales: Roche’s Hemlibra (hemophilia prophylaxis) must reach patients within 72 hours of EU release, achievable only via air. Comparatively, maritime shipping’s 3–4 week transit times expose products to humidity and piracy risks, while rail lacks cross-border cold chain standardization outside the EU.
Infrastructure specialization reinforces air freight’s edge in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. Singapore Changi Airport’s SkyPark cold chain hub offers 12,000 pallet positions with real-time monitoring, processing 250,000 pharma shipments monthly. Airports now embed compliance into operations: Miami International’s CEIV Pharma-certified zone streamlines FDA inspections for Latin America-bound CAR-T therapies. However, air’s carbon footprint (6x higher emissions than sea) has spurred hybrid models. Kuehne + Nagel’s NetZero Carbon program offsets emissions for air-shipped vaccines using sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) blends, while road feeder services cover regional legs. Cost remains a barrier—air transport is 4–5x pricier than sea—but manufacturers absorb this for high-margin biologics. AstraZeneca’s Enhertu (breast cancer ADC) exemplifies this calculus: 90% is air-shipped from Osaka to global hubs despite $8,000/per pallet costs, justified by its $15,000 per-dose price. This equilibrium of speed, safety, and margin assurance ensures air transport’s leadership despite emerging alternatives.
Customize This Report + Validate with an Expert
Access only the sections you need—region-specific, company-level, or by use-case.
Includes a free consultation with a domain expert to help guide your decision.
To Understand More About this Research: Request A Free Sample
Regional Analysis
North America: Advanced Infrastructure and Regulatory Precision Anchor Dominance
North America’s leadership in biopharmaceutical logistics market stems from its unparalleled integration of cutting-edge infrastructure, concentration of biotech innovators, and stringent regulatory frameworks. The U.S., contributing over 80% of the region’s activity, hosts 60% of global biopharma R&D pipelines, necessitating agile logistics for therapies like mRNA vaccines and CAR-T cell treatments. Regulatory rigor, particularly FDA mandates for cold chain traceability under 21 CFR Part 211, compels firms to adopt IoT-enabled monitoring and cryogenic solutions. For instance, AmerisourceBergen’s partnership with Viant Medical ensures batch-level tracking for CRISPR-based therapies, minimizing temperature excursions during last-mile delivery. The dominance of 3PL giants like UPS and FedEx—equipped with solar-powered fleets and blockchain-enabled customs clearance—further consolidates the region’s position. Cross-border efficiency is optimized through hubs like Memphis International Airport, where Delta Cargo’s Pharma Cold Chain logistics shorten transit times for Pfizer’s Paxlovid shipments to Latin America.
Europe: Sustainability and Cross-Border Synergy Drive Steady Growth
Europe’s biopharmaceutical logistics market ecosystem thrives on harmonized regulations, sustainability imperatives, and strategic manufacturing clusters. The EU’s Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) mandates serialization, pushing logistics providers like Kuehne + Nagel to deploy RFID-tagged containers for monoclonal antibodies. Germany and Switzerland, housing Roche and Novartis, leverage rail networks like the PharmaShuttle for low-emission transport of stable biologics between Basel and Milan. Sustainability drives innovation: DPDgroup’s electric vehicle fleet in Paris reduces carbon footprints for Sanofi’s insulin deliveries, while DB Schenker’s hydrogen-powered trucks service AstraZeneca’s UK-to-Nordics vaccine routes. Eastern Europe’s emergence as a clinical trial nexus—Poland’s 30% growth in decentralized trials since 2022—demands precision logistics for temperature-sensitive samples. Challenges like Brexit-induced customs delays are mitigated through digital twin platforms from Zencargo, slashing UK-EU biopharma transit documentation errors by 45%.
Asia-Pacific: Manufacturing Scale and Infrastructure investments Fuel Rapid Expansion
Asia-Pacific’s CAGR of 8.18% reflects its transformation into a biomanufacturing powerhouse and logistics innovation lab in the biopharmaceutical logistics market. China’s WuXi Biologics and India’s Biocon rely on Shanghai Pudong and Hyderabad air hubs, respectively, for global ADC and biosimilar exports. Singapore’s Changi Airport exemplifies infrastructure specialization, handling 250,000 pharma shipments monthly with CEIV-certified cold zones. Japan leads in robotics: Yamato Transport’s AI-driven sorting cuts cell therapy delivery times from Osaka to Tokyo to 6 hours. However, fragmented ASEAN regulations persist—Thailand’s 72-hour customs bottlenecks for mRNA vaccines contrast with Vietnam’s streamlined import lanes for Abbott’s Humira. India’s National Logistics Policy (2022) prioritizes cold chain expansion, deploying solar refrigerators to rural clinics for Serum Institute’s heat-stable vaccines. South Korea’s ILIAS Biologics leverages drone networks with Kakao Mobility to bypass Seoul’s congestion for emergency biologics. While air freight dominates intra-Asia gene therapy transport, cost-driven shifts emerge: Hyundai’s LNG-powered vessels now ship Samsung Bioepis’ biosimilars to Australia at 30% lower costs than air. The region’s growth hinges on bridging infrastructure gaps while balancing speed and sustainability.
Top Companies in the Biopharmaceutical Logistics Market
- CEVA Logistics
- Optimize Courier, LLC
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.
- DHL International GmbH
- FedEx Corporation
- Kuehne + Nagel International AG
- Biocair International Ltd.
- World Courier
- GREEN8 Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Logistics Corporation
- Nippon Express Co., Ltd
- ITOCHU Logistics Corp
- Other Prominent Players
Market Segmentation Overview
By Logistics Type
- Cold Chain Logistics
- Non- Cold Chain Logistics
By Service Type
- Storage Service
- Transportation Service
- Packaging Service
- Monitoring and Tracking Service
By Product Type
- Vaccines
- Blood Products
- Specialty Drug
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Others
By Mode of Transportation
- Air Transport
- Ground Transport
- Water Transport
By End User
- Pharmaceutical & Biotech Companies
- Academic & Research Institutions
- Hospitals and Specialty Clinics
- Others
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Western Europe
- The UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Poland
- Russia
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America
REPORT SCOPE
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value in 2024 | US$ 135.88 Bn |
| Expected Revenue in 2033 | US$ 252.20 Bn |
| Historic Data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Unit | Value (USD Bn) |
| CAGR | 7.24% |
| Segments covered | By Logistics Type, By Service Type, By Product Type, By Mode of Transportation, By End User, By Region |
| Key Companies | CEVA Logistics, Optimize Courier, LLC, United Parcel Service of America, Inc., DHL International GmbH, FedEx Corporation, Kuehne + Nagel International AG, Biocair International Ltd., World Courier, GREEN8 Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Logistics Corporation, Nippon Express Co., Ltd, ITOCHU Logistics Corp, Other Prominent Players |
| Customization Scope | Get your customized report as per your preference. Ask for customization |
LOOKING FOR COMPREHENSIVE MARKET KNOWLEDGE? ENGAGE OUR EXPERT SPECIALISTS.
SPEAK TO AN ANALYST
.svg)